Distance Ladder
... •If you know distance d and brightness B, you can figure this out from: L = 4d2B •To find the distance to another of the same class: •It should have the same luminosity L •Measure its brightness B •Deduce distance from: L = 4d2B ...
... •If you know distance d and brightness B, you can figure this out from: L = 4d2B •To find the distance to another of the same class: •It should have the same luminosity L •Measure its brightness B •Deduce distance from: L = 4d2B ...
88K PDF file
... 3. Chapter 12, Question 5: Albiero, a star in the constellation Cygnus, is a binary system whose components are easily separated in a small amateur telescope. Viewers describe the brighter star as “golden” and the fainter one as “sapphire blue” (a) What does this tell you about the relative tempera ...
... 3. Chapter 12, Question 5: Albiero, a star in the constellation Cygnus, is a binary system whose components are easily separated in a small amateur telescope. Viewers describe the brighter star as “golden” and the fainter one as “sapphire blue” (a) What does this tell you about the relative tempera ...
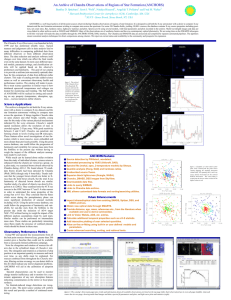
An Archive of Chandra Observations of Regions of Star Formation...
... nuances and judgement calls in data analysis lead to many difficulties in comparing published data from different observers or from different observation dates. The data reduction and analysis software itself changes over time which can affect the final results even on the same dataset. In most case ...
... nuances and judgement calls in data analysis lead to many difficulties in comparing published data from different observers or from different observation dates. The data reduction and analysis software itself changes over time which can affect the final results even on the same dataset. In most case ...
Stars
... The key to locating the North Star in the night sky is to first find the Big Dipper, a constellation of stars known as Ursa Major.. The Big Dipper is perhaps the best known group of stars in the northern sky and is easy to distinguish from all others. Also known as the Great Bear, the Big Dipper is ...
... The key to locating the North Star in the night sky is to first find the Big Dipper, a constellation of stars known as Ursa Major.. The Big Dipper is perhaps the best known group of stars in the northern sky and is easy to distinguish from all others. Also known as the Great Bear, the Big Dipper is ...
distant stars nearby star parallax angle The principle of geometrical
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Section 1
... • Most stars have several types of actual motion. • Stars move across the sky (seen only for close stars). • Some stars may revolve around another star. • Stars either move away from or toward our solar system. ...
... • Most stars have several types of actual motion. • Stars move across the sky (seen only for close stars). • Some stars may revolve around another star. • Stars either move away from or toward our solar system. ...
18 are exactly the same ones as for galactic star clusters of early
... IC 2944 (originally a nebula discovered near A Cen) has come to be adopted as the designation of a cluster near the centre of a large HII region which embraces both IC 2944 and IC 2948. As a cluster it differs in two important respects from NGC 6067; it is immersed in a combined field of bright nebu ...
... IC 2944 (originally a nebula discovered near A Cen) has come to be adopted as the designation of a cluster near the centre of a large HII region which embraces both IC 2944 and IC 2948. As a cluster it differs in two important respects from NGC 6067; it is immersed in a combined field of bright nebu ...
New York City Disciple Code - EarthSpaceScience-Keller
... Either luminosity or never empty. And the spectral class are spectral class is included for most star missing completely Waiter has the ability to know when we want tostages check Most stages include athem Most are missing a description of the description of their core in and when core we want to be ...
... Either luminosity or never empty. And the spectral class are spectral class is included for most star missing completely Waiter has the ability to know when we want tostages check Most stages include athem Most are missing a description of the description of their core in and when core we want to be ...
Stellar Evolution Guiding Questions Stars Evolve
... • Stars shine by thermonuclear reactions • They have a finite life span, because the hydrogen fuel will be exhausted • A year to a star is like a second to a human • To understand the evolution of stars, the approach is to piece together the information gathered for many stars that are at different ...
... • Stars shine by thermonuclear reactions • They have a finite life span, because the hydrogen fuel will be exhausted • A year to a star is like a second to a human • To understand the evolution of stars, the approach is to piece together the information gathered for many stars that are at different ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
... For astronomers, a graph that displays a star’s luminosity on the y-axis and its surface temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell, or H-R diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when all of the known stars were put ...
main sequence
... The amount of time a star spends in this phase depends on its mass. Large, massive stars will have a short main sequence stage while less massive stars will remain in main sequence much longer. Very massive stars will exhaust their fuel in only a few hundred million years. Smaller stars, like the Su ...
... The amount of time a star spends in this phase depends on its mass. Large, massive stars will have a short main sequence stage while less massive stars will remain in main sequence much longer. Very massive stars will exhaust their fuel in only a few hundred million years. Smaller stars, like the Su ...
CP2: KUPKA et al.: Observational signatures of atmospheric velocity
... km/s. The microturbulence is not significantly different from 0. Abundances are found for Ti, Cr, Fe and Ba; Cr is significantly more abundant than the solar value, while Fe is underabundant. ...
... km/s. The microturbulence is not significantly different from 0. Abundances are found for Ti, Cr, Fe and Ba; Cr is significantly more abundant than the solar value, while Fe is underabundant. ...
9 Measuring the properties of stars - Journigan-wiki
... It offers a simple, pictorial summary of stellar properties. Most stars lie on the main sequence with the hotter stars being more luminous. Blue stars are hottest while red stars are the coolest A star’s mass determines its location along the main sequence with more massive stars located at the top. ...
