Introduction to Fluid Mechanics - Pharos University in Alexandria
... Similarity and model testing • Definition : Flow conditions for a model test are completely similar if all relevant dimensionless parameters have the same corresponding values for model and prototype. • Pi model = Pi prototype i = 1 • Enables extrapolation from model to full scale • However, comple ...
... Similarity and model testing • Definition : Flow conditions for a model test are completely similar if all relevant dimensionless parameters have the same corresponding values for model and prototype. • Pi model = Pi prototype i = 1 • Enables extrapolation from model to full scale • However, comple ...
Study of shear thinning and shear thickening in 2D fluids
... Fluids which are made up of more than one type of fluid particles, i.e., these fluids are heterogenous in nature. For these fluids, the relationship between shear stress and shear rate may not be Newtonian type. Several interesting Complex fluids have been synthesized in labs across the world as the ...
... Fluids which are made up of more than one type of fluid particles, i.e., these fluids are heterogenous in nature. For these fluids, the relationship between shear stress and shear rate may not be Newtonian type. Several interesting Complex fluids have been synthesized in labs across the world as the ...
Summary abstracts and conclusions
... inlet temperature, pressure, mass flow, heat flux, buoyancy and flow direction were investigated. An M-shape velocity distribution develops across the tube with increasing heat flux, due to the property variations and the buoyancy. This phenomenon becomes more evident as the heat flux and as x/d in ...
... inlet temperature, pressure, mass flow, heat flux, buoyancy and flow direction were investigated. An M-shape velocity distribution develops across the tube with increasing heat flux, due to the property variations and the buoyancy. This phenomenon becomes more evident as the heat flux and as x/d in ...
Max`sNotes
... This model is common in the mining industry, where ore is crushed and screened. Over sized particles are sent back around through the crusher as shown in model five. The equilibrium position is defined when the input to the system equals the output of the system. In the mineral processing industry t ...
... This model is common in the mining industry, where ore is crushed and screened. Over sized particles are sent back around through the crusher as shown in model five. The equilibrium position is defined when the input to the system equals the output of the system. In the mineral processing industry t ...
Flow sensors
... Absolute humidity – the mass of water vapour per unit volume. Relative humidity (RH) – the ratio of actual vapour pressure (pw - partial pressure of water vapour) to the saturation vapour pressure ps at the same temperature. ...
... Absolute humidity – the mass of water vapour per unit volume. Relative humidity (RH) – the ratio of actual vapour pressure (pw - partial pressure of water vapour) to the saturation vapour pressure ps at the same temperature. ...
Bernoulli`s equation
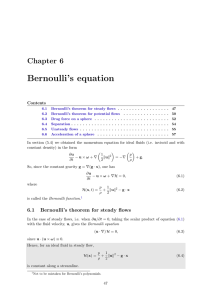
... To express the pressure force on the sphere in terms of the fluid velocity, we use Bernoulli’s theorem for steady potential flows, H = p/ρ + kuk2 /2 = constant, ignoring gravity. At r = a the fluid pressure, p(θ), therefore satisfies p(θ) 1 2 ...
... To express the pressure force on the sphere in terms of the fluid velocity, we use Bernoulli’s theorem for steady potential flows, H = p/ρ + kuk2 /2 = constant, ignoring gravity. At r = a the fluid pressure, p(θ), therefore satisfies p(θ) 1 2 ...
Slide 1
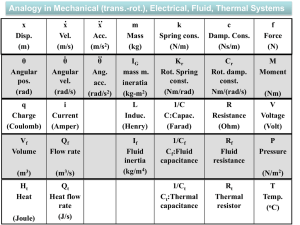
... There is a pressure P4 in the pipe #4 due to the placement of pipe #4 in the vertical direction because the flow is opposite to the gravity in pipe #4. So, the voltage supply V4 is placed in the circuit due to the analogy. The positive end of the V4 is connected to the point A. The current produced ...
... There is a pressure P4 in the pipe #4 due to the placement of pipe #4 in the vertical direction because the flow is opposite to the gravity in pipe #4. So, the voltage supply V4 is placed in the circuit due to the analogy. The positive end of the V4 is connected to the point A. The current produced ...
Aerodynamics Notes 2
... moving or stationary solid body, caused by the flow of surrounding fluid around the body. The figure below shows the large wake generated behind the a small boat. This wake is in essence "wasted" energy that the ship generates. This wasted energy was not used to propel the boat forward, but rather t ...
