Practice photosynthesis/Respiration
... 59) CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they A) fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells. ...
... 59) CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they A) fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells. ...
C 4 plants
... yields energy – Used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane – Protons move from stroma into the thylakoid space • Flow of H+ back across the thylakoid membrane – Energizes ATP synthase, which – Enzymatically produces ATP from ADP + Pi • This method of producing ATP is called chemiosmosis • Photosy ...
... yields energy – Used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane – Protons move from stroma into the thylakoid space • Flow of H+ back across the thylakoid membrane – Energizes ATP synthase, which – Enzymatically produces ATP from ADP + Pi • This method of producing ATP is called chemiosmosis • Photosy ...
Answer/Explanatory Notes
... complex/accessory pigments (not: antenna/light harvesting/ primary pigment) ...
... complex/accessory pigments (not: antenna/light harvesting/ primary pigment) ...
Respiration in the presence of oxygen.
... Germinating seed need oxygen to respire to provide the energy for growth. 9/ Why do we use germinating seeds rather than a small plant green? In a green plant, both photosynthesis and respiration will take place when light is present. Photosynthesis releases oxygen, respiration takes up oxygen. Phot ...
... Germinating seed need oxygen to respire to provide the energy for growth. 9/ Why do we use germinating seeds rather than a small plant green? In a green plant, both photosynthesis and respiration will take place when light is present. Photosynthesis releases oxygen, respiration takes up oxygen. Phot ...
translation no. 4849
... leads to the organic nutrients produced by photosynthesis in plants. Since the source of supply of our life energy is the prolific growth of plants on the earth, it can be said that the source of all organic life is the radiant energy from the sun which is utilized by these plants. Everyone knows th ...
... leads to the organic nutrients produced by photosynthesis in plants. Since the source of supply of our life energy is the prolific growth of plants on the earth, it can be said that the source of all organic life is the radiant energy from the sun which is utilized by these plants. Everyone knows th ...
Lesson Overview - Midland Park School
... In order to conserve water, most plants under bright, hot conditions close the small openings in their leaves that normally admit carbon dioxide. This causes carbon dioxide within the leaves to fall to very low levels, slowing down or even stopping photosynthesis. C4 and CAM plants have biochemical ...
... In order to conserve water, most plants under bright, hot conditions close the small openings in their leaves that normally admit carbon dioxide. This causes carbon dioxide within the leaves to fall to very low levels, slowing down or even stopping photosynthesis. C4 and CAM plants have biochemical ...
Experiment 4: Bacteria in the environment
... the wire loops that are used to transfer bacteria between cultures. All glass culture tubes are "flamed" at the lip before and after a sample is removed. Care must be taken to not get hair or skin in contact with any of the culture media both before and following inoculation with bacteria. Always wa ...
... the wire loops that are used to transfer bacteria between cultures. All glass culture tubes are "flamed" at the lip before and after a sample is removed. Care must be taken to not get hair or skin in contact with any of the culture media both before and following inoculation with bacteria. Always wa ...
Bil 255 Spring photosynthesis Mallery 1
... the oxygenase second reaction. The uptake of O2 by RUBISCO forms two 3carbon molecules: [reaction] 1) one is 3-phosphoglyceric acid [3PGA] just as in the Calvin cycle 2) the other is 2P-glycolate. and involves 3 organelles: chloroplast, peroxisome, and mitochondria. photosynthesis ...
... the oxygenase second reaction. The uptake of O2 by RUBISCO forms two 3carbon molecules: [reaction] 1) one is 3-phosphoglyceric acid [3PGA] just as in the Calvin cycle 2) the other is 2P-glycolate. and involves 3 organelles: chloroplast, peroxisome, and mitochondria. photosynthesis ...
photosystem - HCC Learning Web
... • The initial incorporation of carbon from the atmosphere into organic compounds is called carbon fixation. – This lowers the amount of carbon in the air. – Deforestation reduces the ability of the biosphere to absorb carbon by reducing the amount of photosynthetic plant life. ...
... • The initial incorporation of carbon from the atmosphere into organic compounds is called carbon fixation. – This lowers the amount of carbon in the air. – Deforestation reduces the ability of the biosphere to absorb carbon by reducing the amount of photosynthetic plant life. ...
Algae - immaculateheartacademy.org
... Most green algae live in freshwater, but some live in oceans, moist soil, on tree trunks, snow, even in the fur of sloths. ...
... Most green algae live in freshwater, but some live in oceans, moist soil, on tree trunks, snow, even in the fur of sloths. ...
Bacteria Pa Bien o Mal
... through photosynthesis larger than most bacterial cells commonly grow on water and surfaces that stay wet…such as rivers, creeks and dams Some live in salt water, snow, and acid water of hot springs food source for animals that live in the ...
... through photosynthesis larger than most bacterial cells commonly grow on water and surfaces that stay wet…such as rivers, creeks and dams Some live in salt water, snow, and acid water of hot springs food source for animals that live in the ...
