Study of the X-ray Source Population and the Dark Matter
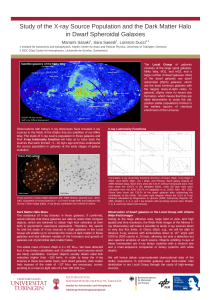
... The existence of X-ray binaries in these galaxies, if confirmed, would indicate that these galaxies are able to retain their compact objects, which are believed to obtain high kick velocities at their birth in asymmetric supernova explosions. Therefore, the search for and the study of X-ray sources ...
... The existence of X-ray binaries in these galaxies, if confirmed, would indicate that these galaxies are able to retain their compact objects, which are believed to obtain high kick velocities at their birth in asymmetric supernova explosions. Therefore, the search for and the study of X-ray sources ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 2) What is the name of the galaxy we live in? What type of galaxy is it? Where is our solar system found within this galaxy? Milky Way It is a Spiral Galaxy. Our solar system is found near the end of one arm of the spiral. ...
... 2) What is the name of the galaxy we live in? What type of galaxy is it? Where is our solar system found within this galaxy? Milky Way It is a Spiral Galaxy. Our solar system is found near the end of one arm of the spiral. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... supernova core can collapse to a point, forming a black hole Gravity is so strong not even light can escape Beyond a black hole’s event horizon gravity operates as it would before the mass collapsed Matter emitted by a star over its life time is recycled and can become part of a new nebula ...
... supernova core can collapse to a point, forming a black hole Gravity is so strong not even light can escape Beyond a black hole’s event horizon gravity operates as it would before the mass collapsed Matter emitted by a star over its life time is recycled and can become part of a new nebula ...
Hubble’s Law & Black Holes at a Galaxy’s Center
... Black Hole at the Center of the Milky Way Galaxy ...
... Black Hole at the Center of the Milky Way Galaxy ...
LIGO Star Chart
... super giant and that if our sun were to be replaced by Betelgeuse the surface of the star’s atmosphere would extend almost to the orbit of Jupiter! Betelgeuse is a very old star that is a prime candidate for self-destruction in a supernova explosion. If we were to begin seeing the explosion today, i ...
... super giant and that if our sun were to be replaced by Betelgeuse the surface of the star’s atmosphere would extend almost to the orbit of Jupiter! Betelgeuse is a very old star that is a prime candidate for self-destruction in a supernova explosion. If we were to begin seeing the explosion today, i ...
How the universe began
... • Does this make the Earth the centre of the universe? • Scientists don’t think this is true • Blow up a balloon with spots all over it – all the spots get further away from each other ...
... • Does this make the Earth the centre of the universe? • Scientists don’t think this is true • Blow up a balloon with spots all over it – all the spots get further away from each other ...
File - Mr. Pelton Science
... • Masses of galaxies have a wide range from 1 million to 1 trillion times the mass of our Sun. • Dwarf ellipticals = 1 million x Sun’s mass • Large spirals = 100 billion x Sun’s mass • Giant ellipticals = 1 trillion x Sun’s mass ...
... • Masses of galaxies have a wide range from 1 million to 1 trillion times the mass of our Sun. • Dwarf ellipticals = 1 million x Sun’s mass • Large spirals = 100 billion x Sun’s mass • Giant ellipticals = 1 trillion x Sun’s mass ...
Stellar Lives (continued). Galaxies.
... The Origin of Elements How do we know that elements are produced inside stars? If massive stars do produce heavy elements and disperse them in space, then the total amount of heavy elements should gradually increase with time. We should expect stars born recently to contain more heavy elements than ...
... The Origin of Elements How do we know that elements are produced inside stars? If massive stars do produce heavy elements and disperse them in space, then the total amount of heavy elements should gradually increase with time. We should expect stars born recently to contain more heavy elements than ...
2.3 Peculiar galaxies
... Black hole accretion discs. If the available gas simply fell radially downwards towards the black hole, the energy it would gain would be kinetic energy, and it wouldn’t give much radiation; it would just disappear down the black hole. However, if, as is very likely, the gas is rotating around the b ...