... It offers a simple, pictorial summary of stellar properties. Most stars lie on the main sequence with the hotter stars being more luminous. Blue stars are hottest while red stars are the coolest A star’s mass determines its location along the main sequence with more massive stars located at the top. ...
PHYSICS – Astrophysics Section I
... made from Earth or from space near the Earth Discuss Galileo’s use of the telescope to identify features of the Moon In 1609, Galileo constructed his own powerful telescope after hearing about its ability to make objects look closer. He used it to observe many phenomenon of the Solar System, includi ...
... made from Earth or from space near the Earth Discuss Galileo’s use of the telescope to identify features of the Moon In 1609, Galileo constructed his own powerful telescope after hearing about its ability to make objects look closer. He used it to observe many phenomenon of the Solar System, includi ...
Lecture18
... • Stars come in many luminosities • If astronomers could tell what the luminosity of a star ...
... • Stars come in many luminosities • If astronomers could tell what the luminosity of a star ...
Stellar Evolution
... As the helium in the core fuses to carbon, the core becomes hotter and hotter, and the helium burns faster and faster. When the helium is exhausted, the star is now similar to its condition just as it left the main sequence, except now there are two shells: a hydrogen-burning shell and a heliumb ...
... As the helium in the core fuses to carbon, the core becomes hotter and hotter, and the helium burns faster and faster. When the helium is exhausted, the star is now similar to its condition just as it left the main sequence, except now there are two shells: a hydrogen-burning shell and a heliumb ...
The Milky Way - TCNJ | The College of New Jersey
... So Can Stochastic Star Formation • Random birth of Massive Stars • Their SN explosions compress nearby clouds & make new stars • Differential rotation of galaxy yields spiral appearance by streching the stars out • This best explains "rattier", broken-up spirals (like the Milky Way, though some Den ...
... So Can Stochastic Star Formation • Random birth of Massive Stars • Their SN explosions compress nearby clouds & make new stars • Differential rotation of galaxy yields spiral appearance by streching the stars out • This best explains "rattier", broken-up spirals (like the Milky Way, though some Den ...
Analysis of Two Pulsating X-ray Sources
... itself is the stellar core of a Sun-sized star at the end of its evolutionary history – a rotating carbon core. The light curve above is produced by the dynamics of the system and not the white dwarf itself, which emits most of its radiation in X-rays. More massive stars, which catastrophically coll ...
... itself is the stellar core of a Sun-sized star at the end of its evolutionary history – a rotating carbon core. The light curve above is produced by the dynamics of the system and not the white dwarf itself, which emits most of its radiation in X-rays. More massive stars, which catastrophically coll ...
1.2.43The stellar populations of the Milky Way
... Pop. II stars occupy the spheroid – the stellar halo and bulge – and turn out to be the oldest stars known, with ages in the range (12 to 15) × 1091yr. Conspicuous examples are globular-cluster stars. Little or no interstellar gas is still associated with Pop. II stars, which is consistent with star ...
... Pop. II stars occupy the spheroid – the stellar halo and bulge – and turn out to be the oldest stars known, with ages in the range (12 to 15) × 1091yr. Conspicuous examples are globular-cluster stars. Little or no interstellar gas is still associated with Pop. II stars, which is consistent with star ...
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... astronomers were able to record and analyze the spectra of stars. Spectroscopy revealed that stars show a wide range of different types of spectra, but at the time it was not known why. Astronomers at the Harvard College Observatory obtained spectra for over 20,000 stars in hopes of understanding ho ...
... astronomers were able to record and analyze the spectra of stars. Spectroscopy revealed that stars show a wide range of different types of spectra, but at the time it was not known why. Astronomers at the Harvard College Observatory obtained spectra for over 20,000 stars in hopes of understanding ho ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... nebulae, such as Andromeda galaxy and the Crab nebula, were recorded by Messier. Today most nebulae and galaxies are referred to by their Messier number. Thus, for example, M 31 refers to the Andromeda galaxy and M1 to the Crab nebula. These celestial objects came to be called nebulae (Latin for clo ...
... nebulae, such as Andromeda galaxy and the Crab nebula, were recorded by Messier. Today most nebulae and galaxies are referred to by their Messier number. Thus, for example, M 31 refers to the Andromeda galaxy and M1 to the Crab nebula. These celestial objects came to be called nebulae (Latin for clo ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... change in temperature by two spectral classes during one cycle of change from maximum to minimum. To better understand the degree of variation for individual variable stars, it is necessary to plot them at both extremes of their cycles on the H-R diagram – both at maximum absolute magnitude (MVmax) ...
... change in temperature by two spectral classes during one cycle of change from maximum to minimum. To better understand the degree of variation for individual variable stars, it is necessary to plot them at both extremes of their cycles on the H-R diagram – both at maximum absolute magnitude (MVmax) ...
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Light from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with absorption lines. Each line indicates an ion of a certain chemical element, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that ion. The relative abundance of the different ions varies with the temperature of the photosphere. The spectral class of a star is a short code summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature and density.Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest (O type) to the coolest (M type). Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. A8, A9, F0, F1 form a sequence from hotter to cooler). The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such class D for white dwarfs and class C for carbon stars.In the MK system a luminosity class is added to the spectral class using Roman numerals. This is based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum which vary with the density of the atmosphere and so distinguish giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity class 0 or Ia+ stars for hypergiants, class I stars for supergiants, class II for bright giants, class III for regular giants, class IV for sub-giants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd for sub-dwarfs, and class D for white dwarfs. The full spectral class for the Sun is then G2V, indicating a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K.