Measuring stars Part I
... Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolute visual magnitude to Deneb without knowing its distance in the ...
... Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolute visual magnitude to Deneb without knowing its distance in the ...
Stars: the Hertzsprung
... star burns hydrogen into helium. • This causes the other properties to change with time and we can track these changes via motion of the star in the HR diagram. ...
... star burns hydrogen into helium. • This causes the other properties to change with time and we can track these changes via motion of the star in the HR diagram. ...
Normal Stars - Chandra X
... stars similar to the Sun are essential for understanding the long term behavior of the Sun, and consequently, the long-term weather forecast for Earth. Certain stars, called flare stars, have surfaces that are in a constant state of turmoil. These stars flare almost continually and the flares are a ...
... stars similar to the Sun are essential for understanding the long term behavior of the Sun, and consequently, the long-term weather forecast for Earth. Certain stars, called flare stars, have surfaces that are in a constant state of turmoil. These stars flare almost continually and the flares are a ...
Stars and Constellations
... For the people in the Native American southwest, the sky is not something remote from Earth. Rather, it is a unifying whole, both a window into the universe and an instrument for understanding and measuring its rhythms. Indian people have been watching the sky for many generations and applying its s ...
... For the people in the Native American southwest, the sky is not something remote from Earth. Rather, it is a unifying whole, both a window into the universe and an instrument for understanding and measuring its rhythms. Indian people have been watching the sky for many generations and applying its s ...
Constellations and Asterisms
... for answers to questions about life on earth, or even just for entertainment. There are two sets of constellations: an ancient set, and a more recent set. Ancient constellations are in the shapes of mythological beasts and great heroes; there are 48 of these in total that are still used today. The m ...
... for answers to questions about life on earth, or even just for entertainment. There are two sets of constellations: an ancient set, and a more recent set. Ancient constellations are in the shapes of mythological beasts and great heroes; there are 48 of these in total that are still used today. The m ...
Unit 1
... • Photons have a difficult time moving through a star’s atmosphere • If the photon has the right energy, it will be absorbed by an atom and raise an electron to a higher energy level • Creates absorption spectra, a unique “fingerprint” for the star’s composition. The strength of this spectra is dete ...
... • Photons have a difficult time moving through a star’s atmosphere • If the photon has the right energy, it will be absorbed by an atom and raise an electron to a higher energy level • Creates absorption spectra, a unique “fingerprint” for the star’s composition. The strength of this spectra is dete ...
1. absolute brightness -
... classification of stars according to their spectral characteristics. • They are classified according to the spectral lines observed, originally the amount of Hydrogen the lines seemed to indicate. • Today they are ranked in order of surface temperature. O, B, A, F, G, K, M from hottest to coolest. ...
... classification of stars according to their spectral characteristics. • They are classified according to the spectral lines observed, originally the amount of Hydrogen the lines seemed to indicate. • Today they are ranked in order of surface temperature. O, B, A, F, G, K, M from hottest to coolest. ...
Stars - MrCrabtreesScience
... • We can only see a tiny bit of the light stars produce. • Visible light • Stars emit lots of different kinds of ‘light’ ...
... • We can only see a tiny bit of the light stars produce. • Visible light • Stars emit lots of different kinds of ‘light’ ...
te acher`s guide te acher`s guide
... What are the signs of the zodiac? The signs of the zodiac are twelve different groups of stars that are named after animals or mythical creatures.They are constellations — patterns of stars in the night sky — that appear to create outlines of pictures when viewed from Earth. How are stars born? At f ...
... What are the signs of the zodiac? The signs of the zodiac are twelve different groups of stars that are named after animals or mythical creatures.They are constellations — patterns of stars in the night sky — that appear to create outlines of pictures when viewed from Earth. How are stars born? At f ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
... Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What variable will you be measuring?) Procedure: A. Using the “Mass” slider and the “Create Star” button, create 6 stars with the following masses: DO NOT X-OUT UNTIL YOU ANSWER BOTH QUESTIONS BELOW!! Set Mass To ...
... Dependent Variable: ____________________________ (What variable will you be measuring?) Procedure: A. Using the “Mass” slider and the “Create Star” button, create 6 stars with the following masses: DO NOT X-OUT UNTIL YOU ANSWER BOTH QUESTIONS BELOW!! Set Mass To ...
