here.
... Bars represent number of new antimicrobial agents approved by the FDA during the period listed. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Bad Bugs, No Drugs. July 2004; Spellberg B et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1279-1286; New antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:1912 ...
... Bars represent number of new antimicrobial agents approved by the FDA during the period listed. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Bad Bugs, No Drugs. July 2004; Spellberg B et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1279-1286; New antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:1912 ...
Chapter 9- Physical Methods for Control
... 4) Ultrahigh-Temperature Sterilizationflash heating to rid of ALL microbes, extremely hot for 1 second (dairy creamer) ...
... 4) Ultrahigh-Temperature Sterilizationflash heating to rid of ALL microbes, extremely hot for 1 second (dairy creamer) ...
PowerPoint
... • Can react with organic matter to form carcinogenic compounds – THMs (trihalomethanes) ...
... • Can react with organic matter to form carcinogenic compounds – THMs (trihalomethanes) ...
NSF Grantees Meeting 12/4/07
... Infection occurs in approximately 0.5 – 5% of all hip and knee replacements. It is a catastrophic problem, because bacteria that colonize an implant surface develop into biofilms where they are as much as 10,000 times more resistant to antibiotics than planktonic bacteria. The most effective therapy ...
... Infection occurs in approximately 0.5 – 5% of all hip and knee replacements. It is a catastrophic problem, because bacteria that colonize an implant surface develop into biofilms where they are as much as 10,000 times more resistant to antibiotics than planktonic bacteria. The most effective therapy ...
Bacteria Virtual Lab Procedure Analysis
... sauerkraut. A few bacteria cause disease and are known as pathogens. Some examples of diseases caused by bacteria include tuberculosis, pneumonia, strep throat, and ear infections. Because bacteria multiply so rapidly, it is often necessary to control their growth in the human body, in food, and in ...
... sauerkraut. A few bacteria cause disease and are known as pathogens. Some examples of diseases caused by bacteria include tuberculosis, pneumonia, strep throat, and ear infections. Because bacteria multiply so rapidly, it is often necessary to control their growth in the human body, in food, and in ...
Posters – Infectious diseases and Vaccines NAME OF THE
... many antibiotics. Issue: The society, both in the community and the hospitals, needs novel antibiotics, and finding new drugs active on the ESKAPE bacteria has stalled for years because it is notoriously difficult ...
... many antibiotics. Issue: The society, both in the community and the hospitals, needs novel antibiotics, and finding new drugs active on the ESKAPE bacteria has stalled for years because it is notoriously difficult ...
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT (PENGAWET)
... Natamycin is active against nearly all molds and yeast, but no effect on bacteria or viruses. Several factors affect the stability & resulting antimycotic activity of natamycin: -pH, 100% natamycin activity is retained at pH 5 - 7 -temperature, high temperature will decrease activity -light, -ox ...
... Natamycin is active against nearly all molds and yeast, but no effect on bacteria or viruses. Several factors affect the stability & resulting antimycotic activity of natamycin: -pH, 100% natamycin activity is retained at pH 5 - 7 -temperature, high temperature will decrease activity -light, -ox ...
XDR GNR
... carbapenems using current Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) breakpoints. As a result of being difficult to detect, such organisms pose significant risks, particularly due to their role in unnoticed spread within institutions a ...
... carbapenems using current Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC) breakpoints. As a result of being difficult to detect, such organisms pose significant risks, particularly due to their role in unnoticed spread within institutions a ...
R_Titball___Antibiotic_workshop
... Penicillin-non susceptible S. pneumoniae (EU pop.-weighted average) Erythromycin-resistant S. pneumoniae (EU pop.-weighted average) Fluoroquinolone-resistant E. coli (EU pop.-weighted average) ...
... Penicillin-non susceptible S. pneumoniae (EU pop.-weighted average) Erythromycin-resistant S. pneumoniae (EU pop.-weighted average) Fluoroquinolone-resistant E. coli (EU pop.-weighted average) ...
Chemical Agents
... • Destroys vegetative bacteria and fungi, • Chlorine gas is sporicidal • Can react with organic matter to form carcinogenic compounds ...
... • Destroys vegetative bacteria and fungi, • Chlorine gas is sporicidal • Can react with organic matter to form carcinogenic compounds ...
