instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
Stars
... • Temperature is also related to luminosity and absolute magnitude. Hotter stars put out more light than stars with lower temperatures. • Distance can be determined by calculating a star’s luminosity based on its temperature. ...
... • Temperature is also related to luminosity and absolute magnitude. Hotter stars put out more light than stars with lower temperatures. • Distance can be determined by calculating a star’s luminosity based on its temperature. ...
Spectroscopic Variability of Supergiant Star HD14134, B3Ia
... Hα profile in the spectrum of the star HD14134 had the shape of an inverse P Cygni profile (Fig.1a). Another variability pattern, where Hα appears only in weak emission (13/02/2016). The Hα line was absent in the spectra of December 29-30, 2013 and of February 15, 2016, while two carbon lines CII (λ 6 ...
... Hα profile in the spectrum of the star HD14134 had the shape of an inverse P Cygni profile (Fig.1a). Another variability pattern, where Hα appears only in weak emission (13/02/2016). The Hα line was absent in the spectra of December 29-30, 2013 and of February 15, 2016, while two carbon lines CII (λ 6 ...
Spectroscopic Variability of Supergiant Star HD14134, B3Ia
... Hα profile in the spectrum of the star HD14134 had the shape of an inverse P Cygni profile (Fig.1a). Another variability pattern, where Hα appears only in weak emission (13/02/2016). The Hα line was absent in the spectra of December 29-30, 2013 and of February 15, 2016, while two carbon lines CII (λ 6 ...
... Hα profile in the spectrum of the star HD14134 had the shape of an inverse P Cygni profile (Fig.1a). Another variability pattern, where Hα appears only in weak emission (13/02/2016). The Hα line was absent in the spectra of December 29-30, 2013 and of February 15, 2016, while two carbon lines CII (λ 6 ...
Annual report 2004 - Département d`Astrophysique, Géophysique et
... In the framework of a long-term spectroscopic and photometric monitoring of slowly pulsating B stars we studied thoroughly the northern target star HD 147394. We performed an end-to-end analysis, consisting of a frequency analysis, a mode identification from line-profile variations and a comparison ...
... In the framework of a long-term spectroscopic and photometric monitoring of slowly pulsating B stars we studied thoroughly the northern target star HD 147394. We performed an end-to-end analysis, consisting of a frequency analysis, a mode identification from line-profile variations and a comparison ...
WHAT MAKES A STAR SO SPECIAL Abstract
... Star spectra are divided into groups called classes. The main spectral classes are named as follows: O, B, A, F, G, K and M. The hottest stars are from class O, while the coldest stars are from class M. Each class is divided into 10 subclasses that are named with numbers from 0 to 9, which are added ...
... Star spectra are divided into groups called classes. The main spectral classes are named as follows: O, B, A, F, G, K and M. The hottest stars are from class O, while the coldest stars are from class M. Each class is divided into 10 subclasses that are named with numbers from 0 to 9, which are added ...
Chapter 19 Stars Galaxies and the Universe
... When telescopes were developed, scientists discovered this system had flaws. They could see more stars with the telescope than with the naked eye. They could also see the differences in brightness more clearly. The old system for classifying brightness was too general to include the dimmest stars th ...
... When telescopes were developed, scientists discovered this system had flaws. They could see more stars with the telescope than with the naked eye. They could also see the differences in brightness more clearly. The old system for classifying brightness was too general to include the dimmest stars th ...
Observing Stellar Evolution
... Many stars have multiple names and appear in multiple catalogs. It is confusing. Software that maps the sky can use one or more of the designations to identify a star, but not all. Astronomy is an old science and over time many names and catalogs have been developed. Those of us who are amateur astr ...
... Many stars have multiple names and appear in multiple catalogs. It is confusing. Software that maps the sky can use one or more of the designations to identify a star, but not all. Astronomy is an old science and over time many names and catalogs have been developed. Those of us who are amateur astr ...
The Spectra ot Novae
... something of the pre-outburst stage, but this view is not unassailable. The only extant record of a pre-nova spectrum, that of Nova Aquilae 1918, is faint and difficult of interpretation (CANNON, 1920). The earliest spectroscopically recorded stage is about two magnitudes below maximum on the rise. ...
