System Type: Septic Tank to Soil Absorption Trenches
... media to remove the smaller suspended particles (TSS) and organic material (BOD). Research confirms that 2 to 4 feet of unsaturated soil is needed to completely remove bacteria, viruses and protozoans from sewage. ...
... media to remove the smaller suspended particles (TSS) and organic material (BOD). Research confirms that 2 to 4 feet of unsaturated soil is needed to completely remove bacteria, viruses and protozoans from sewage. ...
Seasons, Solar Intensity, and Latitude
... Majority of the rock in the Earth’s surface. Know examples of igneous rocks, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Acid rain and its effect on soil. Types of soils and its amount Examples of volcanoes, Earthquakes, Tsunamis, and Erosion Know the different types of plates. Dust Bowl of 1930’s, geological tim ...
... Majority of the rock in the Earth’s surface. Know examples of igneous rocks, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Acid rain and its effect on soil. Types of soils and its amount Examples of volcanoes, Earthquakes, Tsunamis, and Erosion Know the different types of plates. Dust Bowl of 1930’s, geological tim ...
Plant Physiology - Tufts University
... 4) Evaluate the idea that plants such as wheat, corn, tea and tomato have exploited humans to become widely successful far beyond their native ranges. ...
... 4) Evaluate the idea that plants such as wheat, corn, tea and tomato have exploited humans to become widely successful far beyond their native ranges. ...
11_chapter 5
... (Aure´lie Violette et al. 2010). The weathering of silicate rocks has an impact on global environmental changes. During silicate weathering reactions, CO2 is consumed leading to the sequestration of atmospheric CO2 on a long term (Cockell et al. 2011). Thus, weathering of silicate minerals, acts as ...
... (Aure´lie Violette et al. 2010). The weathering of silicate rocks has an impact on global environmental changes. During silicate weathering reactions, CO2 is consumed leading to the sequestration of atmospheric CO2 on a long term (Cockell et al. 2011). Thus, weathering of silicate minerals, acts as ...
Notes Part 2
... • Very important organisms on the ancient Earth – Helped to make Earth “habitable” for life to evolve • Marine bacteria are important – Producers, decomposers, food sources, symbionts, pathogens, modifiers of sediments. Bacteria reproduce mainly by asexual reproduction Bacteria have three main shape ...
... • Very important organisms on the ancient Earth – Helped to make Earth “habitable” for life to evolve • Marine bacteria are important – Producers, decomposers, food sources, symbionts, pathogens, modifiers of sediments. Bacteria reproduce mainly by asexual reproduction Bacteria have three main shape ...
3D ROCKS AND SOILS
... particles – very small pieces of a substance permeable – lets water through non-permeable – does not let water through sand – small rounded particles of rock soil – natural material made when rocks are worn away - contains different sized particles of rock, animal and plant matter and air types of r ...
... particles – very small pieces of a substance permeable – lets water through non-permeable – does not let water through sand – small rounded particles of rock soil – natural material made when rocks are worn away - contains different sized particles of rock, animal and plant matter and air types of r ...
Phosphorus
... • P comes from the chemical weathering of apatite rock. • The higher the ph of the soil the more Hydrogen ions are given up to form the 2 orthophosphate ions. • Decomposing organic matter, humus and microbes. – 20-50% of soil P is in O.M. ...
... • P comes from the chemical weathering of apatite rock. • The higher the ph of the soil the more Hydrogen ions are given up to form the 2 orthophosphate ions. • Decomposing organic matter, humus and microbes. – 20-50% of soil P is in O.M. ...
Do Now: What processes creates the small rocks in soil?
... • refers to the size of the particles and the amount of moisture. • indicates if soil is physically or chemically weathered and the climate. Determine which soil is drier? More suitable for plants? Composed of more sand? Chemically Weathered? Physically weathered? ...
... • refers to the size of the particles and the amount of moisture. • indicates if soil is physically or chemically weathered and the climate. Determine which soil is drier? More suitable for plants? Composed of more sand? Chemically Weathered? Physically weathered? ...
Emerging aspects in Microbial Geotechnology and Ground
... improve mechanical properties of soil in situ. They can replace energy demanding, expensive and environmentally unfriendly methods with significant reduction in cost. • Most suitable microorganisms for large‐scale construction and environmental problems are facultative anaerobic and microaerophilic ...
... improve mechanical properties of soil in situ. They can replace energy demanding, expensive and environmentally unfriendly methods with significant reduction in cost. • Most suitable microorganisms for large‐scale construction and environmental problems are facultative anaerobic and microaerophilic ...
plagiarism - Teacher Pages
... workers," and created jobs for immigrants. In turn, growing populations increased the size of urban areas. Fall River was one of these manufacturing hubs that were also "centers of commerce and trade" (Williams 1) ...
... workers," and created jobs for immigrants. In turn, growing populations increased the size of urban areas. Fall River was one of these manufacturing hubs that were also "centers of commerce and trade" (Williams 1) ...
Chapter 10
... Soil Horizons: series of layers or zones with a distinct texture and composition Soil profile: a cross-sectional view of horizons in soil O-horizon: top layer, surface litter which is leaves and debris A-horizon: topsoil layer: some inorganic materials and humus which is partially decomposed organic ...
... Soil Horizons: series of layers or zones with a distinct texture and composition Soil profile: a cross-sectional view of horizons in soil O-horizon: top layer, surface litter which is leaves and debris A-horizon: topsoil layer: some inorganic materials and humus which is partially decomposed organic ...
