Nervous system slides
... ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ...
... ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - Involved in regulating hunger, thirst, emotion, sex drive - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
... - Involved in regulating hunger, thirst, emotion, sex drive - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
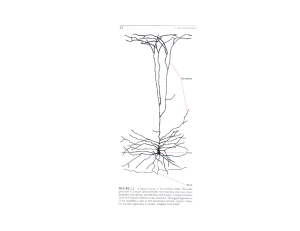
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... The cortex is organized horizontally into six laminae, and vertically into groups of cells linked synaptically across the horizontal laminae. ...
... The cortex is organized horizontally into six laminae, and vertically into groups of cells linked synaptically across the horizontal laminae. ...
Myers` Psychology for AP
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain 8. Describe the distinct functions of the brain’s two hemispheres, and discuss research findings on brain organization and handedness. LO #7 9. Describe research that leads cognitive neuroscientists to infer how the brains dual-processing affects our percep ...
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain 8. Describe the distinct functions of the brain’s two hemispheres, and discuss research findings on brain organization and handedness. LO #7 9. Describe research that leads cognitive neuroscientists to infer how the brains dual-processing affects our percep ...
Slide ()
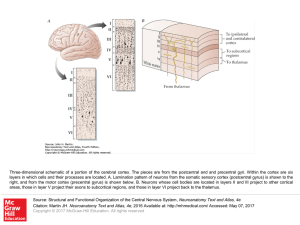
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
vocab - sociallyconsciousbird.com
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
Topology - UCSB Physics
... The topology of the central nervous system has been, and remains today a topic of considerable study. It is known that for humans, the central nervous system starts in the embryo as a plate, eventually deforming into a tube, one end of which thickens to become the brain (the remainder being the spin ...
... The topology of the central nervous system has been, and remains today a topic of considerable study. It is known that for humans, the central nervous system starts in the embryo as a plate, eventually deforming into a tube, one end of which thickens to become the brain (the remainder being the spin ...
Learning Activity 1
... 3 The cerebral cortex consists mainly of neurons. 4 Cortical areas may be classifi ed as: • sensory cortex areas, which receive and process information from our different senses • motor cortex area, which receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements • association cortex ...
... 3 The cerebral cortex consists mainly of neurons. 4 Cortical areas may be classifi ed as: • sensory cortex areas, which receive and process information from our different senses • motor cortex area, which receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements • association cortex ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
chapter 3 study guide
... The forebrain (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system (see below)) The limbic system (hippocampus, amygdala) The cerebrum, cerebral cortex, and corpus callosum The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The f ...
... The forebrain (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system (see below)) The limbic system (hippocampus, amygdala) The cerebrum, cerebral cortex, and corpus callosum The occipital lobe (primary visual cortex) The parietal lobe (primary somatosensory cortex) The temporal lobe (primary auditory cortex) The f ...
Chapter 7 (Part 2) Study Guide File
... 7. What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? What part of the brain creates CSF? Where does CSF flow within the brain? ...
... 7. What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? What part of the brain creates CSF? Where does CSF flow within the brain? ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... 3. Cerebellum: critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-relea ...
... 3. Cerebellum: critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-relea ...
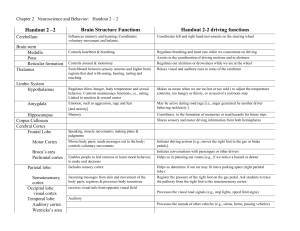
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Regulates our alertness or drowsiness while we are at the wheel ...
... Regulates our alertness or drowsiness while we are at the wheel ...
Like crumpled paper balls: the evolution of the mammalian cerebral
... Prof. Suzana Herculano-Houzel - Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil Larger brains tend to have larger and more folded cortices, and gyrification has long been considered a mechanism that allows for larger neurons in the cerebral cortex – but why is the cetacean cortex much more folded tha ...
... Prof. Suzana Herculano-Houzel - Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil Larger brains tend to have larger and more folded cortices, and gyrification has long been considered a mechanism that allows for larger neurons in the cerebral cortex – but why is the cetacean cortex much more folded tha ...
A synaptic memory trace for cortical receptive field plasticity
... Neural networks of the cerebral cortex continually change throughout life, allowing us to learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordinati ...
... Neural networks of the cerebral cortex continually change throughout life, allowing us to learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordinati ...
Slide ()
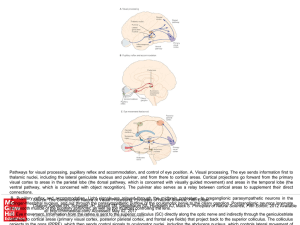
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Crossword Puzzle
... these lobes contain the sensory cortex 5. extension of a neuron that sends impulses to other nerve cells or to muscles or glands 6. the thin outer covering of the cerebral hemispheres 7. part of the limbic system involved in regulation of the emotions of fear and rage 8. large band of neural fibers ...
... these lobes contain the sensory cortex 5. extension of a neuron that sends impulses to other nerve cells or to muscles or glands 6. the thin outer covering of the cerebral hemispheres 7. part of the limbic system involved in regulation of the emotions of fear and rage 8. large band of neural fibers ...
Document
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... What are the four lobes in the cortex? What is the frontal lobe responsible for? The parietal lobe? The temporal lobe? The occipital lobe? What is an experience-dependent brain? What is plasticity? What is an experience-expectant brain? What are two types of brain injury? Can your brain ...
... What are the four lobes in the cortex? What is the frontal lobe responsible for? The parietal lobe? The temporal lobe? The occipital lobe? What is an experience-dependent brain? What is plasticity? What is an experience-expectant brain? What are two types of brain injury? Can your brain ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
... auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not in ...
... auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas of the cerebral cortex that are not in ...
specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
Karen Iler Kirk - Purdue University
... •Single-neuron extracellular recording -awake animals •Sound and electrical stimulation •Neuroanatomy •Intracellular recording in brain slices -synaptics, dynamic clamp •Modeling of neurons and circuits ...
... •Single-neuron extracellular recording -awake animals •Sound and electrical stimulation •Neuroanatomy •Intracellular recording in brain slices -synaptics, dynamic clamp •Modeling of neurons and circuits ...
Myers Module Six
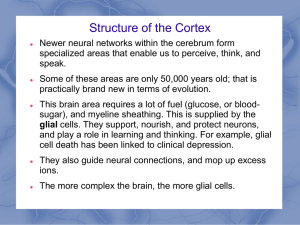
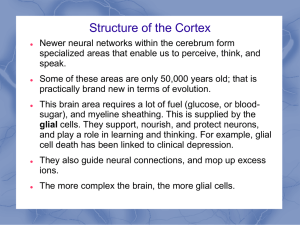
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
studyingbrainpost
... Studying Cognitive Psychology: How the brain influences the mind and behavior ...
... Studying Cognitive Psychology: How the brain influences the mind and behavior ...
Cortical cooling
Neuroscientists generate various studies to help explain many of the complex connections and functions of the brain. Most studies utilize animal models that have varying degrees of comparison to the human brain; for example, small rodents are less comparable than non-human primates. One of the most definitive ways of determining which sections of the brain contribute to certain behavior or function is to deactivate a section of the brain and observe what behavior is altered. Investigators have a wide range of options for deactivating neural tissue, and one of the more recently developed methods being used is deactivation through cooling. Cortical cooling refers to the cooling methods restricted to the cerebral cortex, where most higher brain processes occur. Below is a list of current cooling methods, their advantages and limitations, and some studies that have used cooling to elucidate neural functions.