... moving or stationary solid body, caused by the flow of surrounding fluid around the body. The figure below shows the large wake generated behind the a small boat. This wake is in essence "wasted" energy that the ship generates. This wasted energy was not used to propel the boat forward, but rather t ...
CHAPTER 5 THE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF FLOW
... b) the conservation of momentum entering and leaving the control volume; this energy balance is called the equation of motion. In describing the momentum of a fluid, we should note that in the case of a solid body, its mass is readily defined and has the dimension, M; the same is true for its moment ...
... b) the conservation of momentum entering and leaving the control volume; this energy balance is called the equation of motion. In describing the momentum of a fluid, we should note that in the case of a solid body, its mass is readily defined and has the dimension, M; the same is true for its moment ...
ap physics b lesson 64, 76 fluid mechanics
... The average sea level density of air at 25°C and 1 atm is 1.29kg/m3. The density decreases rapidly with altitude. The total mass of a column of air extending from the top of the atmosphere down to seal level whose cross sectional area is 1m2 is 10, 330kg and its weight is 101300N. Thus the atmospher ...
... The average sea level density of air at 25°C and 1 atm is 1.29kg/m3. The density decreases rapidly with altitude. The total mass of a column of air extending from the top of the atmosphere down to seal level whose cross sectional area is 1m2 is 10, 330kg and its weight is 101300N. Thus the atmospher ...
Section_36_Turbulenc..
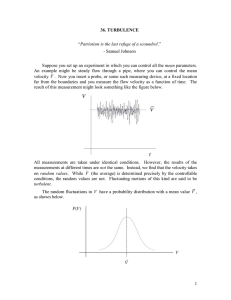
... turbulence is said to be isotropic. Isotropic turbulence has no preferred direction in space. If the random flow looks the same on all spatial scales, the turbulence is said to be self-similar. A rigorous theoretical study of turbulence requires a statistical description. Here we will not go that fa ...
... turbulence is said to be isotropic. Isotropic turbulence has no preferred direction in space. If the random flow looks the same on all spatial scales, the turbulence is said to be self-similar. A rigorous theoretical study of turbulence requires a statistical description. Here we will not go that fa ...
Fluids - Teach Engineering
... equally in all directions. • Change in pressure disperses equally throughout the fluid. • Force acts at right angles to any surface in contact with the fluid. ...
... equally in all directions. • Change in pressure disperses equally throughout the fluid. • Force acts at right angles to any surface in contact with the fluid. ...
Chapter 14
... to flow; viscosity is the fluid analog of friction between solids. An object moving through a nonviscous fluid would experience no viscous drag force—that is, no resistive force due to viscosity; it could move at constant speed through the fluid. ...
... to flow; viscosity is the fluid analog of friction between solids. An object moving through a nonviscous fluid would experience no viscous drag force—that is, no resistive force due to viscosity; it could move at constant speed through the fluid. ...
p.1 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF AN EXPERIMENTAL
... the optical access to the helium bath and choice of suitable tracer particles. At the pressure of 1 bar 4He is liquid, if the temperature is lower than 4.2 K. It is called normal helium (or He I) at temperatures larger than 2.17 K and is characterised by extremely low values of the kinematic viscosi ...
... the optical access to the helium bath and choice of suitable tracer particles. At the pressure of 1 bar 4He is liquid, if the temperature is lower than 4.2 K. It is called normal helium (or He I) at temperatures larger than 2.17 K and is characterised by extremely low values of the kinematic viscosi ...
Buoyancy and Archimedes` principle
... pascal 1 Pa = 1 N.m Re = ρ v L / η newton 1 N = 1 kg.m.s [Re] ≡ [kg.m-3] [m.s-1][m] 1 Pa.s = kg.m.s . m .s [Pa.s] ≡ kg x m x m x s2.m2 = [1] m3 s kg.m.s Re is a dimensionless number ...
... pascal 1 Pa = 1 N.m Re = ρ v L / η newton 1 N = 1 kg.m.s [Re] ≡ [kg.m-3] [m.s-1][m] 1 Pa.s = kg.m.s . m .s [Pa.s] ≡ kg x m x m x s2.m2 = [1] m3 s kg.m.s Re is a dimensionless number ...
Moving-particle Semi
... The paper presents a method and a numerical scheme for the analysis of incompressible flows. This scheme is very often used in fluid’s animation applications. ...
... The paper presents a method and a numerical scheme for the analysis of incompressible flows. This scheme is very often used in fluid’s animation applications. ...