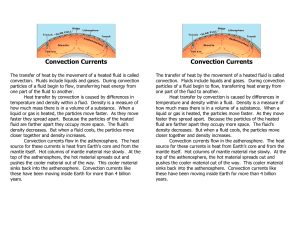
Currents experiment
... What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it ...
... What are the three types of heat transfer? How is heat transferred through space? What is a convection current? In general, what happens to the density of a fluid as it ...
Mechanical model of the turbulence generation in the
... describe the flow of the working medium at hand. However it is the validity of the initial assumptions that is ultimately responsible for the reliability of results of computations. The issue is further complicated by the fact that flow patterns of working media flowing through various channels are ...
... describe the flow of the working medium at hand. However it is the validity of the initial assumptions that is ultimately responsible for the reliability of results of computations. The issue is further complicated by the fact that flow patterns of working media flowing through various channels are ...
control volume approach and continuity principle
... the problem you want to solve. Steady flow problems are often easier than unsteady ones, so control volume b) may be preferable. ...
... the problem you want to solve. Steady flow problems are often easier than unsteady ones, so control volume b) may be preferable. ...
Buoyancy
... particle during the course of motion with time (fig *) The fluid particles may change their shape, size and state as they move. As mass of fluid particles remains constant throughout the motion, the basic laws of mechanics can be applied to them at all times. The task of following large number of fl ...
... particle during the course of motion with time (fig *) The fluid particles may change their shape, size and state as they move. As mass of fluid particles remains constant throughout the motion, the basic laws of mechanics can be applied to them at all times. The task of following large number of fl ...
1 - vnhsphysics
... The density of a substance is mass per unit volume. It has units of kilograms per cubic meter (or grams per cubic centimeter) in the metric system: =m/V PRESSURE Pressure is force exerted per unit area: P=F/A Pressure [Pascals] = Force [Newtons] / Area [m2] BASIC LAW OF FLUID PRESSURE The pressur ...
... The density of a substance is mass per unit volume. It has units of kilograms per cubic meter (or grams per cubic centimeter) in the metric system: =m/V PRESSURE Pressure is force exerted per unit area: P=F/A Pressure [Pascals] = Force [Newtons] / Area [m2] BASIC LAW OF FLUID PRESSURE The pressur ...
boundary-layer thickness - Icivil-Hu
... mutually interact, ultimately leading to a fully turbulent boundary layer at the transition point, which nominally occurs at a Reynolds number of 3 × 106(Retr 3 × 106). For purposes of simplicity in this text, it will be assumed that the boundary layer changes from laminar to turbulent flow at a Rey ...
... mutually interact, ultimately leading to a fully turbulent boundary layer at the transition point, which nominally occurs at a Reynolds number of 3 × 106(Retr 3 × 106). For purposes of simplicity in this text, it will be assumed that the boundary layer changes from laminar to turbulent flow at a Rey ...
Correction for housner`s equation of bending vibration of a pipe line
... The system under consideration consists of a uniform tubular beam of length l, internal radius a, conveying uncompressible fluid of density p, flowing axially with a constant velocity o 9 It is assumed that the bending vibration of the pipe is one of a beam, and the disturbed flow of the fluid in th ...
... The system under consideration consists of a uniform tubular beam of length l, internal radius a, conveying uncompressible fluid of density p, flowing axially with a constant velocity o 9 It is assumed that the bending vibration of the pipe is one of a beam, and the disturbed flow of the fluid in th ...
Demonstration 1: Fluid Properties, Viscosity
... the finite size and shape of the body. A number of experiments have been performed to determine CD for several geometries. These experiments show that the variation of CD depends primarily on a parameter called the Reynolds number Re, defined by ...
... the finite size and shape of the body. A number of experiments have been performed to determine CD for several geometries. These experiments show that the variation of CD depends primarily on a parameter called the Reynolds number Re, defined by ...
CM2110 Chapter 2 - Chemical Engineering
... Force= lbf = lbforce= defined as 1 unit mass (1 lbmass) times acceleration of gravity (ft/s2) a = g = acceleration of gravity = 32.174 ft/s2 = 9.8066 m/s2= 980.66 cm/s2 1 lbf = 32.174 lbm .ft/s2 ...
... Force= lbf = lbforce= defined as 1 unit mass (1 lbmass) times acceleration of gravity (ft/s2) a = g = acceleration of gravity = 32.174 ft/s2 = 9.8066 m/s2= 980.66 cm/s2 1 lbf = 32.174 lbm .ft/s2 ...
The Material Derivative The equations above apply to a fluid
... Putting all these components together and dividing by ρδV we ...
... Putting all these components together and dividing by ρδV we ...
School of Physics - The University of Sydney
... flow changes from laminar to turbulent will depend to some extent on the shape of the object. As a rough guide, however, we can also say in this case that the transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs around a value of 2000. With increasing Reynolds number, before the flow becomes fully turbu ...
... flow changes from laminar to turbulent will depend to some extent on the shape of the object. As a rough guide, however, we can also say in this case that the transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs around a value of 2000. With increasing Reynolds number, before the flow becomes fully turbu ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Any change in the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the containing vessel. Pascal’s Principle explains the working of hydraulic lifts ...
... Any change in the pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the containing vessel. Pascal’s Principle explains the working of hydraulic lifts ...