printer-friendly version of benchmark
... the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of time on the main sequence. Based on precise measurements and computer modeling, our Sun is expected to have a main sequence lifetime of 10 billion years. A star with a mass of 15 MSun ...
... the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of time on the main sequence. Based on precise measurements and computer modeling, our Sun is expected to have a main sequence lifetime of 10 billion years. A star with a mass of 15 MSun ...
Spectral analysis for the RV Tau star R Sct: In this section, we will
... redness (cooler) in spectra. For example, an early G star might be G1 or G3 while a late G star might be G7 or G9. Similarly early spectra type stars are OBA while late spectral type stars are GKM. RV Tau and SR variables are giant and supergiant stars therefore they have luminosity classes of III, ...
... redness (cooler) in spectra. For example, an early G star might be G1 or G3 while a late G star might be G7 or G9. Similarly early spectra type stars are OBA while late spectral type stars are GKM. RV Tau and SR variables are giant and supergiant stars therefore they have luminosity classes of III, ...
Star Birth - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... Why Do Stars Evolve? Stellar Nuclear Fusion • The core temperature rises to about 10 million K after the star’s contraction from a molecular core fragment. • Stars of low mass like the Sun (<1.5 M) use the protonproton chain to generate energy. • Stars of mass greater than 1.5 M have higher core t ...
... Why Do Stars Evolve? Stellar Nuclear Fusion • The core temperature rises to about 10 million K after the star’s contraction from a molecular core fragment. • Stars of low mass like the Sun (<1.5 M) use the protonproton chain to generate energy. • Stars of mass greater than 1.5 M have higher core t ...
Document
... < .08 Msun (failed stars). Brown Dwarfs do not get hot enough to fuse H, but they do fuse Deuterium for a very short time. Deuterium is an isotope of H, with a neutron. About 1,000 Brown Dwarfs have been found. They radiate in the infrared ...
... < .08 Msun (failed stars). Brown Dwarfs do not get hot enough to fuse H, but they do fuse Deuterium for a very short time. Deuterium is an isotope of H, with a neutron. About 1,000 Brown Dwarfs have been found. They radiate in the infrared ...
Continuous Spectrum—Kirchoff`s First Law
... • It depends on the state of ionization of the element. • It depends on whether atoms of that element are in the proper energy state to absorb light of that wavelength. • It depends on how easy it is for the transition to take place. Ca+ lines and H Balmer lines are about equally strong in an F2 sta ...
... • It depends on the state of ionization of the element. • It depends on whether atoms of that element are in the proper energy state to absorb light of that wavelength. • It depends on how easy it is for the transition to take place. Ca+ lines and H Balmer lines are about equally strong in an F2 sta ...
center of mass
... 7. The absolute magnitude of any star is equal to its apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Use this definition, how light intensity changes with distance, and how the stellar magnitude system is set up to determine the following. If a star's apparent visual magnitude is less than its abso ...
... 7. The absolute magnitude of any star is equal to its apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Use this definition, how light intensity changes with distance, and how the stellar magnitude system is set up to determine the following. If a star's apparent visual magnitude is less than its abso ...
Chapter 09
... 7. The absolute magnitude of any star is equal to its apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Use this definition, how light intensity changes with distance, and how the stellar magnitude system is set up to determine the following. If a star's apparent visual magnitude is less than its abso ...
... 7. The absolute magnitude of any star is equal to its apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Use this definition, how light intensity changes with distance, and how the stellar magnitude system is set up to determine the following. If a star's apparent visual magnitude is less than its abso ...
Spagna
... Kinematics of Pre-MS population in the Chamaeleon Star Forming Region The Chamaeleon region is one of the most active SFR near the Sun, including 3 large dark clouds (Cha I, Cha II and Cha III) and several small isolated clouds with 100
... Kinematics of Pre-MS population in the Chamaeleon Star Forming Region The Chamaeleon region is one of the most active SFR near the Sun, including 3 large dark clouds (Cha I, Cha II and Cha III) and several small isolated clouds with 100
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-ISSN: 2278-4861.