Mon Oct 22, 2012 MOON IN CAPRICORNUS The moon is waxing
... a member of our Milky Way, but instead another galaxy, comprising 300 billion stars and approximately two and a half million light years away. One light year, the distance light can travel in a year, is roughly six trillion miles. So when you see the Andromeda Galaxy, you’re looking at something tha ...
... a member of our Milky Way, but instead another galaxy, comprising 300 billion stars and approximately two and a half million light years away. One light year, the distance light can travel in a year, is roughly six trillion miles. So when you see the Andromeda Galaxy, you’re looking at something tha ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... Temperature-Luminosity diagrams Astronomers measure the temperatures and luminosities of many stars and plot them on a diagram called the Hertzsprung-Russell (or H-R) diagram. For historical reasons they plot temperatures increasing to the left (not right) and luminosities increasing upward. They a ...
... Temperature-Luminosity diagrams Astronomers measure the temperatures and luminosities of many stars and plot them on a diagram called the Hertzsprung-Russell (or H-R) diagram. For historical reasons they plot temperatures increasing to the left (not right) and luminosities increasing upward. They a ...
The Stars
... • A: Temperatures from 8000-10,000K. They appear white. Strong absorption lines of hydrogen. Examples: Vega, Altair, Sirius. • F: slightly hotter than the Sun. Absorption lines of metals appear. Procyon is an F star. • G: temperatures between 5000 and 6000K. Appear yellow. ...
... • A: Temperatures from 8000-10,000K. They appear white. Strong absorption lines of hydrogen. Examples: Vega, Altair, Sirius. • F: slightly hotter than the Sun. Absorption lines of metals appear. Procyon is an F star. • G: temperatures between 5000 and 6000K. Appear yellow. ...
Morning Announcements
... Tables I and II. 1) For each star, indicate its position on the graph below with a small ―x. The Sun (G2, 4.8) has been plotted for you. Plot the bright stars (Table I) and near stars (Table II) in different colors by using, for instance, pencil for the bright ones and blue ink for the near ones. NO ...
... Tables I and II. 1) For each star, indicate its position on the graph below with a small ―x. The Sun (G2, 4.8) has been plotted for you. Plot the bright stars (Table I) and near stars (Table II) in different colors by using, for instance, pencil for the bright ones and blue ink for the near ones. NO ...
Homework 5 (stellar properties)
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... •Lacaille extended Bayer's notation by using lower case (and some upper case) Latin letters. •John Flamsteed (1646-1719) First Royal Astronomer of England •Assigned stars “numbers”, starting with 1 in the west, and working eastward. •Hence Vega is ...
... •Lacaille extended Bayer's notation by using lower case (and some upper case) Latin letters. •John Flamsteed (1646-1719) First Royal Astronomer of England •Assigned stars “numbers”, starting with 1 in the west, and working eastward. •Hence Vega is ...
Russell Diagram
... A binary star system consists of one star that is twice as massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
... A binary star system consists of one star that is twice as massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
The Universe
... Nuclear Fusion – Two atoms are pushed together so hard they ‘fuse’ into one and create a different element ...
... Nuclear Fusion – Two atoms are pushed together so hard they ‘fuse’ into one and create a different element ...
Charcteristic of Stars Powerpoint C
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its size and temperature. A larger star tends to be brighter than a smaller star. A hotter star tends to be brighter than a cooler star. • How bright a star appears depends on both its distance from Earth and how bright the star truly is. Because of these t ...
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its size and temperature. A larger star tends to be brighter than a smaller star. A hotter star tends to be brighter than a cooler star. • How bright a star appears depends on both its distance from Earth and how bright the star truly is. Because of these t ...
Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. It is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of heavier elements. ...
... A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. It is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of heavier elements. ...
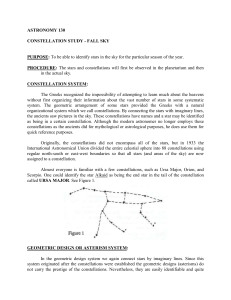
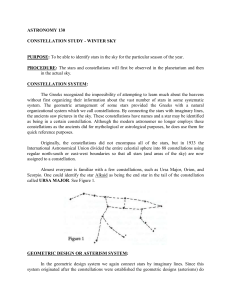
ASTRONOMY 130
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.