Luminosity
... Color–the hottest stars are “red hot” Color–the hottest stars are “bluish white” Spectral type 1 and 3 2 and 3 ...
... Color–the hottest stars are “red hot” Color–the hottest stars are “bluish white” Spectral type 1 and 3 2 and 3 ...
Astronomy.Practice.Quiz3
... c. neutron star d. supernova 6. What is the next stage in the Sun’s life cycle? a. white dwarf b. red giant c. planetary nebula ...
... c. neutron star d. supernova 6. What is the next stage in the Sun’s life cycle? a. white dwarf b. red giant c. planetary nebula ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... globules (dark clouds) and giant gaseous pillars (emission nebulae), followed by circumstellar disks, and progressing to evolved massive stars in the young starburst cluster.To the upper right of center is the evolved blue supergiant called Sher 25. The star has a unique circumstellar ring of glowin ...
... globules (dark clouds) and giant gaseous pillars (emission nebulae), followed by circumstellar disks, and progressing to evolved massive stars in the young starburst cluster.To the upper right of center is the evolved blue supergiant called Sher 25. The star has a unique circumstellar ring of glowin ...
Reading the Stars
... 1. Examine color-magnitude diagrams of clusters of stars. Since a cluster of stars is a group of stars that were formed at the same time from the same cloud of gas and dust, we can learn a lot about the stars within that cluster. A color-magnitude diagram is a kind of H-R Diagram. The horizontal axi ...
... 1. Examine color-magnitude diagrams of clusters of stars. Since a cluster of stars is a group of stars that were formed at the same time from the same cloud of gas and dust, we can learn a lot about the stars within that cluster. A color-magnitude diagram is a kind of H-R Diagram. The horizontal axi ...
PHY111 Stellar Evolution
... luminosity as they evolve, but do change in colour (so they must change in size) ...
... luminosity as they evolve, but do change in colour (so they must change in size) ...
Astronomy Library wk 7.cwk (WP)
... We’ll see later. But first we’ll take a detour to examine the evolution of low mass stars. ...
... We’ll see later. But first we’ll take a detour to examine the evolution of low mass stars. ...
1st EXAM VERSION C - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... A. *It is not possible to measure the star's mass accurately. B. There are several ways to measure its mass accurately. C. Its mass can be measured accurately only if its luminosity and temperature can be measured. D. Its mass can be measured accurately only if its distance can be found. 42. A refle ...
... A. *It is not possible to measure the star's mass accurately. B. There are several ways to measure its mass accurately. C. Its mass can be measured accurately only if its luminosity and temperature can be measured. D. Its mass can be measured accurately only if its distance can be found. 42. A refle ...
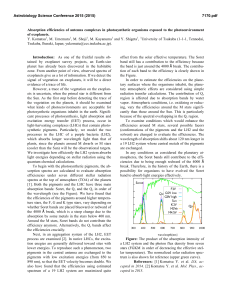
Absorption efficiencies of antenna complexes in photosynthetic
... efficiencies under seven different stellar radiation spectra at the top of atmosphere (TOA) of the planets [1]. Both the pigments and the LHC have three main absorption bands: Soret, the Qx and the Qy in order of the wavelength (see the Figure). We have found that the efficiencies of the pigments ar ...
... efficiencies under seven different stellar radiation spectra at the top of atmosphere (TOA) of the planets [1]. Both the pigments and the LHC have three main absorption bands: Soret, the Qx and the Qy in order of the wavelength (see the Figure). We have found that the efficiencies of the pigments ar ...
Chapter 09 - The Independent School
... in astronomy is very difficult. To discover the properties of stars, astronomers must use their telescopes and spectrographs in ingenious ways to learn the secrets hidden in starlight. The result is a family portrait of the stars. Here you will find answers to five essential questions about stars: • ...
... in astronomy is very difficult. To discover the properties of stars, astronomers must use their telescopes and spectrographs in ingenious ways to learn the secrets hidden in starlight. The result is a family portrait of the stars. Here you will find answers to five essential questions about stars: • ...
ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... Given measured ∆λ, and the wavelength of the atomic line were are looking at, l, we can then get velocity v of object using the speed of light c ...
... Given measured ∆λ, and the wavelength of the atomic line were are looking at, l, we can then get velocity v of object using the speed of light c ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... not change much, so there will be a region in this diagram where a human spends most of their lifetime. The following visualization emphasizes these concepts: http://opencourse.uoregon.edu/pub/astr122/pod4.pps (click to start the animated sequence) The HR diagram (named after astronomers Hertzsprung ...
... not change much, so there will be a region in this diagram where a human spends most of their lifetime. The following visualization emphasizes these concepts: http://opencourse.uoregon.edu/pub/astr122/pod4.pps (click to start the animated sequence) The HR diagram (named after astronomers Hertzsprung ...
A Stars
... – Objective Prism Photography – obtained spectra of >100,000 stars – hired women as “computers” to analyze spectra ASTR111 Lecture 13 ...
... – Objective Prism Photography – obtained spectra of >100,000 stars – hired women as “computers” to analyze spectra ASTR111 Lecture 13 ...
giant molecular clouds
... In stars slightly more massive than the sun, a more powerful energy generation mechanism than the PP chain takes over: ...
... In stars slightly more massive than the sun, a more powerful energy generation mechanism than the PP chain takes over: ...
Mapping the Stars
... A Tool for Studying Stars • The combination of research done between Danish astronomer (Hertzsprung) and American astronomer (Henry Norris Russell) on the brightness and temperature of stars resulted in a graph called what? • H-R diagram • What does the diagram show? • It shows the relationship bet ...