... using atomic, ionic and stellar data. By using this method together with the new intensity formula it has been possible to determine the mean electron temperature in different laboratory plasmas and in the optical layers of a star without knowing so much about the chemical composition of the star. T ...
... using atomic, ionic and stellar data. By using this method together with the new intensity formula it has been possible to determine the mean electron temperature in different laboratory plasmas and in the optical layers of a star without knowing so much about the chemical composition of the star. T ...
Exercises - Leiden Observatory
... are taking place. From the timescales of such changes - usually oscillations with a characteristic period - we may roughly estimate the average density of the Star. The sun has been observed to oscillate with a period of minutes, white dwarfs with periods of a few tens of seconds. Estimate the avera ...
... are taking place. From the timescales of such changes - usually oscillations with a characteristic period - we may roughly estimate the average density of the Star. The sun has been observed to oscillate with a period of minutes, white dwarfs with periods of a few tens of seconds. Estimate the avera ...
McDonald Observatory Planet Search - tls
... • Long period variations are most likely due to giant planets around stars with Mstar > 1 Mסּ • Short period variations are due to radial pulsations in the fundamental and overtone modes • Pulsations can be used to get funamental parameters of ...
... • Long period variations are most likely due to giant planets around stars with Mstar > 1 Mסּ • Short period variations are due to radial pulsations in the fundamental and overtone modes • Pulsations can be used to get funamental parameters of ...
The coronal temperatures of low-mass main
... of the coronal properties of saturated stars. For example, if RX is the relevant parameter, then this would indicate that temperature scales somehow with how far a star is below the saturation threshold in rotation, given that saturation happens at a single mass-independent value of RX . It would fu ...
... of the coronal properties of saturated stars. For example, if RX is the relevant parameter, then this would indicate that temperature scales somehow with how far a star is below the saturation threshold in rotation, given that saturation happens at a single mass-independent value of RX . It would fu ...
Lecture12
... Cepheid variable stars are very luminous and can be observed over very large distances. Why are such stars important to astronomers? A. They confirm the theory of nuclear fusion as the energy source for stars. B. They can be used as distance indicators because their luminosity can be determined fro ...
... Cepheid variable stars are very luminous and can be observed over very large distances. Why are such stars important to astronomers? A. They confirm the theory of nuclear fusion as the energy source for stars. B. They can be used as distance indicators because their luminosity can be determined fro ...
Chapter 12 Star Stuff How do stars form?
... The relationship between apparent brightness and luminosity depends on distance: ...
... The relationship between apparent brightness and luminosity depends on distance: ...
Notes 6 - University of Northern Iowa
... Another fun feature of an AGB star is the start of very strong winds. These stars are very high up on the HR diagram so they are pretty luminous to begin with. This can put them over the Eddington Luminosity briefly. The stellar winds are helped along when there are particles that easily absorb ener ...
... Another fun feature of an AGB star is the start of very strong winds. These stars are very high up on the HR diagram so they are pretty luminous to begin with. This can put them over the Eddington Luminosity briefly. The stellar winds are helped along when there are particles that easily absorb ener ...
Grzegorz Nowak, Andrzej Niedzielski, Aleksander Wolszczan, Pawe
... Red giants represent later phase of evolution of the main sequence stars. The planet induced Doppler shifts are easy to detect in radial velocity measurements of these stars, because they have lower effective temperatures and lower rotational velocities compared to their main sequence progenitors. T ...
... Red giants represent later phase of evolution of the main sequence stars. The planet induced Doppler shifts are easy to detect in radial velocity measurements of these stars, because they have lower effective temperatures and lower rotational velocities compared to their main sequence progenitors. T ...
Ay 112 Midterm review
... luminosity. They can be used out to about 20 Mpc (the Virgo cluster). There are Several varieties of Cepheids and the P-‐L relation is different for Population I and II. This caused historical e ...
... luminosity. They can be used out to about 20 Mpc (the Virgo cluster). There are Several varieties of Cepheids and the P-‐L relation is different for Population I and II. This caused historical e ...
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars
... What are giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs? Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: Those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and ...
... What are giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs? Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: Those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and ...