Antibiotic Resistance
... new agent introduced than the bacteria develops a means to resist it. At present we are faced with certain bacterial pathogens that are resistant to all currently available antimicrobial agents. While new antimicrobial agents are regularly developed, there have been a very limited number of new agen ...
... new agent introduced than the bacteria develops a means to resist it. At present we are faced with certain bacterial pathogens that are resistant to all currently available antimicrobial agents. While new antimicrobial agents are regularly developed, there have been a very limited number of new agen ...
Chapter 13
... Alteration of Targets • This mechanism usually affects bacterial ribosomes • The mutation alters the DNA such that the protein produced or target is modified • Antimicrobial agents can no longer bind to the target ...
... Alteration of Targets • This mechanism usually affects bacterial ribosomes • The mutation alters the DNA such that the protein produced or target is modified • Antimicrobial agents can no longer bind to the target ...
Coeus Technology, Inc.
... causes oxidative stress and the generation of hydrogen peroxide. This causes a chemical reaction resulting in oxidative damage to cells. Excess copper causes a decline in the membrane integrity of microbes, leading to leakage of specific essential cell nutrients, such as potassium and glutamate. Thi ...
... causes oxidative stress and the generation of hydrogen peroxide. This causes a chemical reaction resulting in oxidative damage to cells. Excess copper causes a decline in the membrane integrity of microbes, leading to leakage of specific essential cell nutrients, such as potassium and glutamate. Thi ...
Chapter 51 Clinical Use of Antimicrobial Agents
... Selection of antimicrobial agents depends on host factors and pharmacological factors. ...
... Selection of antimicrobial agents depends on host factors and pharmacological factors. ...
Escherichia coli ST131: a model for high-risk transmission
... This project will connect a large number of transnational academic resources to investigate the transmission success of Escherichia coli ST131 clone. E. coli is the most common cause of urinary tract and bloodstream infections worldwide. A recent WHO report states that resistance to one of the most ...
... This project will connect a large number of transnational academic resources to investigate the transmission success of Escherichia coli ST131 clone. E. coli is the most common cause of urinary tract and bloodstream infections worldwide. A recent WHO report states that resistance to one of the most ...
Microbes on Surfaces
... – Influenza may persist for several days to weeks on dust, cotton sheets, and glass slides (Edward, 1941); 24-48 hours on other hard surfaces (Bean et al, 1982) – RSV was reduced by 2 log10 after 24 hours (Kingston, 1968) – Parainfluenza virus may persist up to 12 days on plastic surfaces (Parkinson ...
... – Influenza may persist for several days to weeks on dust, cotton sheets, and glass slides (Edward, 1941); 24-48 hours on other hard surfaces (Bean et al, 1982) – RSV was reduced by 2 log10 after 24 hours (Kingston, 1968) – Parainfluenza virus may persist up to 12 days on plastic surfaces (Parkinson ...
Chemotherapeutic Agents
... kill most bacteria, but not Mycobacterium tuberculosis or endospores safe and easy to use, but inactivated by hard water and soap E.g Benzalkonium chloride and Cetylpyridinium ...
... kill most bacteria, but not Mycobacterium tuberculosis or endospores safe and easy to use, but inactivated by hard water and soap E.g Benzalkonium chloride and Cetylpyridinium ...
Module 6 Exam Review 1. Compared to eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic
... 37. Streptokinase and staphylokinase break down and prevent _________. clots 38. Gram-positive organisms primarily secrete ________________. exotoxins 39. Upon their deaths, Gram-negative bacteria release __________________. endotoxins 40. Certain bacterial species can survive for very long periods ...
... 37. Streptokinase and staphylokinase break down and prevent _________. clots 38. Gram-positive organisms primarily secrete ________________. exotoxins 39. Upon their deaths, Gram-negative bacteria release __________________. endotoxins 40. Certain bacterial species can survive for very long periods ...
Press Release- First Patient Enrolled in the New Drugs
... pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus,” said Hasan Jafri, EFPIA Lead for the SAATELLITE study, Senior Director, Clinical Research and Development, Infectious Disease & Vaccines, MedImmune. “Novel biologics under investigation such as MEDI4893 may offer a unique opportunity to help prevent these ...
... pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus,” said Hasan Jafri, EFPIA Lead for the SAATELLITE study, Senior Director, Clinical Research and Development, Infectious Disease & Vaccines, MedImmune. “Novel biologics under investigation such as MEDI4893 may offer a unique opportunity to help prevent these ...
(BACTERIOCIN-LIKE INHIBITORY SUBSTANCES) PRODUCED BY
... Bacteriocins are antimicrobial peptides ribosomally synthesized by prokaryotes with activity against micro-organisms related to the producer species. Many bacteriocins have been suggested as alternative agents either in food biopreservation or in prevention/treatment of bacterial infections due to t ...
... Bacteriocins are antimicrobial peptides ribosomally synthesized by prokaryotes with activity against micro-organisms related to the producer species. Many bacteriocins have been suggested as alternative agents either in food biopreservation or in prevention/treatment of bacterial infections due to t ...
Lab6-Antimicrobial
... microorganisms in the host. Selective Toxicity: This means that the agent used must inhibit or kill the microorganism without seriously harming the host. Based on their origin, there are 2 general classes of antimicrobial chemotherapeutic agents: 1. Antibiotics: substances produced as metabolic pr ...
... microorganisms in the host. Selective Toxicity: This means that the agent used must inhibit or kill the microorganism without seriously harming the host. Based on their origin, there are 2 general classes of antimicrobial chemotherapeutic agents: 1. Antibiotics: substances produced as metabolic pr ...
The Effect of Microbes on Textile Material: A Review on the Way
... 1.1 Low moisture content and application of biocides in textiles It was suggested [1] that microbial activity (mildew and rotting) can be minimized by keeping susceptible materials dry, as surface growth will only occur when the relative humidity is high. The question is what of those places that hu ...
... 1.1 Low moisture content and application of biocides in textiles It was suggested [1] that microbial activity (mildew and rotting) can be minimized by keeping susceptible materials dry, as surface growth will only occur when the relative humidity is high. The question is what of those places that hu ...
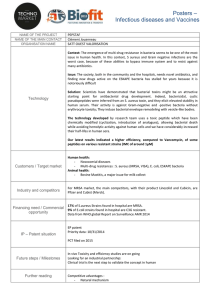
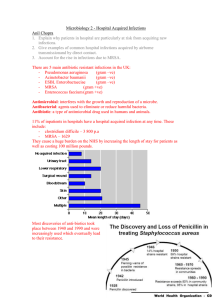
Microbiology 2 – Hospital Acquired Infections
... 1. Explain why patients in hospital are particularly at risk from acquiring new infections. 2. Give examples of common hospital infections acquired by airborne transmissionand by direct contact. 3. Account for the rise in infections due to MRSA. There are 5 main antibiotic resistant infections in th ...
... 1. Explain why patients in hospital are particularly at risk from acquiring new infections. 2. Give examples of common hospital infections acquired by airborne transmissionand by direct contact. 3. Account for the rise in infections due to MRSA. There are 5 main antibiotic resistant infections in th ...
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
... Infectious Diseases. McGraw-Hill. Laurence L.Brunton, J. S. 2006. Goodman & Gilman's the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw Hill. Longo, F. K. 2012. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. McGraw-Hill. M Sinha, H. S. 2007. Mechanisms of Resistance to Carbapenems in MeropenemResistant ...
... Infectious Diseases. McGraw-Hill. Laurence L.Brunton, J. S. 2006. Goodman & Gilman's the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw Hill. Longo, F. K. 2012. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. McGraw-Hill. M Sinha, H. S. 2007. Mechanisms of Resistance to Carbapenems in MeropenemResistant ...
Use of Artificial Intelligence in the Design of Small
... The number of compounds required for synthesis in order to place 10 different groups in 4 positions of benzene ring is 104 In silico modeling is thus necessary to search through small parts of chemical space in a reasonable time and cost-effective manner. A type of chemoinformatic computer modeling ...
... The number of compounds required for synthesis in order to place 10 different groups in 4 positions of benzene ring is 104 In silico modeling is thus necessary to search through small parts of chemical space in a reasonable time and cost-effective manner. A type of chemoinformatic computer modeling ...