Chapter 19 Star Formation
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
Heavy Metal from Ancient Superstars
... Primordial Epoch -The Big Bang (hydrogen, helium, lithium) Epoch of Massive Stars – the first few million years Ca, O, and the “mystery metals” Supernova Epoch - r-process elements from 8-10 MSun SNII The first few 10’s of millions of years ...
... Primordial Epoch -The Big Bang (hydrogen, helium, lithium) Epoch of Massive Stars – the first few million years Ca, O, and the “mystery metals” Supernova Epoch - r-process elements from 8-10 MSun SNII The first few 10’s of millions of years ...
A new low proper motion catalogue of bright M
... they often can be confused for reddened stars or distant red giants. Because of this their identification in large surveys has been difficult. With exoplanet research now moving from the time of discovery to the time of characterization, methods to obtain information about the exoplanet’s atmosphere ...
... they often can be confused for reddened stars or distant red giants. Because of this their identification in large surveys has been difficult. With exoplanet research now moving from the time of discovery to the time of characterization, methods to obtain information about the exoplanet’s atmosphere ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... and B for some of the stars in your cluster and also a finding chart so that the stars with published values can be identified on your images. There is a great resource to help with this on the web: http://www.univie.ac.at/webda/Welcome.html http://www.univie.ac.at/webda/cgi-bin/ocl_page.cgi?dirname ...
... and B for some of the stars in your cluster and also a finding chart so that the stars with published values can be identified on your images. There is a great resource to help with this on the web: http://www.univie.ac.at/webda/Welcome.html http://www.univie.ac.at/webda/cgi-bin/ocl_page.cgi?dirname ...
Star A
... In a double-line spectroscopic binary, two distinct sets of spectral lines—one for each component star—shift back and forth as the stars move. Because we see particular lines alternately approaching and receding, we know that the objects emitting the lines are in orbit. Media Clip In the more commo ...
... In a double-line spectroscopic binary, two distinct sets of spectral lines—one for each component star—shift back and forth as the stars move. Because we see particular lines alternately approaching and receding, we know that the objects emitting the lines are in orbit. Media Clip In the more commo ...
1 Sep: 6.13am BST 15 Sep: 6.43am BST 30 Sep: 7.14am BST
... Observatory Australia. While it is presently at Mag 8.0, it’s been reported as a hazy patch in binoculars or small telescope. It is predicted to brighten to around Mag 6.0 towards the end of 2011 into 2012 and a finder and light curve chart are reproduced below. Daily information on the comet’s posi ...
... Observatory Australia. While it is presently at Mag 8.0, it’s been reported as a hazy patch in binoculars or small telescope. It is predicted to brighten to around Mag 6.0 towards the end of 2011 into 2012 and a finder and light curve chart are reproduced below. Daily information on the comet’s posi ...
Virtual HR Diagram Lab
... 8. Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating-alternately growing bigger and smaller- ...
... 8. Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating-alternately growing bigger and smaller- ...
Spectroscopy Lecture 10
... apparent magnitudes: (B, V, ...) colour indices: absolute magnitudes (d from parallax): ...
... apparent magnitudes: (B, V, ...) colour indices: absolute magnitudes (d from parallax): ...
Stars and Nebulae
... nearby star or stars. Reflection nebulae are usually blue, because blue light scatters more easily. Emission and reflection nebulae are often seen together and are sometimes both referred to as diffuse nebulae. In some nebulae, the star formation regions are so dense and thick that light cannot get ...
... nearby star or stars. Reflection nebulae are usually blue, because blue light scatters more easily. Emission and reflection nebulae are often seen together and are sometimes both referred to as diffuse nebulae. In some nebulae, the star formation regions are so dense and thick that light cannot get ...
Slide 1
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
CONSTELLATION TUCANA, THE TOUCAN
... spectroscopic binary, which means that the two stars have not been individually resolved using a telescope, but the presence of the companion has been inferred from measuring changes in the spectrum of the primary. The orbital period of the binary system is 4197.7 days (11.5 years). Nothing is known ...
... spectroscopic binary, which means that the two stars have not been individually resolved using a telescope, but the presence of the companion has been inferred from measuring changes in the spectrum of the primary. The orbital period of the binary system is 4197.7 days (11.5 years). Nothing is known ...
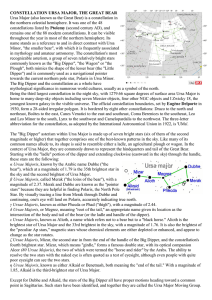
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
... Ursa Major (also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its ...
Oct 06, 2001
... This is a” thinking” question: Star A appears brighter than Star B, but Star A actually gives off less energy than Star B. The apparent magnitude and absolute magnitudes for Star A are m = 1 and M = -2, respectively. Use this information to answer the following two questions. 13) Which of the follow ...
... This is a” thinking” question: Star A appears brighter than Star B, but Star A actually gives off less energy than Star B. The apparent magnitude and absolute magnitudes for Star A are m = 1 and M = -2, respectively. Use this information to answer the following two questions. 13) Which of the follow ...