STApr18
... Both (B-V) and spectral type are poor luminosity indicators for M dwarfs: small error in (B-V), large error in MV. Systematics kill.... Surveys tended to overestimate sp. type & overestimate redness underestimate luminosity, distance overestimate density By early 80s, M dwarfs were eliminated as p ...
... Both (B-V) and spectral type are poor luminosity indicators for M dwarfs: small error in (B-V), large error in MV. Systematics kill.... Surveys tended to overestimate sp. type & overestimate redness underestimate luminosity, distance overestimate density By early 80s, M dwarfs were eliminated as p ...
Quantum effects in astrophysics
... Although the spectral nature of light can be seen in a rainbow, it was not until 1666 that Newton showed that the white light from the sun could be dispersed into a continuous series of colors. Newton introduced the word "spectrum" to describe this phenomenon. (The word spectrum is from the Latin fo ...
... Although the spectral nature of light can be seen in a rainbow, it was not until 1666 that Newton showed that the white light from the sun could be dispersed into a continuous series of colors. Newton introduced the word "spectrum" to describe this phenomenon. (The word spectrum is from the Latin fo ...
chapter 7 review questions
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? F 5. An absorption spectrum is also called a bright line spectrum. GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What kind of spectra do you see when you look at celestial objects? T. 6. Hydrogen alpha is the longest wavelength Balmer line. F ...
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? F 5. An absorption spectrum is also called a bright line spectrum. GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What kind of spectra do you see when you look at celestial objects? T. 6. Hydrogen alpha is the longest wavelength Balmer line. F ...
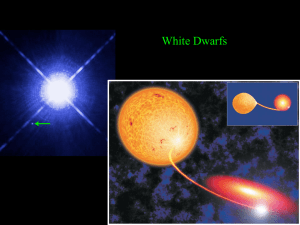
white dwarf supernova
... • The smallest stars form helium white dwarfs. • Sun-sized stars form carbon white dwarfs. • Larger (but still “low-mass”) stars form white dwarfs with a mix of heavier elements • A teaspoon of this material – held up against gravity by electron degeneracy pressure – would weigh several tons on Eart ...
... • The smallest stars form helium white dwarfs. • Sun-sized stars form carbon white dwarfs. • Larger (but still “low-mass”) stars form white dwarfs with a mix of heavier elements • A teaspoon of this material – held up against gravity by electron degeneracy pressure – would weigh several tons on Eart ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... Science Olympiad Reach for the Stars Event (2017) Webinar Transcript Slide 1: This presentation is an overview of the content and resources for the National Science Olympiad (NSO) Division B 2017 Reach for the Stars Event (RFTS). The NSO 2017 national competition will be held at Wright State Univers ...
... Science Olympiad Reach for the Stars Event (2017) Webinar Transcript Slide 1: This presentation is an overview of the content and resources for the National Science Olympiad (NSO) Division B 2017 Reach for the Stars Event (RFTS). The NSO 2017 national competition will be held at Wright State Univers ...
A Chandra Observation of the Massive Star-Forming
... from an evaporating gaseous globule (EGG) for the first time A significant population of X-ray emitting low mass stars (~700) detected, increasing the cluster known members by a factor of 40 ...
... from an evaporating gaseous globule (EGG) for the first time A significant population of X-ray emitting low mass stars (~700) detected, increasing the cluster known members by a factor of 40 ...
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Light from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with absorption lines. Each line indicates an ion of a certain chemical element, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that ion. The relative abundance of the different ions varies with the temperature of the photosphere. The spectral class of a star is a short code summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature and density.Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest (O type) to the coolest (M type). Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. A8, A9, F0, F1 form a sequence from hotter to cooler). The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such class D for white dwarfs and class C for carbon stars.In the MK system a luminosity class is added to the spectral class using Roman numerals. This is based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum which vary with the density of the atmosphere and so distinguish giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity class 0 or Ia+ stars for hypergiants, class I stars for supergiants, class II for bright giants, class III for regular giants, class IV for sub-giants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd for sub-dwarfs, and class D for white dwarfs. The full spectral class for the Sun is then G2V, indicating a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K.