Document
... is called its main sequence lifetime. – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity. • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars.. • High-mass stars are more luminous than low-mass stars. • High mass sta ...
... is called its main sequence lifetime. – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity. • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars.. • High-mass stars are more luminous than low-mass stars. • High mass sta ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... Compare absolute and apparent magnitudes • If we know the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of a star, we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
... Compare absolute and apparent magnitudes • If we know the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of a star, we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
the lives of stars
... sky. People named these patterns, called constellations and told stories about them. This picture shows one of the most easily recognized constellations. The ancient Greeks thought this group of stars looked like a hunter from one of their myths, so they named it Orion after a great hunter. The patt ...
... sky. People named these patterns, called constellations and told stories about them. This picture shows one of the most easily recognized constellations. The ancient Greeks thought this group of stars looked like a hunter from one of their myths, so they named it Orion after a great hunter. The patt ...
Star Cycle2013
... fuse it together. You actually end up with less energy than you started with! So instead of generating pressure to hold up the outer layers, the iron fusion actually takes it out of the core. Thus, there is nothing left to combat gravity from the outer layers. ...
... fuse it together. You actually end up with less energy than you started with! So instead of generating pressure to hold up the outer layers, the iron fusion actually takes it out of the core. Thus, there is nothing left to combat gravity from the outer layers. ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
HR Diagram and Life of a star
... the sun ( but has a much smaller diameter than the sun) it creates a Neutron Star which spins and emits a steady beam of radiation and light out of its poles. *Neutron stars are so Dense that a teaspoon of a neutron star on EARTH would weigh a billion tons. * If the neutron star is spinning it will ...
... the sun ( but has a much smaller diameter than the sun) it creates a Neutron Star which spins and emits a steady beam of radiation and light out of its poles. *Neutron stars are so Dense that a teaspoon of a neutron star on EARTH would weigh a billion tons. * If the neutron star is spinning it will ...
HR-Diagram
... This time there is so much energy because of the large mass of the outer star that the collapse causes a Super Nova Explosion. NOW…if the CORE of the star has a mass of 3x or less the size of the sun ( but has a much smaller diameter than the sun) it creates a Neutron Star which spins and emits a st ...
... This time there is so much energy because of the large mass of the outer star that the collapse causes a Super Nova Explosion. NOW…if the CORE of the star has a mass of 3x or less the size of the sun ( but has a much smaller diameter than the sun) it creates a Neutron Star which spins and emits a st ...
The night sky in October and November
... It alternately fades and shines brightly. In 1572 an astronomer named Tycho Brahe saw a new bright star near Cassiopeia, and called it a “nova” or new. It only lasted a few days. He thought he had witnessed the first instance of this phenomenon. He was wrong as several other civilizations saw the sa ...
... It alternately fades and shines brightly. In 1572 an astronomer named Tycho Brahe saw a new bright star near Cassiopeia, and called it a “nova” or new. It only lasted a few days. He thought he had witnessed the first instance of this phenomenon. He was wrong as several other civilizations saw the sa ...
File
... Once born, stars are self-illuminating…they ____________________________________________! Main sequence = ______________ yellow stars (like our sun!) + ______________ blue stars As a star runs out of energy, it ______________ into a red ______________ or a red ______________________ After stars die, ...
... Once born, stars are self-illuminating…they ____________________________________________! Main sequence = ______________ yellow stars (like our sun!) + ______________ blue stars As a star runs out of energy, it ______________ into a red ______________ or a red ______________________ After stars die, ...
Presentation for perspective graduate students 2006
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
8.1 Stars
... neutrons only about 15 km across, it is called a neutron star. Neutron stars are made of the densest material known ...
... neutrons only about 15 km across, it is called a neutron star. Neutron stars are made of the densest material known ...
Astronomy 1 – Winter 2011
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
Stars: radius and mass
... – Optical double stars – stars that appear close together, but are not physically conected. – Binary stars, or binaries – stars that are gravitationally bound and orbit one another. ...
... – Optical double stars – stars that appear close together, but are not physically conected. – Binary stars, or binaries – stars that are gravitationally bound and orbit one another. ...
