Friday, Oct. 10
... magnitude means a decrease in light by a factor of 2.5 The Sun has an absolute magnitude of about 5. A star with an absolute magnitude of 6 emits about 2.5 times less light than the Sun does. A star with an absolute magnitude of 0 (that’s 5 magnitudes smaller than the Sun) emits about 2.5x2.5x2.5x2. ...
... magnitude means a decrease in light by a factor of 2.5 The Sun has an absolute magnitude of about 5. A star with an absolute magnitude of 6 emits about 2.5 times less light than the Sun does. A star with an absolute magnitude of 0 (that’s 5 magnitudes smaller than the Sun) emits about 2.5x2.5x2.5x2. ...
Astronomy Study Guide #2
... 05. What two parameters does the brightness of a star depend on? 06. What is the stellar spectral classification sequence? 07. What do studies of binary stars help us learn? 08. Solar granulation is evidence for what aspect of energy transport? 09. In traveling from the center of the sun to the top ...
... 05. What two parameters does the brightness of a star depend on? 06. What is the stellar spectral classification sequence? 07. What do studies of binary stars help us learn? 08. Solar granulation is evidence for what aspect of energy transport? 09. In traveling from the center of the sun to the top ...
Star Classification
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
Making H-R Diagrams - PLC-METS
... see them the same. The apparent magnitude of a star is the amount of light received on Earth or the brightness of the star as seen from Earth. This is different than the absolute magnitude because the absolute magnitude is based upon the amount of light the star gives off. This difference is the rea ...
... see them the same. The apparent magnitude of a star is the amount of light received on Earth or the brightness of the star as seen from Earth. This is different than the absolute magnitude because the absolute magnitude is based upon the amount of light the star gives off. This difference is the rea ...
Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star
... • Space acts as a nursery full of the stuff needed to give birth to stars.. – Gas – Dust The Space Nursery provides both these materials in the clouds in the atmosphere of space! ...
... • Space acts as a nursery full of the stuff needed to give birth to stars.. – Gas – Dust The Space Nursery provides both these materials in the clouds in the atmosphere of space! ...
The Life Cycle of the Stars
... babies, children, teenagers, adults and even senior citizens. Like humans, stars pass through different stages in their lives. They are born, they mature and, eventually, they die. However, unlike humans, the typical star may last for millions or billions of years. While we cannot witness the comple ...
... babies, children, teenagers, adults and even senior citizens. Like humans, stars pass through different stages in their lives. They are born, they mature and, eventually, they die. However, unlike humans, the typical star may last for millions or billions of years. While we cannot witness the comple ...
Stars Unit 1-2: Stars
... in size, they vary even more in density! – Our sun has a density about 1.4 times greater than water. – Betelgeuse (don’t say it two more times!) is one-millionth the density of the sun. – Sirius is so dense, that one teaspoon of it would weigh more than a ton on earth! ...
... in size, they vary even more in density! – Our sun has a density about 1.4 times greater than water. – Betelgeuse (don’t say it two more times!) is one-millionth the density of the sun. – Sirius is so dense, that one teaspoon of it would weigh more than a ton on earth! ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical Societies, this is IT
... minutes a day in most of the United States and four to five minutes a day in Canada. The year's most outstanding array of stars, centered in Orion, are now high in the sky soon after nightfall. The moon is new on February 20th. A team of astronomers from the University of Florida may have discovered ...
... minutes a day in most of the United States and four to five minutes a day in Canada. The year's most outstanding array of stars, centered in Orion, are now high in the sky soon after nightfall. The moon is new on February 20th. A team of astronomers from the University of Florida may have discovered ...
a star is born reading
... quickly than red ones. They are also brighter. They are like the spotlights in the dark auditorium. Yellow stars have a shorter life span than red ones, only ten billion years or so. Our Sun is about five billion years old. Toward the end of its life, it will become much larger. It will swallow up t ...
... quickly than red ones. They are also brighter. They are like the spotlights in the dark auditorium. Yellow stars have a shorter life span than red ones, only ten billion years or so. Our Sun is about five billion years old. Toward the end of its life, it will become much larger. It will swallow up t ...
25 Study Guide
... reviewing their notes for a few minutes each day, students will need to spend less time studying for tests. ...
... reviewing their notes for a few minutes each day, students will need to spend less time studying for tests. ...
Binary Stars (Professor Powerpoint)
... causing a periodic variation in brightness. Spectroscopic Binary - two stars that are found to orbit one another through observations of the Doppler effect in their spectral lines . At least half of the stars in the sky are binaries. Eclipsing Binary stars are also referred to as Extrinsic Variable ...