Soil Study Guide
... Moist slippery earth usually red in color. Clay is often found in Georgia. Plants do not generally grow well in clay. ...
... Moist slippery earth usually red in color. Clay is often found in Georgia. Plants do not generally grow well in clay. ...
File
... Temperature and Moisture influence the speed of chemical reactions, which in turn, control how fast rocks weather and dead organisms decompose. ...
... Temperature and Moisture influence the speed of chemical reactions, which in turn, control how fast rocks weather and dead organisms decompose. ...
Fertilizers - PNW District
... Solid – usually ‘spikes’ to push into soil around plant, very slow to dissolve ...
... Solid – usually ‘spikes’ to push into soil around plant, very slow to dissolve ...
Alternative Analytical Technology (AAT) for testing Soil nutrients
... Alternative Analytical Technology (AAT) for testing Soil nutrients “Approaches to enhance the integrated knowledge system on soil nutrient analysis, site specific validation, demonstration and popularization of Alternative Analytical Technology (AAT) – Phase II” has been focusing on establishing reg ...
... Alternative Analytical Technology (AAT) for testing Soil nutrients “Approaches to enhance the integrated knowledge system on soil nutrient analysis, site specific validation, demonstration and popularization of Alternative Analytical Technology (AAT) – Phase II” has been focusing on establishing reg ...
Plant Food Information
... No deficiencies if soil pH is above 5.0 Deficiencies are easily taken care of with lime (even high Mg lime) ...
... No deficiencies if soil pH is above 5.0 Deficiencies are easily taken care of with lime (even high Mg lime) ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... Also find bacteria, actinomycetes, protozoa associated with root surface = rhizosphere • Plants feed them lots of C! • They help make nutrients available • N-fixing bacteria supply N to many plant spp ...
... Also find bacteria, actinomycetes, protozoa associated with root surface = rhizosphere • Plants feed them lots of C! • They help make nutrients available • N-fixing bacteria supply N to many plant spp ...
The role of calcium and magnesium in agriculture
... The role of calcium and magnesium in agriculture For healthy plants, an adequate supply of calcium compounds in the soil is required. This is because calcium is an essential constituent of plants. Not only are they a principle factor in controlling the pH of the soil but also they affect the plants ...
... The role of calcium and magnesium in agriculture For healthy plants, an adequate supply of calcium compounds in the soil is required. This is because calcium is an essential constituent of plants. Not only are they a principle factor in controlling the pH of the soil but also they affect the plants ...
Role play activity with the Nitrogen Cycle
... 4. To begin the cycle, the air students should give their free nitrogen (white cards) to the nodule bacteria students, who should attach, or “fix” each white card to one of their blue cards with tape. This combination of white and blue cards represents a nitrogen compound. 5. Work as a group to move ...
... 4. To begin the cycle, the air students should give their free nitrogen (white cards) to the nodule bacteria students, who should attach, or “fix” each white card to one of their blue cards with tape. This combination of white and blue cards represents a nitrogen compound. 5. Work as a group to move ...
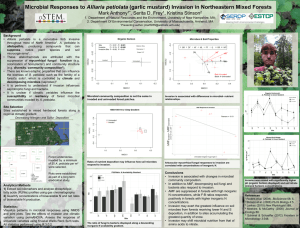
Slide 1
... • Alliaria petiolata is a non-native forb invasive throughout most of North America1. A. petiolata is allelopathic, producing compounds that can suppress native plant species and soil microorganisms1. • These allelochemicals are attributed with the suppression of mycorrhizal fungal function (e.g. co ...
... • Alliaria petiolata is a non-native forb invasive throughout most of North America1. A. petiolata is allelopathic, producing compounds that can suppress native plant species and soil microorganisms1. • These allelochemicals are attributed with the suppression of mycorrhizal fungal function (e.g. co ...
WLVL 05-10-11 Fertilizer
... bones of animals. Inorganic means from non-living sources. Rock phosphate, a common source of phosphorus, comes from rocks, a non-living material. The term natural describes the manure, the bonemeal, and the rock phosphate. All are naturally occurring. The term synthetic describes such products as n ...
... bones of animals. Inorganic means from non-living sources. Rock phosphate, a common source of phosphorus, comes from rocks, a non-living material. The term natural describes the manure, the bonemeal, and the rock phosphate. All are naturally occurring. The term synthetic describes such products as n ...
Application of zeolite to reduce nitrates
... Application of zeolite to reduce nitrates concentration in growing media and soil Areas like the Albenga plain in Liguria Region (Italy) are classified as “areas vulnerable to nitrates” and are under specific legislation to limit nitrate contamination of superficial and deep water bodies. The additi ...
... Application of zeolite to reduce nitrates concentration in growing media and soil Areas like the Albenga plain in Liguria Region (Italy) are classified as “areas vulnerable to nitrates” and are under specific legislation to limit nitrate contamination of superficial and deep water bodies. The additi ...
Glossary for the Lithosphere
... micro-organisms, including many bacteria and fungi, which break down and digest dead organic matter. organisms that feed on dead organic matter, often in or on the soil, e.g. earthworms, millipedes and woodlice. They break down dead organic matter that can be further digested by decomposers. the nat ...
... micro-organisms, including many bacteria and fungi, which break down and digest dead organic matter. organisms that feed on dead organic matter, often in or on the soil, e.g. earthworms, millipedes and woodlice. They break down dead organic matter that can be further digested by decomposers. the nat ...