Exercise 9
... Astronomers use the right ascension (RA) to determine the position along the celestial equator of an object (think of it as sort of a space longitude). By tradition, the RA is measured counterclockwise in units of hours and minutes, starting at 0 hours and coming back, after one full circle, to 24 h ...
... Astronomers use the right ascension (RA) to determine the position along the celestial equator of an object (think of it as sort of a space longitude). By tradition, the RA is measured counterclockwise in units of hours and minutes, starting at 0 hours and coming back, after one full circle, to 24 h ...
34ReviewNuclear
... B. Studying absorption lines in stars C. Studying binary star orbits D. Studying the brightnesses of stars E. Only by estimation Hotter stars will be bluer, cooler stars will be redder. However, there’s a possibility you might get confused by intervening dust between us and the star, which might mak ...
... B. Studying absorption lines in stars C. Studying binary star orbits D. Studying the brightnesses of stars E. Only by estimation Hotter stars will be bluer, cooler stars will be redder. However, there’s a possibility you might get confused by intervening dust between us and the star, which might mak ...
Quantum Well Electron Gain Structures and Infrared
... Mercury/Venus too hot Earth – just right Mars – was OK once (?), but now cold Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune too cold (though some moons may be OK) ...
... Mercury/Venus too hot Earth – just right Mars – was OK once (?), but now cold Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune too cold (though some moons may be OK) ...
AST101_lect_12
... Apparent magnitudes (m): what we see Absolute magnitudes (M): pegged to luminosity M is the magnitude you would see at a distance of 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) M = 4.8 Distance modulus (DM): a measure of distance DM = m - M = 5 log(d) -5 ...
... Apparent magnitudes (m): what we see Absolute magnitudes (M): pegged to luminosity M is the magnitude you would see at a distance of 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) M = 4.8 Distance modulus (DM): a measure of distance DM = m - M = 5 log(d) -5 ...
CHAPTER 10, Stellar Motions
... Stellar Motions and the Solar Neighborhood 10-1. The Solar Neighborhood The Solar Neighborhood is the volume of space around the Sun extending to a distance of 100 parsecs. Some properties of the Solar Neighborhood are: 1. The solar neighborhood contains about 500 x 103 stars, most of which are very ...
... Stellar Motions and the Solar Neighborhood 10-1. The Solar Neighborhood The Solar Neighborhood is the volume of space around the Sun extending to a distance of 100 parsecs. Some properties of the Solar Neighborhood are: 1. The solar neighborhood contains about 500 x 103 stars, most of which are very ...
Star Gazing
... Correctly hold and orient a star chart and use it to find stars and constellations. Practice star hopping to locate stars and constellations. *Explain why the date and time are included on star charts State the magnitude scale for stars. Given a star’s magnitude, identify if it is bright or faint. I ...
... Correctly hold and orient a star chart and use it to find stars and constellations. Practice star hopping to locate stars and constellations. *Explain why the date and time are included on star charts State the magnitude scale for stars. Given a star’s magnitude, identify if it is bright or faint. I ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: 11.1 Properties of Stars
... Sometimes we can only detect a “wobble” of one star (can’t see the fainter one). ...
... Sometimes we can only detect a “wobble” of one star (can’t see the fainter one). ...
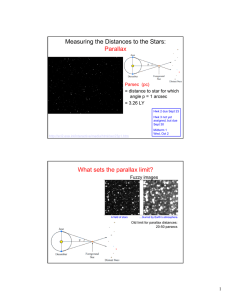
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
star
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
... Contains two (or sometimes more) stars which orbit around their common center of mass. Importance - only when a star is in a binary system that we have the possibility of deriving its true mass. The period – watching the system for many years. The more unequal the masses are, the The distance betwe ...
here - British Astronomical Association
... Professionals need the observations (too many VS and too few professionals to observe them). VS tell us so much about stellar evolution and ultimately, the fate of our own Sun. It is one of the few areas where an amateur can make a contribution to science – and you don’t even need a ...
... Professionals need the observations (too many VS and too few professionals to observe them). VS tell us so much about stellar evolution and ultimately, the fate of our own Sun. It is one of the few areas where an amateur can make a contribution to science – and you don’t even need a ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.