Cells
... 1. Which of the following is the only cell organelle that is capable of converting light energy into chemical energy? A. mitochondrion B. vacuole C. chloroplast D. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have whip-like projections that help propel the cell through liquid. What is th ...
... 1. Which of the following is the only cell organelle that is capable of converting light energy into chemical energy? A. mitochondrion B. vacuole C. chloroplast D. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have whip-like projections that help propel the cell through liquid. What is th ...
BIOLOGY WORKSHEET 1. Robert Hooks : Robert Brown : : Cells
... period of time is called biomagnification. DDT is a harmful insecticide with very high potential of bioaccumulation and magnification through foodchain. At present its use is not recommended and even banned in a number of countries. Over time , it gradually builds up in foodchain.: insectssmall pre ...
... period of time is called biomagnification. DDT is a harmful insecticide with very high potential of bioaccumulation and magnification through foodchain. At present its use is not recommended and even banned in a number of countries. Over time , it gradually builds up in foodchain.: insectssmall pre ...
Stem Cells
... Key opportunities in discovery and design using stem cell biology There are many new scientific and medical opportunities presented by the ability to manipulate stem cells from humans and model organisms in vivo and in vitro. These range from the discovery of new biological control pathways to the ...
... Key opportunities in discovery and design using stem cell biology There are many new scientific and medical opportunities presented by the ability to manipulate stem cells from humans and model organisms in vivo and in vitro. These range from the discovery of new biological control pathways to the ...
THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell
... a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These events can be divided in two main parts: interphase (in between divisions phase grouping G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase), during which the cell is forming and carries on with its normal metabolic functions; the mitotic p ...
... a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These events can be divided in two main parts: interphase (in between divisions phase grouping G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase), during which the cell is forming and carries on with its normal metabolic functions; the mitotic p ...
anidevlt - CowanScience
... The distribution of mRNA, proteins, and other cytplasmic material in the unfertilized egg greatly impacts development Cleavage after fertilization divides the cytoplasm so that newly formed nuclei are exposed to different environments depending on their location in the embryo The different envi ...
... The distribution of mRNA, proteins, and other cytplasmic material in the unfertilized egg greatly impacts development Cleavage after fertilization divides the cytoplasm so that newly formed nuclei are exposed to different environments depending on their location in the embryo The different envi ...
chapter42_part1 - Lower Cape May Regional School District
... • A complex pathway involving many genes governs somite formation – any mutation that disrupts this pathway so that somites do not form is lethal during development ...
... • A complex pathway involving many genes governs somite formation – any mutation that disrupts this pathway so that somites do not form is lethal during development ...
Course Guide - Universitat de València
... based on extracellular signal molecules produced by cells to communicate with their neighbors or distant cells. Also, an elaborate protein system allows cells to respond external signals. Extracellular components, plant cell wall and extracellular matrix of animal cells, establish fundamental differ ...
... based on extracellular signal molecules produced by cells to communicate with their neighbors or distant cells. Also, an elaborate protein system allows cells to respond external signals. Extracellular components, plant cell wall and extracellular matrix of animal cells, establish fundamental differ ...
2.1 Cell Theory
... the enucleated cell body. 6. The cells then stimulated to divide forming a clone. 7. The cell mass forms a blastocyst. 8. The inner cell mass becomes a source of totipotent stem cells. Totipotent means they are capable of being stimulated to become one of any type of cell. 9. Cells are stimulated us ...
... the enucleated cell body. 6. The cells then stimulated to divide forming a clone. 7. The cell mass forms a blastocyst. 8. The inner cell mass becomes a source of totipotent stem cells. Totipotent means they are capable of being stimulated to become one of any type of cell. 9. Cells are stimulated us ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
English_Tumbuh Kembang hewan2005-01
... Back legs (after 2 ½ months) Front legs (after 2 ½ - 3 months) Metamorphosis is done (more then 3 months) In leaf caterpillars metamorphosis happens perfectly (holometabola). It means the change of one phase to another is observed clearly. The metamorphosis of dragon fly is not perfect (hemi ...