Ch 19 Directed Reading
... 8. The band of colors that make up white light is called a(n) ______________________. 9. A spectrum that shows all the colors is called a(n) ______________________spectrum. 10. A tool that breaks a star’s light into colors is called a(n) ______________________. ...
... 8. The band of colors that make up white light is called a(n) ______________________. 9. A spectrum that shows all the colors is called a(n) ______________________spectrum. 10. A tool that breaks a star’s light into colors is called a(n) ______________________. ...
High-Speed Ballistic Stellar Interlopers
... Astronomers have discovered a new class of bright, high-velocity stars speeding through the galaxy. Called “ballistic stellar interlopers,” the stars are plowing through dense regions of interstellar gas at velocities possibly as high as 100,000 miles per hour. As they do, they create brilliant arro ...
... Astronomers have discovered a new class of bright, high-velocity stars speeding through the galaxy. Called “ballistic stellar interlopers,” the stars are plowing through dense regions of interstellar gas at velocities possibly as high as 100,000 miles per hour. As they do, they create brilliant arro ...
Luminosity - UCF Physics
... measure its distance and apparent brightness: Luminosity = 4π (distance)2 x (Brightness) Note that there is a huge range in stellar ...
... measure its distance and apparent brightness: Luminosity = 4π (distance)2 x (Brightness) Note that there is a huge range in stellar ...
Target Stars for Earth-like Planet Searches with the Terrestrial
... basic parameters for an Earth-like planet near each of the stars, including the diameter of the Habitable Zone (HZ). For these purposes, the HZ is defined as the distance from the star at which an Earth-like planet would have the same equilibrium temperature as Earth. (3) Select those stars for whic ...
... basic parameters for an Earth-like planet near each of the stars, including the diameter of the Habitable Zone (HZ). For these purposes, the HZ is defined as the distance from the star at which an Earth-like planet would have the same equilibrium temperature as Earth. (3) Select those stars for whic ...
Introduction and first data set
... All observations were made though a filter (the V filter) that allows light in the wavelength range 0.45-0.55 m to pass. Fluxes are quoted in W m-2 nm-1, ie. the rate at which energy hits a unit area of the telescope, per unit wavelength range the instrument is sensitive to. ...
... All observations were made though a filter (the V filter) that allows light in the wavelength range 0.45-0.55 m to pass. Fluxes are quoted in W m-2 nm-1, ie. the rate at which energy hits a unit area of the telescope, per unit wavelength range the instrument is sensitive to. ...
Astronomy
... 5. Describe some of the different kinds of star charts available: Seasonal star charts good for a specific date and time, planispheres good all year, equatorial star charts good all year for +60 to -60 declination ...
... 5. Describe some of the different kinds of star charts available: Seasonal star charts good for a specific date and time, planispheres good all year, equatorial star charts good all year for +60 to -60 declination ...
stargazing - davis.k12.ut.us
... Stars in the sky have fascinated people throughout the ages. Many years ago when people were out tending their flocks, sailing their ships, traveling or just star gazing, they noticed how some stars were always visible at night. Other stars were only visible during certain months of the year. People ...
... Stars in the sky have fascinated people throughout the ages. Many years ago when people were out tending their flocks, sailing their ships, traveling or just star gazing, they noticed how some stars were always visible at night. Other stars were only visible during certain months of the year. People ...
Lecture 2
... about the changes that stars undergo with time. But before that let’s look at the intrinsic differences between stars. ...
... about the changes that stars undergo with time. But before that let’s look at the intrinsic differences between stars. ...
Summer Triangle (Winter in the south hemisphere) Lyra
... the silence of being followed by a ghost. So, in great worry that she was not really there, he turned around, only to see the spirit of his wife pulled back into the underworld for eternity. Notable Stars Alpha Lyrae, the harp star, is commonly known as Vega 織女星. This name comes from an Arabic word ...
... the silence of being followed by a ghost. So, in great worry that she was not really there, he turned around, only to see the spirit of his wife pulled back into the underworld for eternity. Notable Stars Alpha Lyrae, the harp star, is commonly known as Vega 織女星. This name comes from an Arabic word ...
MS Word
... subcatagories. Thus you can have a B2 star, as well as a G8 star. There are A0 stars and F7 stars. Look at each of the tables and under ‘spectral type’ you will see these classifications. Remember that B0 stars are the hottest and M9 stars are the coolest. Thus the left side of an H-R diagram is for ...
... subcatagories. Thus you can have a B2 star, as well as a G8 star. There are A0 stars and F7 stars. Look at each of the tables and under ‘spectral type’ you will see these classifications. Remember that B0 stars are the hottest and M9 stars are the coolest. Thus the left side of an H-R diagram is for ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... If stellar mass objects greater than 50 M do survive gravitational instabilities during birth, these objects would collapse very rapidly from protostar state and burn their thermonuclear fuel so quickly (i.e., within 10 million years) that few of these objects would be seen. When these hypermassive ...
... If stellar mass objects greater than 50 M do survive gravitational instabilities during birth, these objects would collapse very rapidly from protostar state and burn their thermonuclear fuel so quickly (i.e., within 10 million years) that few of these objects would be seen. When these hypermassive ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.