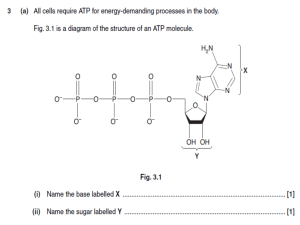
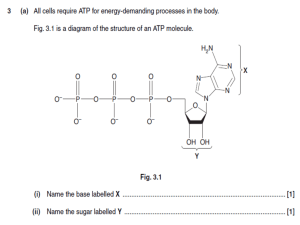
ATP, Photosynthesis and Respiration
... PSII absorbs energy. e- from double bonds in the head of ChloroA become energized and move to a higher energy level. They are captured by a primary electron acceptor. Photolysis: H2O gets split apart into 2 e- , 2 H+, and one oxygen atom.. The ereplace those lost by ChloroA. 2 oxygen molecules combi ...
... PSII absorbs energy. e- from double bonds in the head of ChloroA become energized and move to a higher energy level. They are captured by a primary electron acceptor. Photolysis: H2O gets split apart into 2 e- , 2 H+, and one oxygen atom.. The ereplace those lost by ChloroA. 2 oxygen molecules combi ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
File - 6th grade science weebly
... Photosynthesis provides the oxygen gas in the atmosphere that most living organisms need. ...
... Photosynthesis provides the oxygen gas in the atmosphere that most living organisms need. ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
Microbes Bacteria
... on Earth billions of years ago. Bacteria helped shape and change the young planet's environment, eventually creating atmospheric oxygen that enabled other, more complex life Marconi 2007 forms to develop. ...
... on Earth billions of years ago. Bacteria helped shape and change the young planet's environment, eventually creating atmospheric oxygen that enabled other, more complex life Marconi 2007 forms to develop. ...
A. TRANSLOCATION Translocation is the movement of dissolved
... concentration of sugars in leaves where they are produced is usually higher than that in the sinks. Only a fraction of the products of photosynthesis remain at the site of production in fully expanded leaves, most of them are translocated to other organs where they are either used as building blocks ...
... concentration of sugars in leaves where they are produced is usually higher than that in the sinks. Only a fraction of the products of photosynthesis remain at the site of production in fully expanded leaves, most of them are translocated to other organs where they are either used as building blocks ...
CO 2 fixation in CAM plants
... Photosynthesis is considered the most important process for all living organisms (except for anaerobic bacteria which can fix CO2 without using hydrogen of H2O as a source of proton). Photosynthesis is simply a light-driven series of chemical reactions that convert the energy-poor compound, CO2, to ...
... Photosynthesis is considered the most important process for all living organisms (except for anaerobic bacteria which can fix CO2 without using hydrogen of H2O as a source of proton). Photosynthesis is simply a light-driven series of chemical reactions that convert the energy-poor compound, CO2, to ...
unit 3 – cellular energy processes
... Write a summary equation for photosynthesis. Explain the role of REDOX reactions in photosynthesis. Explain why the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll differs from the action spectrum for photosynthesis. List the wavelengths of light that are most effective for photosynthesis. Explain what happens ...
... Write a summary equation for photosynthesis. Explain the role of REDOX reactions in photosynthesis. Explain why the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll differs from the action spectrum for photosynthesis. List the wavelengths of light that are most effective for photosynthesis. Explain what happens ...
intermediary metabolism
... chloroplast membrane as such and not as H2CO3 or HCO-3. Each mesophyll cell of plants may contain 20 to 50 chloroplasts, sometimes even 100 or more depending on the species, cell type and growth conditions. Algae cells, also have chloroplasts but often each cell has one large chloroplast. Some proka ...
... chloroplast membrane as such and not as H2CO3 or HCO-3. Each mesophyll cell of plants may contain 20 to 50 chloroplasts, sometimes even 100 or more depending on the species, cell type and growth conditions. Algae cells, also have chloroplasts but often each cell has one large chloroplast. Some proka ...
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria /saɪˌænoʊbækˈtɪəriə/, also known as Cyanophyta, is a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis. The name ""cyanobacteria"" comes from the color of the bacteria (Greek: κυανός (kyanós) = blue). They are often called blue-green algae (but some consider that name a misnomer, as cyanobacteria are prokaryotic and algae should be eukaryotic, although other definitions of algae encompass prokaryotic organisms).By producing gaseous oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis, cyanobacteria are thought to have converted the early reducing atmosphere into an oxidizing one, causing the ""rusting of the Earth"" and causing the Great Oxygenation Event, dramatically changing the composition of life forms on Earth by stimulating biodiversity and leading to the near-extinction of anaerobic organisms (that is, oxygen-intolerant). Symbiogenesis argues that the chloroplasts found in plants and eukaryotic algae evolved from cyanobacterial ancestors via endosymbiosis. Cyanobacteria are arguably the most successful group of microorganisms on earth. They are the most genetically diverse; they occupy a broad range of habitats across all latitudes, widespread in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems, and they are found in the most extreme niches such as hot springs, salt works, and hypersaline bays. Photoautotrophic, oxygen-producing cyanobacteria created the conditions in the planet's early atmosphere that directed the evolution of aerobic metabolism and eukaryotic photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria fulfill vital ecological functions in the world's oceans, being important contributors to global carbon and nitrogen budgets.– Stewart and Falconer