... Back legs (after 2 ½ months) Front legs (after 2 ½ - 3 months) Metamorphosis is done (more then 3 months) In leaf caterpillars metamorphosis happens perfectly (holometabola). It means the change of one phase to another is observed clearly. The metamorphosis of dragon fly is not perfect (hemi ...
Lab on chip for rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases
... steps from sample preparation to detection on the innovative diagnostic platform, we are aiming for a time-to-result of less than two hours. In addition to medical applications such as proteomic, genomic and microbiological tests, the future areas of application also comprise environmental analyses ...
... steps from sample preparation to detection on the innovative diagnostic platform, we are aiming for a time-to-result of less than two hours. In addition to medical applications such as proteomic, genomic and microbiological tests, the future areas of application also comprise environmental analyses ...
chapter42_part1wUnderline
... • Enzymes, mRNAs, yolk, and other materials are localized in specific parts of the cytoplasm of unfertilized eggs. This cytoplasmic localization establishes polarity (an orientation of the fertilized cell) in the egg and thus influences early development. • Cleavage divides a fertilized egg into a n ...
... • Enzymes, mRNAs, yolk, and other materials are localized in specific parts of the cytoplasm of unfertilized eggs. This cytoplasmic localization establishes polarity (an orientation of the fertilized cell) in the egg and thus influences early development. • Cleavage divides a fertilized egg into a n ...
The Basic Unit of Life.
... Similarly, there are different kinds of cells in animals, including humans, that have different kinds of functions. For example, skin cells are flat and wide to protect other cells that are underneath them. Muscles are made of long, thread-like cells that let the body move. Nerve cells transport mes ...
... Similarly, there are different kinds of cells in animals, including humans, that have different kinds of functions. For example, skin cells are flat and wide to protect other cells that are underneath them. Muscles are made of long, thread-like cells that let the body move. Nerve cells transport mes ...
Keywords - 기초의과학연구센터 MRC
... NSC grafts by TMT. IGF-1 neutralization also reduced the number of ERK positive grafted NSCs. We also examined if genetic deletion of IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) may render grafted NSCs unresponsive to activity-based training. NSCs obtained from IGF-1R (+/-) were more susceptible to the cellular stresse ...
... NSC grafts by TMT. IGF-1 neutralization also reduced the number of ERK positive grafted NSCs. We also examined if genetic deletion of IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) may render grafted NSCs unresponsive to activity-based training. NSCs obtained from IGF-1R (+/-) were more susceptible to the cellular stresse ...
ex vivo bioengineering of lung - HELENA
... • Gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out) √ • Filters (prevent particles and pathogens from entering the body) √ • Other design requirements: • Portable • Long life cycle • Bridge to transplantation • Alternative options need to be explored ...
... • Gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out) √ • Filters (prevent particles and pathogens from entering the body) √ • Other design requirements: • Portable • Long life cycle • Bridge to transplantation • Alternative options need to be explored ...
High School Biology 1 Cells Unit
... that contain a variety of membrane‐bound organelles. 8. Cell organelles are specific for the func�on(s) they have; these organelles work together for the benefit of the cell. 9. The cell membrane regulates the passage of materials into ...
... that contain a variety of membrane‐bound organelles. 8. Cell organelles are specific for the func�on(s) they have; these organelles work together for the benefit of the cell. 9. The cell membrane regulates the passage of materials into ...
CHAPTER 27 Reproduction and Embryonic Development
... • All of these multiple births were by women who had taken fertility drugs because they couldn’t become pregnant naturally • Couples turn to fertility drugs to overcome their natural reproductive limitations ...
