Xie-EGM-RPI-2011 - Rensselaer Hartford Campus
... • COMSOL Multi-physics has been used to model the steady laminar flow and convective heat transfer of an electrically conducting fluid subjected to an applied electromagnetic field in two simple flow configurations, namely, flow between parallel plates (Hartmann flow) and flow around a backward faci ...
... • COMSOL Multi-physics has been used to model the steady laminar flow and convective heat transfer of an electrically conducting fluid subjected to an applied electromagnetic field in two simple flow configurations, namely, flow between parallel plates (Hartmann flow) and flow around a backward faci ...
B12a - damtp - University of Cambridge
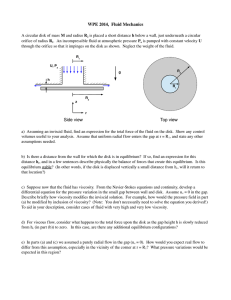
... the fluid. Calculate the velocity profile and find the volume flux (per unit width) of fluid down the wall. 3. A long, horizontal, two-dimensional container of depth h, filled with viscous fluid, has rigid, stationary bottom and end walls and a rigid top wall that moves with velocity (U, 0) in Carte ...
... the fluid. Calculate the velocity profile and find the volume flux (per unit width) of fluid down the wall. 3. A long, horizontal, two-dimensional container of depth h, filled with viscous fluid, has rigid, stationary bottom and end walls and a rigid top wall that moves with velocity (U, 0) in Carte ...
UNDERVISNING I TPM VED HiB
... r = Fluid Density [kg/m3] V = Fluid Velocity [m/s] g = Gravitational Acceleration Constant [m/s2] h = Pressure Height or Submergence [m] ...
... r = Fluid Density [kg/m3] V = Fluid Velocity [m/s] g = Gravitational Acceleration Constant [m/s2] h = Pressure Height or Submergence [m] ...
Solution of the 3D Linearized Euler Equations for Acoustical
... The application of numerical simulation in aerocaoustics has been considerably augmented in the last few years. New numerical methods and supercomputers allow to calculate a nearly exact flow around complex bodies. For the calculation of flow generated acoustical sources it is necessary to obtain a ...
... The application of numerical simulation in aerocaoustics has been considerably augmented in the last few years. New numerical methods and supercomputers allow to calculate a nearly exact flow around complex bodies. For the calculation of flow generated acoustical sources it is necessary to obtain a ...
Tripura Bojjawar BIEN 501 Physiological
... b) Principle of conservation of mass c) Equation of motion d) None ...
... b) Principle of conservation of mass c) Equation of motion d) None ...
GEF 2500 Problem set 3 U
... A dry parcel that is ascending adiabatically through the atmosphere will generally cool as it moves to lower pressure and expands and its potential temperature stays the same. How can this be consistent with your answer in (a)? ...
... A dry parcel that is ascending adiabatically through the atmosphere will generally cool as it moves to lower pressure and expands and its potential temperature stays the same. How can this be consistent with your answer in (a)? ...
Fluid Dynamics
... r is the radius of the tube through with the fluid is flowing is the density of the fluid is the coefficient of viscosity of the fluid ...
... r is the radius of the tube through with the fluid is flowing is the density of the fluid is the coefficient of viscosity of the fluid ...
Fluid Mechanics - Princeton High School
... Syringe hydraulic lift • I raise a 10 N rock with a hydraulic piston that is 13 mm in radius using water connected to a 1.5 mm radius syringe. How much force is necessary for this lift to raise the rock? ...
... Syringe hydraulic lift • I raise a 10 N rock with a hydraulic piston that is 13 mm in radius using water connected to a 1.5 mm radius syringe. How much force is necessary for this lift to raise the rock? ...
Chap 4-che 312
... pass around a solid body (spheres), significant additional frictional losses will occur and this is called form drag ...
... pass around a solid body (spheres), significant additional frictional losses will occur and this is called form drag ...
Real fluids Viscosity
... Fluids which flow easily (water, petrol) have smaller viscosities than “thick” liquids (honey, glycerine). Viscosity is highly dependent on temperature. The viscosity of a liquid decreases as T increases, while for a gas η increases as T increases. ...
... Fluids which flow easily (water, petrol) have smaller viscosities than “thick” liquids (honey, glycerine). Viscosity is highly dependent on temperature. The viscosity of a liquid decreases as T increases, while for a gas η increases as T increases. ...
Lecture Presentation Chp-10
... where, A is the duct crosssectional area and is the fluid mass flow rate (e.g., kg/s). For an incompressible fluid, the density is constant. ...
... where, A is the duct crosssectional area and is the fluid mass flow rate (e.g., kg/s). For an incompressible fluid, the density is constant. ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... liquid around the sphere is laminar As the molecules its passing through will stick to the surface as it travels, a viscous drag (F) is created This force was shown to be related to the radius of the sphere, the velocity of the sphere and the coefficient of viscosity ( η ) ...
... liquid around the sphere is laminar As the molecules its passing through will stick to the surface as it travels, a viscous drag (F) is created This force was shown to be related to the radius of the sphere, the velocity of the sphere and the coefficient of viscosity ( η ) ...