ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
O star
... Hipparchus called the brightest stars in the sky “stars of the first magnitude” and the faintest stars the eye could see “stars of the sixth magnitude.” Thus there were five magnitudes difference between the brightest and faintest stars (6-1). It turns out that a difference of five magnitudes corres ...
... Hipparchus called the brightest stars in the sky “stars of the first magnitude” and the faintest stars the eye could see “stars of the sixth magnitude.” Thus there were five magnitudes difference between the brightest and faintest stars (6-1). It turns out that a difference of five magnitudes corres ...
Astronomy Part 2 - Malvern Troop 7
... a) List the names of the five most visible planets. Explain which ones can appear in phases similar to lunar phases and which ones cannot, and explain why. b) Find out when each of the five most visible planets that you identified in requirement 5a will be observable in the evening sky during the ne ...
... a) List the names of the five most visible planets. Explain which ones can appear in phases similar to lunar phases and which ones cannot, and explain why. b) Find out when each of the five most visible planets that you identified in requirement 5a will be observable in the evening sky during the ne ...
Issue 118 - Apr 2014
... see add ( to the magnitude of the dimmest star you can identify i.e. <13.2. Add a question mark or colon if you are not sure of your estimate (i.e. 13.2: or 13.2?). Visit the AAVSO web site. Take time to look around, you will find a lot of interesting information. Register with AAVSO and you will re ...
... see add ( to the magnitude of the dimmest star you can identify i.e. <13.2. Add a question mark or colon if you are not sure of your estimate (i.e. 13.2: or 13.2?). Visit the AAVSO web site. Take time to look around, you will find a lot of interesting information. Register with AAVSO and you will re ...
Lecture
... – O star: ~ 1 million years – G star (Sun): ~ 10 billion years – M star : ~ 5,000 billion years ...
... – O star: ~ 1 million years – G star (Sun): ~ 10 billion years – M star : ~ 5,000 billion years ...
Slides from Lecture04
... • The brightest stars were labeled “1st magnitude” stars • Successively fainter stars were catalogued as 2nd magnitude, 3rd magnitude, etc. • Faintest stars (visible to the “naked eye”) were catalogued by Greek astronomers as 6th magnitude stars. • Astronomers continue to use this “magnitude” system ...
... • The brightest stars were labeled “1st magnitude” stars • Successively fainter stars were catalogued as 2nd magnitude, 3rd magnitude, etc. • Faintest stars (visible to the “naked eye”) were catalogued by Greek astronomers as 6th magnitude stars. • Astronomers continue to use this “magnitude” system ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... periodic table of the elements. The periodic table is an arrangement of all the known elements in order of increasing atomic number. The reason why the elements are arranged as they are in the periodic table is to fit them all, with their widely diverse physical and chemical properties, into a logic ...
... periodic table of the elements. The periodic table is an arrangement of all the known elements in order of increasing atomic number. The reason why the elements are arranged as they are in the periodic table is to fit them all, with their widely diverse physical and chemical properties, into a logic ...
Stars and Galaxies
... • Polaris/North Star, 700+ light-years – Important in navigation – End of Little Dipper which is part of: – Ursa Minor/Little Bear – constellation of stars • Group of stars which people can see at one time • Imaginary figures ...
... • Polaris/North Star, 700+ light-years – Important in navigation – End of Little Dipper which is part of: – Ursa Minor/Little Bear – constellation of stars • Group of stars which people can see at one time • Imaginary figures ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
Lecture 10-11 - OSU Astronomy
... Edward Pickering & Williamina Fleming made a first attempt to classify ~10,000 stars by their spectra: • Sorted by Hydrogen absorption-line strength • Spectral Type “A” = strongest Hydrogen lines • followed by types B, C, D, etc. (weaker) ...
... Edward Pickering & Williamina Fleming made a first attempt to classify ~10,000 stars by their spectra: • Sorted by Hydrogen absorption-line strength • Spectral Type “A” = strongest Hydrogen lines • followed by types B, C, D, etc. (weaker) ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... light to travel a particular distance and is just a measurement scientists use to account for distance in space. Parallax- the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations. For close stars scientists use parallax to measure the distance to those stars. Apparent Ma ...
... light to travel a particular distance and is just a measurement scientists use to account for distance in space. Parallax- the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations. For close stars scientists use parallax to measure the distance to those stars. Apparent Ma ...
Abs-Apar Mag
... • Hipparchus (maybe Ptolemy?) – 2000 BCE – A ranking system – Brightest stars = 1st class, then 2nd, 3rd… – 6th magnitude are faintest stars seen at night – Result: lower number = brighter “There is no other rule for classing the stars but the estimation of the observer; and hence it is that some as ...
... • Hipparchus (maybe Ptolemy?) – 2000 BCE – A ranking system – Brightest stars = 1st class, then 2nd, 3rd… – 6th magnitude are faintest stars seen at night – Result: lower number = brighter “There is no other rule for classing the stars but the estimation of the observer; and hence it is that some as ...