... Black hole accretion discs. If the available gas simply fell radially downwards towards the black hole, the energy it would gain would be kinetic energy, and it wouldn’t give much radiation; it would just disappear down the black hole. However, if, as is very likely, the gas is rotating around the b ...
Slide 1
... known as red giants, white dwarfs, neutron stars, black holes and exploding stars called novae and supernovae. In addition there are quasars (quasistellar radio sources’’), which, if we judge their distance correctly, are galaxies thousands of times brighter than ordinary galaxies. Furthermore, ther ...
... known as red giants, white dwarfs, neutron stars, black holes and exploding stars called novae and supernovae. In addition there are quasars (quasistellar radio sources’’), which, if we judge their distance correctly, are galaxies thousands of times brighter than ordinary galaxies. Furthermore, ther ...
solar.gmu.edu
... •A quasar’s luminosity can be calculated from its apparent brightness and the distance using the inverse-square law •Even though small, the luminosity of a quasar (1038 to 1042 Watts) can be very larger, i.e., several thousand times more than the entire Milly Way Galaxies (1037). •A quasar has emiss ...
... •A quasar’s luminosity can be calculated from its apparent brightness and the distance using the inverse-square law •Even though small, the luminosity of a quasar (1038 to 1042 Watts) can be very larger, i.e., several thousand times more than the entire Milly Way Galaxies (1037). •A quasar has emiss ...
main characteristics of the emission from elliptical galaxies
... environment; surrounded by a looser region which fades away with no detailed contour. In general, ellipticals are mainly composed of red giants and stars on the asymptotic giant branch, born at the same time in an early burst of star formation activity. We have then a very small fraction of hot, you ...
... environment; surrounded by a looser region which fades away with no detailed contour. In general, ellipticals are mainly composed of red giants and stars on the asymptotic giant branch, born at the same time in an early burst of star formation activity. We have then a very small fraction of hot, you ...
Chapter 34: Cosmology FYI 1. Radar Ranging 2. Triangulation idea
... P4: Consider light observed on earth that was emitted by atoms moving with stars or galaxies. Which statements are true? a. You can actually see little red atoms that have been shifted to the left. They have small beady red eyes and cannot be trusted. b. The spectral colors emitted by the atoms movi ...
... P4: Consider light observed on earth that was emitted by atoms moving with stars or galaxies. Which statements are true? a. You can actually see little red atoms that have been shifted to the left. They have small beady red eyes and cannot be trusted. b. The spectral colors emitted by the atoms movi ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... When you look at an object 1 light away, you are looking at what it looked like 1 year ago. When you look at an object 1 million light years away, you are looking at it 1 million years ago. The universe is thought to be 13.66 billion years old, so when you look back 12.7 billion years - are you lo ...
... When you look at an object 1 light away, you are looking at what it looked like 1 year ago. When you look at an object 1 million light years away, you are looking at it 1 million years ago. The universe is thought to be 13.66 billion years old, so when you look back 12.7 billion years - are you lo ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... Galaxy Formation – Is the End in Sight? LESSONS FROM THE PAST ...
... Galaxy Formation – Is the End in Sight? LESSONS FROM THE PAST ...
PH607lec12
... 4. A compact radio source called SgrA* which is quite unlike any another radio source in the Galaxy. 5.. Radial velocities and proper motions of both stars and gas which imply the existence of a large, unseen, compact object. Large means a mass =~ 2.5 x 106 M 6.. Black hole. The discovery that the r ...
... 4. A compact radio source called SgrA* which is quite unlike any another radio source in the Galaxy. 5.. Radial velocities and proper motions of both stars and gas which imply the existence of a large, unseen, compact object. Large means a mass =~ 2.5 x 106 M 6.. Black hole. The discovery that the r ...
Active Galactic Nuclei
... 3. The brightness will not change in less than 10 days. 4. The brightness will not change in less than 100 days. ...
... 3. The brightness will not change in less than 10 days. 4. The brightness will not change in less than 100 days. ...
