Section 27.2
... 27.2 Temperature and luminosity H-R diagrams are useful because they help astronomers categorize stars into groups: Main sequence stars, like the Sun, are in a very stable part of their life cycle. White dwarfs are hot and dim and cannot be seen without a telescope. Red giants are cool and ...
... 27.2 Temperature and luminosity H-R diagrams are useful because they help astronomers categorize stars into groups: Main sequence stars, like the Sun, are in a very stable part of their life cycle. White dwarfs are hot and dim and cannot be seen without a telescope. Red giants are cool and ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF STARS
... looks from Earth depends on both its distance and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in 2 different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. Astronomers can measure apparent brightnes ...
... looks from Earth depends on both its distance and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in 2 different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. Astronomers can measure apparent brightnes ...
3.6 spectral classes
... • Absorption spectra are used to classify stars into nine principal types, called spectral classes. • Hydrogen lines are much stronger in the spectra of some stars than in the Sun’s spectrum. • Astronomers once mistakenly thought that these stars had more hydrogen than other stars. • They classified ...
... • Absorption spectra are used to classify stars into nine principal types, called spectral classes. • Hydrogen lines are much stronger in the spectra of some stars than in the Sun’s spectrum. • Astronomers once mistakenly thought that these stars had more hydrogen than other stars. • They classified ...
DR 19.2 - Cobb Learning
... ______ 23. high-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ______ 24. cool stars with absolute magnitude ______ 25. stars in the band that runs along the middle of the H-R diagram WHEN STARS GET OLD ______ 26. Which one of the following statements is NOT true of supernovas? a. They are exp ...
... ______ 23. high-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ______ 24. cool stars with absolute magnitude ______ 25. stars in the band that runs along the middle of the H-R diagram WHEN STARS GET OLD ______ 26. Which one of the following statements is NOT true of supernovas? a. They are exp ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 12 - 9th Edition 1. Consider a star
... history of the universe. 17. What are Cepheid variables, and how are they related to the instability strip? Answer: Cepheids are stars which pulsate in brightness in a distinctive way due to a thermal instability. A higher-mass star becomes a Cepheid when its evolutionary path takes it across the in ...
... history of the universe. 17. What are Cepheid variables, and how are they related to the instability strip? Answer: Cepheids are stars which pulsate in brightness in a distinctive way due to a thermal instability. A higher-mass star becomes a Cepheid when its evolutionary path takes it across the in ...
Lecture11
... •How does the temperature of an interstellar cloud affect its ability to form stars? •A) Star formation is so complicated that it is not possible to say how one quantity, such as temperature, affects it •B) Higher temperatures inhibit star formation •C) Higher temperatures help star formation •D) St ...
... •How does the temperature of an interstellar cloud affect its ability to form stars? •A) Star formation is so complicated that it is not possible to say how one quantity, such as temperature, affects it •B) Higher temperatures inhibit star formation •C) Higher temperatures help star formation •D) St ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 17 Nature of Stars
... Measuring Distances to Nearby Stars: Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by parallax, the apparent shift of a star against the background stars observed as the Earth moves along its orbit. Parallax measurements made from orbit, above the blurring effects of the atmosphere, are much more ...
... Measuring Distances to Nearby Stars: Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by parallax, the apparent shift of a star against the background stars observed as the Earth moves along its orbit. Parallax measurements made from orbit, above the blurring effects of the atmosphere, are much more ...
ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... • I will be away Monday-Thursday inclusive at the Division of Planetary Sciences meeting • Monday and Wednesday's lecture will be given by Professor Hickson (last year's ASTR 200 ...
... • I will be away Monday-Thursday inclusive at the Division of Planetary Sciences meeting • Monday and Wednesday's lecture will be given by Professor Hickson (last year's ASTR 200 ...
The Milky Way
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
29.2 Measuring the Stars - Mr. Tobin`s Earth Science Class
... stars including Sun (which is at the center because it has an average temperature and luminosity.) • Stars here fuse hydrogen. • As hydrogen runs out stars fuse helium ...
... stars including Sun (which is at the center because it has an average temperature and luminosity.) • Stars here fuse hydrogen. • As hydrogen runs out stars fuse helium ...
Level 4 Constellations North Star, South Star
... Constellations are groupings of stars that form easily recognized and remembered patterns, such as Orion and the Big Dipper. The Big Dipper is actually an asterism, not a constellation, because it is only part of the constellation Ursa Major (the Big Bear). Actually, the stars in the majority of all ...
... Constellations are groupings of stars that form easily recognized and remembered patterns, such as Orion and the Big Dipper. The Big Dipper is actually an asterism, not a constellation, because it is only part of the constellation Ursa Major (the Big Bear). Actually, the stars in the majority of all ...
lesson 5-8 quiz.show.pps
... It happens in late September. It occurs one time a year. It is the beginning of fall in the southern hemisphere. ...