Star Fromation and ISM
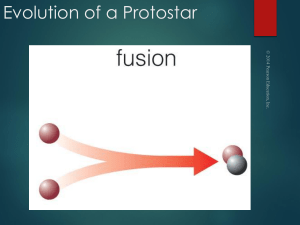
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to f ...
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to f ...
constellations are not real!
... totally imaginary things that poets, farmers and astronomers have made up over the past 6,000 years (and probably even more!). The real purpose for the constellations is to help us tell which stars are which, nothing more ...
... totally imaginary things that poets, farmers and astronomers have made up over the past 6,000 years (and probably even more!). The real purpose for the constellations is to help us tell which stars are which, nothing more ...
THE LIFE CYCLES OF STARS (3)
... This line was discovered experimentally from observations of stars well before the theory of star condensation was worked out, and in fact the end point of the calculations was made to be this line. How it was discovered is the subject of today's talk. We shall need to understand how we measure the ...
... This line was discovered experimentally from observations of stars well before the theory of star condensation was worked out, and in fact the end point of the calculations was made to be this line. How it was discovered is the subject of today's talk. We shall need to understand how we measure the ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing surface temperature on ...
... Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing surface temperature on ...
s%nffi - mrtavares
... a process known as nuclear fusion. This nuclear reaction converts four hydrogen nuclei into the nucleus of a helium atom. Tremendous energy is released. W During nuclear fusion, energy is released because solne matter is actually converted to energyr as shown in Figure 18. How does this process work ...
... a process known as nuclear fusion. This nuclear reaction converts four hydrogen nuclei into the nucleus of a helium atom. Tremendous energy is released. W During nuclear fusion, energy is released because solne matter is actually converted to energyr as shown in Figure 18. How does this process work ...
The H-R Diagram
... images. These are relatively rare – need wide separations, like out to Pluto and beyond – to separate the stars on images • Spectroscopic binaries: by far the most common, binary pairs are usually so close you can only see a blended image of both stars. It is the Doppler Shifts in the spectra of one ...
... images. These are relatively rare – need wide separations, like out to Pluto and beyond – to separate the stars on images • Spectroscopic binaries: by far the most common, binary pairs are usually so close you can only see a blended image of both stars. It is the Doppler Shifts in the spectra of one ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... Cassiopeia (KAS-ee-uh-PEE-uh), the Queen. Is one of the so-called circumpolar constellations, which means that it may be observed on any evening of the year. Look for the obvious letter M, or W, floating opposite the Big Dipper, with Polaris in between. Here we will find a beautiful, true binary sta ...
... Cassiopeia (KAS-ee-uh-PEE-uh), the Queen. Is one of the so-called circumpolar constellations, which means that it may be observed on any evening of the year. Look for the obvious letter M, or W, floating opposite the Big Dipper, with Polaris in between. Here we will find a beautiful, true binary sta ...
The (Stellar) Parallax View
... The most basic technique is called the Stellar Parallax method. Everyone has seen parallax in action, even if they don’t know the word. Parallax is the apparent movement of an object against a background due to a change in the observer’s position. Here is a little experiment to demonstrate this effe ...
... The most basic technique is called the Stellar Parallax method. Everyone has seen parallax in action, even if they don’t know the word. Parallax is the apparent movement of an object against a background due to a change in the observer’s position. Here is a little experiment to demonstrate this effe ...
Chapter 09 - The Independent School
... Trigonometric Parallax: Star appears slightly shifted from different positions of the Earth on its orbit The farther away the star is (larger d), the smaller the parallax angle p. ...
... Trigonometric Parallax: Star appears slightly shifted from different positions of the Earth on its orbit The farther away the star is (larger d), the smaller the parallax angle p. ...
The Birth, Life, and Death of Stars
... Born in Ulm, Germany in 1879 and died in Princeton in 1955 Questions the basic tenets of Quantum Mechanics: God does not play dice with the Universe ... Yet, is awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics: ... for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect 1905 Einstein’s Miracle Year while wo ...
... Born in Ulm, Germany in 1879 and died in Princeton in 1955 Questions the basic tenets of Quantum Mechanics: God does not play dice with the Universe ... Yet, is awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics: ... for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect 1905 Einstein’s Miracle Year while wo ...
Distances to the Stars in Leo
... luminosity class. We can use the luminosity to find its absolute magnitude and thus its distance. Finding the distances to stars based upon their spectral type and luminosity is known as spectroscopic parallax (even though no parallax determination or trigonometry is involved). This method is neithe ...
... luminosity class. We can use the luminosity to find its absolute magnitude and thus its distance. Finding the distances to stars based upon their spectral type and luminosity is known as spectroscopic parallax (even though no parallax determination or trigonometry is involved). This method is neithe ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.