APOD 2016 Calendar
... formed, extremely bright, massive stars. That galaxy, AM 0644-741, is known as a ring galaxy and was caused by an immense galaxy collision. When galaxies collide, they pass through each other — their individual stars rarely come into contact. The ring-like shape is the result of the gravitational di ...
... formed, extremely bright, massive stars. That galaxy, AM 0644-741, is known as a ring galaxy and was caused by an immense galaxy collision. When galaxies collide, they pass through each other — their individual stars rarely come into contact. The ring-like shape is the result of the gravitational di ...
The Sun, Stars, and Beyond
... • Irregularly shaped galaxies also exist, though fewer in number. • A galaxy’s shape is determined by its rate of spin, and if it has been subject to any collisions or mergers. • These all contain 100 billion stars or more, and there are 100 billion galaxies out there! ...
... • Irregularly shaped galaxies also exist, though fewer in number. • A galaxy’s shape is determined by its rate of spin, and if it has been subject to any collisions or mergers. • These all contain 100 billion stars or more, and there are 100 billion galaxies out there! ...
Galaxy Powerpoint Notes
... because you’re in one! Unfortunately, galaxies are massive, and we can’t see as much as we wish, and that is why with the assistance of telescopes, astronomers have been able to identify certain things in space. Our galaxy (the Milky Way, in case you didn’t know), is made up of stars, gas, dust, a s ...
... because you’re in one! Unfortunately, galaxies are massive, and we can’t see as much as we wish, and that is why with the assistance of telescopes, astronomers have been able to identify certain things in space. Our galaxy (the Milky Way, in case you didn’t know), is made up of stars, gas, dust, a s ...
Galaxies • Test 3 (New date) – Thurs, 9 April
... there must have been gas 20 Myrs ago. (Compare to age of the sun, 4.5Byrs.) ...
... there must have been gas 20 Myrs ago. (Compare to age of the sun, 4.5Byrs.) ...
Hoag`s Object
... an outer 45″ diameter of 121±4 kly (39.9±1.7 kpc), which is slightly larger than the Milky Way Galaxy.[1][a] The gap separating the two stellar populations may contain some star clusters that are almost too faint to see. As rare as this type of galaxy is, another more distant currently unnamed ring ...
... an outer 45″ diameter of 121±4 kly (39.9±1.7 kpc), which is slightly larger than the Milky Way Galaxy.[1][a] The gap separating the two stellar populations may contain some star clusters that are almost too faint to see. As rare as this type of galaxy is, another more distant currently unnamed ring ...
Historical overview
... divided into normal (S’s) and barred (SB’s) ordered by ratio of bulge to disk (a,ab,b,bc,c,cd,d) also referred to “early-type” (a-b) and “late-type” (c-d) spirals special class: S0 (‘lenticular’) are a transition between elliptical and spiral, with bulge and disk but no spiral arms ...
... divided into normal (S’s) and barred (SB’s) ordered by ratio of bulge to disk (a,ab,b,bc,c,cd,d) also referred to “early-type” (a-b) and “late-type” (c-d) spirals special class: S0 (‘lenticular’) are a transition between elliptical and spiral, with bulge and disk but no spiral arms ...
Introduction to Galaxies - West Jefferson Local Schools
... Recall, luminosity of stars scales with mass of stars… therefore, luminosity of galaxy scales with number of stars (and thus, mass of stars). Thus, luminosity of galaxy gives mass of galaxy. Going backwards… measure the velocity to “weigh” the galaxy to obtain luminosity. ...
... Recall, luminosity of stars scales with mass of stars… therefore, luminosity of galaxy scales with number of stars (and thus, mass of stars). Thus, luminosity of galaxy gives mass of galaxy. Going backwards… measure the velocity to “weigh” the galaxy to obtain luminosity. ...
Galaxy Zoo

Galaxy Zoo is a crowdsourced astronomy project which invites people to assist in the morphological classification of large numbers of galaxies. (e.g.) It is an example of citizen science as it enlists the help of members of the public to help in scientific research. There have been seven versions up to July 2014, which are outlined in this article. Galaxy Zoo is part of the Zooniverse, a group of citizen science projects.