... It happens in late September. It occurs one time a year. It is the beginning of fall in the southern hemisphere. ...
Planetarium Key Points
... degree an hour, 1 deg every 4 minutes Fixed stars seem to be engraved on the surface of celestial sphere Mobile stars move along the ecliptic line from West to Est, that is their direct motion; some of them sometime move in retrograde motion from Est to West Also the Sun seems to move along th ...
... degree an hour, 1 deg every 4 minutes Fixed stars seem to be engraved on the surface of celestial sphere Mobile stars move along the ecliptic line from West to Est, that is their direct motion; some of them sometime move in retrograde motion from Est to West Also the Sun seems to move along th ...
Stellar Evolution 1 Star Formation 2 Nebulae
... TEXTBOOK ERROR: Note that Figure 14.3 on Page 365 of the textbook is just a repeat of Figure 14.2 on Page 364. We humans, ever anthropomorphizing, look at stars and imagine them as living things, having a birth, a life, and a death. This unit of the course studies the life cycles of stars. The follo ...
... TEXTBOOK ERROR: Note that Figure 14.3 on Page 365 of the textbook is just a repeat of Figure 14.2 on Page 364. We humans, ever anthropomorphizing, look at stars and imagine them as living things, having a birth, a life, and a death. This unit of the course studies the life cycles of stars. The follo ...
Section 3: Evolution of Stars pages 114-119
... Obj: Explain why some constellations are only visible during certain season Because the earth is in constant motion. The earth orbits the sun so during certain seasons the earth is different locations around the sun so there are different stars visible in the night time sky. Obj: Distinguish be ...
... Obj: Explain why some constellations are only visible during certain season Because the earth is in constant motion. The earth orbits the sun so during certain seasons the earth is different locations around the sun so there are different stars visible in the night time sky. Obj: Distinguish be ...
Stars - Montville.net
... as seen from Earth. Affected by distance 8. What is absolute brightness? The brightness a star would have if it were a standard distance from the Earth. 9. Why is finding a stars brightness so difficult? An astronomer must find the apparent brightness and the distance from the Earth. ...
... as seen from Earth. Affected by distance 8. What is absolute brightness? The brightness a star would have if it were a standard distance from the Earth. 9. Why is finding a stars brightness so difficult? An astronomer must find the apparent brightness and the distance from the Earth. ...
H-R diagram worksheet
... Mark each of the following on the H-R diagram and label it as indicated. You may use page 15 of your ESRT to help you. 6. Draw and label a long diagonal line showing the approximate location of the main sequence. 7. A large circle indicating the area where you find the biggest diameter stars, labele ...
... Mark each of the following on the H-R diagram and label it as indicated. You may use page 15 of your ESRT to help you. 6. Draw and label a long diagonal line showing the approximate location of the main sequence. 7. A large circle indicating the area where you find the biggest diameter stars, labele ...
File - Awakening in Grade 6
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
File
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
Stars & Constellations
... However some constellations can be seen all year round. Some, like Cassiopeia are circumpolar - this means they circle above the pole, so can always been seen (the Earth’s orbit around the sun does not affect their viewing) ...
... However some constellations can be seen all year round. Some, like Cassiopeia are circumpolar - this means they circle above the pole, so can always been seen (the Earth’s orbit around the sun does not affect their viewing) ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... • Some giant stars, in variable numbers If all main sequences are the same (i.e. have the same absolute magnitude at a given temperature), then can create a composite HR diagram (Handout 3) – plausible if all stars formed at same time out of same gas cloud same age and composition Then find distan ...
... • Some giant stars, in variable numbers If all main sequences are the same (i.e. have the same absolute magnitude at a given temperature), then can create a composite HR diagram (Handout 3) – plausible if all stars formed at same time out of same gas cloud same age and composition Then find distan ...
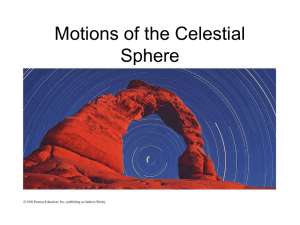
Motions of the Celestial Sphere
... in arcs across the sky that are not perpendicular to horizon. ...
... in arcs across the sky that are not perpendicular to horizon. ...
HR Diagram Lab Handout
... Background: You are about to create your own HR Diagram, a chart that revolutionized the study of stars. You will have a labeled chart and a series of points to plot. From these points, you can deduce a lot of information about stars! Please read the directions in each step of the activity closely b ...
... Background: You are about to create your own HR Diagram, a chart that revolutionized the study of stars. You will have a labeled chart and a series of points to plot. From these points, you can deduce a lot of information about stars! Please read the directions in each step of the activity closely b ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.