... something of the pre-outburst stage, but this view is not unassailable. The only extant record of a pre-nova spectrum, that of Nova Aquilae 1918, is faint and difficult of interpretation (CANNON, 1920). The earliest spectroscopically recorded stage is about two magnitudes below maximum on the rise. ...
Chemical Evolution
... accretion to have occurred > 8Gyr ago. Perhaps more stringent limits come from the different elemental abundances, since timescale for Type Ia SNe only a few Gyr, but need detailed chemical evolution models. Halo can be formed from any system that formed stars early on, for only brief period , an ...
... accretion to have occurred > 8Gyr ago. Perhaps more stringent limits come from the different elemental abundances, since timescale for Type Ia SNe only a few Gyr, but need detailed chemical evolution models. Halo can be formed from any system that formed stars early on, for only brief period , an ...
Starburst Galaxies Under the Microscope: High
... time. In principle, one could use these results then to calculate the speed at which the star formation propagates through the nuclear region. Remarkably however, there is no pattern in the derived ages. Instead, the results point to a situation in which a large area becomes globally unstable, after ...
... time. In principle, one could use these results then to calculate the speed at which the star formation propagates through the nuclear region. Remarkably however, there is no pattern in the derived ages. Instead, the results point to a situation in which a large area becomes globally unstable, after ...
Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk
... higher variance in the yields from different stars will contribute to higher cosmic variance in chemical abundances. If two metals are produced in the same proportions in supernovae, their abundance ratio in the ISM will remain constant. If they are produced at different sites or with different prop ...
... higher variance in the yields from different stars will contribute to higher cosmic variance in chemical abundances. If two metals are produced in the same proportions in supernovae, their abundance ratio in the ISM will remain constant. If they are produced at different sites or with different prop ...
THE DISCOVERY OF - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... to sustain lithium fusion in its core. This nuclear reaction occurs at a slightly lower temperature than hydrogen fusion does; as a result, stars quickly consume whatever lithium they originally had. Even the lowest-mass star burns all its lithium in about 100 million years, whereas all but the most ...
... to sustain lithium fusion in its core. This nuclear reaction occurs at a slightly lower temperature than hydrogen fusion does; as a result, stars quickly consume whatever lithium they originally had. Even the lowest-mass star burns all its lithium in about 100 million years, whereas all but the most ...
103-122
... spectra of 29 disc dwarfs of F type in selected intervals from which abundances of a selection of light through heavy elements are derived using MARCS models and solar gf-values. The basic parameters—Teff and log g—are computed from Strömgren photometric indices. This analysis appears to be the most ...
... spectra of 29 disc dwarfs of F type in selected intervals from which abundances of a selection of light through heavy elements are derived using MARCS models and solar gf-values. The basic parameters—Teff and log g—are computed from Strömgren photometric indices. This analysis appears to be the most ...
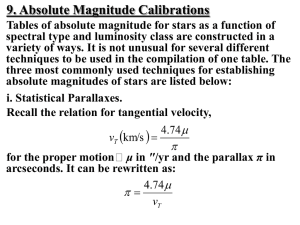
sections 16-18 instructor notes
... For disk stars that are not drifting either perpendicular to the Galactic plane or in the direction of the Galactic centre, it is reasonable to expect that: ≡ 0 and ≡ 0.
However, ≠ 0 since a typical group of stars selected
observationally will always tend to lag behind the solar
LSR. ...
... For disk stars that are not drifting either perpendicular to the Galactic plane or in the direction of the Galactic centre, it is reasonable to expect that:
Kinetic equilibrium of iron in the atmospheres of cool stars
... dictates the individual line fit approach, and it excludes the use of absolute f values. It is important to recognize that the typical abundance scatter obtained from solar spectral analysis of Fe lines is considerably higher than warranted by both observational error and differences in theoretical m ...
... dictates the individual line fit approach, and it excludes the use of absolute f values. It is important to recognize that the typical abundance scatter obtained from solar spectral analysis of Fe lines is considerably higher than warranted by both observational error and differences in theoretical m ...
sections 16-18 instructor notes
... For disk stars that are not drifting either perpendicular to the Galactic plane or in the direction of the Galactic centre, it is reasonable to expect that: ≡ 0 and ≡ 0.
