Electrons and Photons
... bonding occurs, the constituent atoms are “free” to wander around. They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The va ...
... bonding occurs, the constituent atoms are “free” to wander around. They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The va ...
High power, continuous-wave ytterbium-doped fiber - HAL
... such as photochemistry and spectroscopy which require narrow optical bandwidth, laser cooling where the laser wavelength has to be specifically adjusted, metrology or medical treatments. There is also an increasing attention of such sources for parametric applications as for instance frequency conve ...
... such as photochemistry and spectroscopy which require narrow optical bandwidth, laser cooling where the laser wavelength has to be specifically adjusted, metrology or medical treatments. There is also an increasing attention of such sources for parametric applications as for instance frequency conve ...
... 4. Explain the determination of velocity of ultrasonic sound using an acoustical grating. 5. What is meant by SONAR? Explain in detail how SONAR is employed to locate the objects? What are the applications of SONAR? 6. Describe the principle, construction and working of ultrasonic flaw detector. Exp ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due to its ability to directly interact with the electronic, spin, and lattice excitat ...
... optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due to its ability to directly interact with the electronic, spin, and lattice excitat ...
Matter in Intense Laser Fields
... electron in the continuum interacts only with its own parent ion or atom and does not undergo any collision with the neighbouring atom or ion. In ATI, when an electron gains energy equal to the ionization potential of the atom, the electron is moved to a distance where the coulomb potential of the n ...
... electron in the continuum interacts only with its own parent ion or atom and does not undergo any collision with the neighbouring atom or ion. In ATI, when an electron gains energy equal to the ionization potential of the atom, the electron is moved to a distance where the coulomb potential of the n ...
CHAPTER 1 Wave Nature of Light
... • To obtain stimulated emission, the incoming photon should not be absorbed by another atom at E1. • We must have the majority of the atoms at the energy level E2. • When there are more atoms at E2 than at E1 we then have what is called a population inversion. • With only two levels we can never ach ...
... • To obtain stimulated emission, the incoming photon should not be absorbed by another atom at E1. • We must have the majority of the atoms at the energy level E2. • When there are more atoms at E2 than at E1 we then have what is called a population inversion. • With only two levels we can never ach ...
Simultaneous Measurements of Hard X Rays and Second
... laser light, the ratio between the P and the S components of SH was approximately 100, while in the case of Spolarized laser light such a ratio was approximately 2. The experimental results presented here clearly show that laser polarization is a key factor in the interaction regime under investigat ...
... laser light, the ratio between the P and the S components of SH was approximately 100, while in the case of Spolarized laser light such a ratio was approximately 2. The experimental results presented here clearly show that laser polarization is a key factor in the interaction regime under investigat ...
Mission to Mercury
... Ion engines use beams of ions (charged atoms or molecules) to create thrust in accordance with Newton’s 3rd Law. Unlike a chemical rocket which burns fuel very quickly, an ion engine produces much less thrust but can keep running for a long time. This allows a spacecraft to slowly build up speed and ...
... Ion engines use beams of ions (charged atoms or molecules) to create thrust in accordance with Newton’s 3rd Law. Unlike a chemical rocket which burns fuel very quickly, an ion engine produces much less thrust but can keep running for a long time. This allows a spacecraft to slowly build up speed and ...
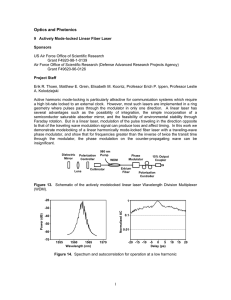
852_1.pdf
... carrier frequency. The interference fringe intensity signal in one channel recorded from the air-sample interface without laser excitation is shown in Figure 2a. The nearly harmonic waveform becomes significantly distorted (Figure 2b) when an acoustic wave travels across the probing point. Two effec ...
... carrier frequency. The interference fringe intensity signal in one channel recorded from the air-sample interface without laser excitation is shown in Figure 2a. The nearly harmonic waveform becomes significantly distorted (Figure 2b) when an acoustic wave travels across the probing point. Two effec ...
Photonic laser thruster

A photonic laser thruster is an amplified laser thruster that generates thrust directly from the laser photon momentum, rather than laser-heating propellant. The concept of single-bounce laser-pushed lightsails that utilize the photon momentum was first developed in the 1960s, however, its conversion of laser power to thrust is highly inefficient, thus has been considered impractical. Over 50 years, there had been numerous theoretical and experimental efforts to increase the conversion efficiency by recycling photons, bouncing them repetitively between two reflective mirrors in an empty optical cavity, without success. In December 2006, Young Bae successfully solved this problem and demonstrated the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor of 100 and a photon thrust of 35 micronewtons by putting the laser energizing media between the two mirrors as in typical lasers, and the photonic laser thruster was born. In August 2015, the photonic laser thruster was demonstrated to increase the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor over 1,000 and to achieve a photon thrust of 3.5 millinewtons at Y.K. Bae Corporation. In addition, Propelling, slowing and stopping of a small satellite, 1U CubeSat, in simulated zero-gravity were demonstrated. The photonic laser thruster was initially developed for use in nanometer precision spacecraft formation, for forming ultralarge space telescopes and radars. The photonic laser thruster is currently developed for high-precision and high-speed maneuver of small spacecraft, such as formation flying, orbit adjustments, drag compensation, and rendezvous and docking. The photonic laser thruster can be used for beaming thrust from a conventional heavy resource vehicle to a more expensive & lightweight mission vehicle, similar to tankers in aerial refueling.The practical usage of the photonic laser thruster for main space propulsion would require extremely high laser powers and overcoming technological challenges in achieving the laser power and fabricating the required optics. Photonic laser thrusters have a very high specific impulse, and can permit spacecraft reach much higher speeds than with conventional rockets, which are limited by the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation. If the photonic laser thruster is scalable for the use in such main space propulsion, multiple photonic laser thrusters can be used to construct a 'photonic railway' that has been proposed as a potential permanent transport infrastructure for interplanetary or interstellar commutes, allowing the transport craft themselves to carry very little fuel.