... A Tool for Studying Stars • The combination of research done between Danish astronomer (Hertzsprung) and American astronomer (Henry Norris Russell) on the brightness and temperature of stars resulted in a graph called what? • H-R diagram • What does the diagram show? • It shows the relationship bet ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Spectral Classes Strange lettering scheme is a historical accident. Spectral Class ...
... Spectral Classes Strange lettering scheme is a historical accident. Spectral Class ...
Document
... • Electrons accelerate down the magnetic field lines toward the lower atmosphere, producing microwave emission • Electrons collide with ions, producing hard x-rays, white light emission from chromosphere • Chromospheric plasma heated to coronal temperatures, hot plasma flows up into the corona • Sho ...
... • Electrons accelerate down the magnetic field lines toward the lower atmosphere, producing microwave emission • Electrons collide with ions, producing hard x-rays, white light emission from chromosphere • Chromospheric plasma heated to coronal temperatures, hot plasma flows up into the corona • Sho ...
Stars
... baseball. Your friend holds a basketball. You know that a basketball is much larger than a baseball. But what seems to happen if you friend carries the basketball to the other end of the field? The basketball looks smaller than the baseball to you. The basketball does not really get smaller. It look ...
... baseball. Your friend holds a basketball. You know that a basketball is much larger than a baseball. But what seems to happen if you friend carries the basketball to the other end of the field? The basketball looks smaller than the baseball to you. The basketball does not really get smaller. It look ...
Conceptual Physics
... 2. Stars spend about 90% of their life: a. As protostars b. On the main sequence c. As red giants d. As planetary nebula e. Forming planets. 3. In a random sample of stars in the Sun’s neighborhood, you would expect about 90% of them: a. To be red giants b. To be white dwarfs c. To be main sequence ...
... 2. Stars spend about 90% of their life: a. As protostars b. On the main sequence c. As red giants d. As planetary nebula e. Forming planets. 3. In a random sample of stars in the Sun’s neighborhood, you would expect about 90% of them: a. To be red giants b. To be white dwarfs c. To be main sequence ...
Lecture 19 - Stellar Lifecycles
... • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The explosion is so energetic that it can outshine the combined light of a galaxy! • Heavy elements are formed in the material blown off the star. These elements a ...
... • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The explosion is so energetic that it can outshine the combined light of a galaxy! • Heavy elements are formed in the material blown off the star. These elements a ...
No Slide Title
... it as seen in four different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum[UV,visible,IR,X-ray].The final picture shows detail.The bright clumps of light are moving outwards at v = 0.5c.The filaments have lower mass and higher velocity than models would predict.There is a pulsar = neutron star at the cent ...
... it as seen in four different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum[UV,visible,IR,X-ray].The final picture shows detail.The bright clumps of light are moving outwards at v = 0.5c.The filaments have lower mass and higher velocity than models would predict.There is a pulsar = neutron star at the cent ...
the lives of stars
... brighter red, then orange. If it gets extremely hot, it might look yellow-white, or even blue-white. Like a coil on a stove, a star’s color is determined by the temperature of the star’s surface. Cool Stars Red ...
... brighter red, then orange. If it gets extremely hot, it might look yellow-white, or even blue-white. Like a coil on a stove, a star’s color is determined by the temperature of the star’s surface. Cool Stars Red ...
HR Diagram Explorer
... Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating – alternately growing bigger and smaller – ...
... Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating – alternately growing bigger and smaller – ...
H-Band spectroscopic classification of OB stars
... Ohio State Infrared Imager and Spectrometer (OSIRIS) on the Perkins 1.8–m telescope of the Ohio Wesleyan and Ohio State Universities at the Lowell Observatory. The Perkins telescope is located on Anderson Mesa near Flagstaff, Arizona. OSIRIS is more fully described by DePoy et al. (1993). The target ...
... Ohio State Infrared Imager and Spectrometer (OSIRIS) on the Perkins 1.8–m telescope of the Ohio Wesleyan and Ohio State Universities at the Lowell Observatory. The Perkins telescope is located on Anderson Mesa near Flagstaff, Arizona. OSIRIS is more fully described by DePoy et al. (1993). The target ...
Wednesday, November 7, 2007
... Brown dwarfs begin life with gravitational contraction, just as stars do. But they just get smaller and dimmer until the contraction is halted by degeneracy pressure. So they are brightest and easiest to discover when young. Have been discovered mainly in star forming regions. Also sometimes found ...
... Brown dwarfs begin life with gravitational contraction, just as stars do. But they just get smaller and dimmer until the contraction is halted by degeneracy pressure. So they are brightest and easiest to discover when young. Have been discovered mainly in star forming regions. Also sometimes found ...
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Light from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with absorption lines. Each line indicates an ion of a certain chemical element, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that ion. The relative abundance of the different ions varies with the temperature of the photosphere. The spectral class of a star is a short code summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature and density.Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest (O type) to the coolest (M type). Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. A8, A9, F0, F1 form a sequence from hotter to cooler). The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such class D for white dwarfs and class C for carbon stars.In the MK system a luminosity class is added to the spectral class using Roman numerals. This is based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum which vary with the density of the atmosphere and so distinguish giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity class 0 or Ia+ stars for hypergiants, class I stars for supergiants, class II for bright giants, class III for regular giants, class IV for sub-giants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd for sub-dwarfs, and class D for white dwarfs. The full spectral class for the Sun is then G2V, indicating a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K.