However, ≠ 0 since a typical group of stars selected
observationally will always tend to lag behind the solar
LSR. ...
... For disk stars that are not drifting either perpendicular to the Galactic plane or in the direction of the Galactic centre, it is reasonable to expect that:
Stellar Evolution : The Life and Death of Our Luminous Neighbors
... (OBAFGKM) each of which is subdivided into 10 subclasses. Thus, the spectral sequence includes B8, B9, A0, A1, etc. A traditional mnemonic for the sequence is Oh, Be, A Fine Girl/Guy, Kiss Me! Although based on the absorption lines, spectral type tells you about the surface temperature of the star. ...
... (OBAFGKM) each of which is subdivided into 10 subclasses. Thus, the spectral sequence includes B8, B9, A0, A1, etc. A traditional mnemonic for the sequence is Oh, Be, A Fine Girl/Guy, Kiss Me! Although based on the absorption lines, spectral type tells you about the surface temperature of the star. ...
The Earth and Man In the Universe
... (" The Theory of the Universe," London. 1750). upon which Kant based his own theory. The great observer soon abandoned this first idea, already grown somewhat ...
... (" The Theory of the Universe," London. 1750). upon which Kant based his own theory. The great observer soon abandoned this first idea, already grown somewhat ...
... 3. THE RR LYRAE STARS IN M15 In Clement’s (2002) data base of variables stars, a total of 158 variable stars are known, from which approximately 104 are RR Lyrae type stars. In this work, 33 known RR Lyrae stars, identified in Figs. 1 and 2 and listed in Table 4, have been studied. For all the stars ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... It might be useful for beginners, but if you already know what types of stars you want to create, you can skip them. Stars are obviously emitting light, otherwise we wouldn’t be able to see them, but they do not only have different luminosities, but also different colors. The color of a star depends ...
... It might be useful for beginners, but if you already know what types of stars you want to create, you can skip them. Stars are obviously emitting light, otherwise we wouldn’t be able to see them, but they do not only have different luminosities, but also different colors. The color of a star depends ...
Constraining the formation of the Milky Way: Ages
... We will show that our new approach works encouragingly well, explaining not only current observations, but also leading to a more clear picture regarding the nature of the MW thick disc. The novelty of our approach is: a) we assume that each particle in our N-body simulation represents one star. Dyn ...
... We will show that our new approach works encouragingly well, explaining not only current observations, but also leading to a more clear picture regarding the nature of the MW thick disc. The novelty of our approach is: a) we assume that each particle in our N-body simulation represents one star. Dyn ...
The HERMES GALAH survey: overview
... thick and thin disk stars overlap. The thin disk stars have [Fe/H] in the range 0.7 to +0.5, while most of the thick disk stars have [Fe/H] between about 1 and 0.3, with tails extending to 2 and 0.1. The similarity of the abundance spread of the thick disk stars near the sun to the globular clusters ...
... thick and thin disk stars overlap. The thin disk stars have [Fe/H] in the range 0.7 to +0.5, while most of the thick disk stars have [Fe/H] between about 1 and 0.3, with tails extending to 2 and 0.1. The similarity of the abundance spread of the thick disk stars near the sun to the globular clusters ...
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Light from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with absorption lines. Each line indicates an ion of a certain chemical element, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that ion. The relative abundance of the different ions varies with the temperature of the photosphere. The spectral class of a star is a short code summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature and density.Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest (O type) to the coolest (M type). Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. A8, A9, F0, F1 form a sequence from hotter to cooler). The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such class D for white dwarfs and class C for carbon stars.In the MK system a luminosity class is added to the spectral class using Roman numerals. This is based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum which vary with the density of the atmosphere and so distinguish giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity class 0 or Ia+ stars for hypergiants, class I stars for supergiants, class II for bright giants, class III for regular giants, class IV for sub-giants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd for sub-dwarfs, and class D for white dwarfs. The full spectral class for the Sun is then G2V, indicating a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K.










![Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014331057_1-996ec6eddf93071c5e835624d4620c7e-300x300.png)