... • All of these multiple births were by women who had taken fertility drugs because they couldn’t become pregnant naturally • Couples turn to fertility drugs to overcome their natural reproductive limitations ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
Sample preparation, probe labeling and hybridization for experiment-1
... plates next day. After three weeks of selection, hundreds of clones on plates were trypsinated and re-plated to form a population of RhoG expressing cells and control cell population with pCI-Neo vector only. These populations were used in the experiments. Control cells (pCI-Neo transfected) and sam ...
... plates next day. After three weeks of selection, hundreds of clones on plates were trypsinated and re-plated to form a population of RhoG expressing cells and control cell population with pCI-Neo vector only. These populations were used in the experiments. Control cells (pCI-Neo transfected) and sam ...
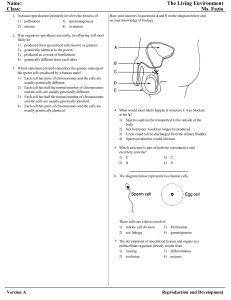
Reproduction and Development
... Base your answers to questions 21 through 24 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Stem Cells If skin is cut, the wound closes within days. If a leg is broken, the fracture will usually mend if the bone is set correctly. Almost all human tissue can repair itself to some extent. ...
... Base your answers to questions 21 through 24 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Stem Cells If skin is cut, the wound closes within days. If a leg is broken, the fracture will usually mend if the bone is set correctly. Almost all human tissue can repair itself to some extent. ...
Developmental Biology
... can reproduce itself indefinitely and differentiate into specialized cells of one or more types • Stem cells isolated from early embryos at the blastocyst stage are called embryonic stem cells; these are able to differentiate into all cell types • The adult body also has stem cells, which replace no ...
... can reproduce itself indefinitely and differentiate into specialized cells of one or more types • Stem cells isolated from early embryos at the blastocyst stage are called embryonic stem cells; these are able to differentiate into all cell types • The adult body also has stem cells, which replace no ...
Chapter 24
... • Within the uterus, a specialized structure called the placenta forms • It is through the placenta that the exchange of nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases between the embryo and the mother take place • The umbilical cord, which contains blood vessels, attaches the embryo to the placenta ...
... • Within the uterus, a specialized structure called the placenta forms • It is through the placenta that the exchange of nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases between the embryo and the mother take place • The umbilical cord, which contains blood vessels, attaches the embryo to the placenta ...
transcript - American Chemical Society
... while the blood stream’s pH is typically 7.4, the inside of a macrophage is pH 4.5. In one set of experiments, which Dr. Murthy describes in the ACS journal Bioconjugate Chemistry, he and his collaborators created polyketal microparticles containing a powerful anti-inflammatory drug that at its norm ...
... while the blood stream’s pH is typically 7.4, the inside of a macrophage is pH 4.5. In one set of experiments, which Dr. Murthy describes in the ACS journal Bioconjugate Chemistry, he and his collaborators created polyketal microparticles containing a powerful anti-inflammatory drug that at its norm ...
cell structure - Madison County Schools
... a variety of circumstances. Amoebas and many other protists eat by engulfing smaller organisms or other food particles, a process called phagocytosis. • The food vacuole formed in this way then fuses with a lysosome, whose enzymes digest the food. • Some human cells also carry out phagocytosis. Amon ...
... a variety of circumstances. Amoebas and many other protists eat by engulfing smaller organisms or other food particles, a process called phagocytosis. • The food vacuole formed in this way then fuses with a lysosome, whose enzymes digest the food. • Some human cells also carry out phagocytosis. Amon ...
Part 2-PP File - shscience.net
... the parents? 5. What controls human reproduction and development? 6. How does a zygote develop and what factors can affect its development? ...
... the parents? 5. What controls human reproduction and development? 6. How does a zygote develop and what factors can affect its development? ...
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. Dolly the Sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. ""Therapeutic cloning"" refers to the potential use of SCNT in regenerative medicine; this approach has been championed as an answer to the many issues concerning embryonic stem cells (ESC) and the destruction of viable embryos for medical use, though questions remain on how homologous the two cell types truly are.