... causing a periodic variation in brightness. Spectroscopic Binary - two stars that are found to orbit one another through observations of the Doppler effect in their spectral lines . At least half of the stars in the sky are binaries. Eclipsing Binary stars are also referred to as Extrinsic Variable ...
December 1, 2011 - Perry Local Schools
... 1. Place the small flashlight on a desk or table near the front of the room. 2. Place the large flashlight on a desk or table near the back of the room. 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and co ...
... 1. Place the small flashlight on a desk or table near the front of the room. 2. Place the large flashlight on a desk or table near the back of the room. 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and co ...
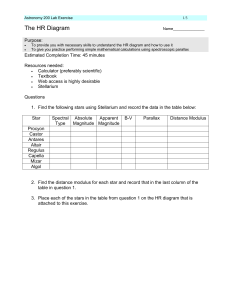
labex7
... radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
Ordinary Stars - Edgewood High School
... of 10,000 K and another a temperature of 5,000 K, how much more energy does the hotter star put out? ...
... of 10,000 K and another a temperature of 5,000 K, how much more energy does the hotter star put out? ...
Lesson 2 Power Notes Outline
... The sun’s middle atmosphere is called the chromosphere. Its temperatures range from 4,225 °C to 6,000 °C. ...
... The sun’s middle atmosphere is called the chromosphere. Its temperatures range from 4,225 °C to 6,000 °C. ...
Stars and the Sun
... – Luminosity: measure of the amount of energy given off. Measured as compared to the Sun (1), logarithmic 102, 104 – Apparent magnitude: as seen from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighter! – Absolute magnitude: if all stars were same distance from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighte ...
... – Luminosity: measure of the amount of energy given off. Measured as compared to the Sun (1), logarithmic 102, 104 – Apparent magnitude: as seen from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighter! – Absolute magnitude: if all stars were same distance from Earth, lower (including negative) is brighte ...
Background Information - Eu-Hou
... In order to plot a HR diagram, the temperature and luminosity of the stars need to be known. The simplest indication of a star’s temperature is its colour. A star’s colour is simply a measure of the amount of light from the star in one filter compared to another. The most common colour system is B-V ...
... In order to plot a HR diagram, the temperature and luminosity of the stars need to be known. The simplest indication of a star’s temperature is its colour. A star’s colour is simply a measure of the amount of light from the star in one filter compared to another. The most common colour system is B-V ...
Chapter 8: Stars
... sequence for a long time, they don’t stay their forever. • Average stars like the Sun, become red giants and then white dwarfs. • Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. ...
... sequence for a long time, they don’t stay their forever. • Average stars like the Sun, become red giants and then white dwarfs. • Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. ...
Measuring the Stars
... the period and semi-major axis of the orbit must be measured. •Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. •Relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect •Speed will be inversely proportional to the mass. This allows us to calculate the mass of each s ...
... the period and semi-major axis of the orbit must be measured. •Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. •Relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect •Speed will be inversely proportional to the mass. This allows us to calculate the mass of each s ...
stars_2nd_edit
... The more massive a star, the faster it uses up its fuel for fusion. Hydrogen, the most common element in the universe, is the primary fuel for fusion in stars. Hydrogen ...
... The more massive a star, the faster it uses up its fuel for fusion. Hydrogen, the most common element in the universe, is the primary fuel for fusion in stars. Hydrogen ...
mass per nucleon
... The Age of the Universe Stars in the oldest clusters have ages of 10-15 billion years From the expansion rate of the universe, we can estimate the time since the Big Bang. Current values are around 13 billion years. Are there stars older than the Universe??? ...
... The Age of the Universe Stars in the oldest clusters have ages of 10-15 billion years From the expansion rate of the universe, we can estimate the time since the Big Bang. Current values are around 13 billion years. Are there stars older than the Universe??? ...
star
... the farther away the star got from you? Absolute brightness-‐ how bright a star really is. Absolute brightness does not depend on how far away ...
... the farther away the star got from you? Absolute brightness-‐ how bright a star really is. Absolute brightness does not depend on how far away ...
SECTION 30.2 Measuring the Stars 1. Constellations are a. the
... 1. Constellations are a. the brightest stars. b. stars over Greece. c. groups of stars named after animals, mythological characters, or everyday objects. d. found only in the northern hemisphere. 2. Ursa Major, or the big dipper, is an example of a a. circumpolar constellation. b. constellation that ...
... 1. Constellations are a. the brightest stars. b. stars over Greece. c. groups of stars named after animals, mythological characters, or everyday objects. d. found only in the northern hemisphere. 2. Ursa Major, or the big dipper, is an example of a a. circumpolar constellation. b. constellation that ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.