Ten-year outcome: patients with schizoaffective disorders
... the sample into three groups: good outcome, remission or recovery during the follow-up year (scores of 1 or 2), indicating adequate or near-adequate functioning in all areas in the past year; moderate impairment (scores of 3 to 6), indicating difficulties in some but not all areas of adjustment duri ...
... the sample into three groups: good outcome, remission or recovery during the follow-up year (scores of 1 or 2), indicating adequate or near-adequate functioning in all areas in the past year; moderate impairment (scores of 3 to 6), indicating difficulties in some but not all areas of adjustment duri ...
chapter 15. anxiety disorders 15.6 anxiety
... authority figures. The clinician should recognize that many patients exhibit at least some social anxiety or selfconsciousness. In fact, community studies suggest that roughly a third of all people consider themselves to be far more anxious than other people in social situations. Such anxiety only b ...
... authority figures. The clinician should recognize that many patients exhibit at least some social anxiety or selfconsciousness. In fact, community studies suggest that roughly a third of all people consider themselves to be far more anxious than other people in social situations. Such anxiety only b ...
Chronic complex dissociative disorders and borderline personality
... typically found to be the most prevalent DD in general population and clinical studies with a prevalence rates up to 8.3% in the community reviewed in [23]. Across general population studies, the most severe DD, dissociative identity disorder (DID) has a prevalence of approximately 1% and has been f ...
... typically found to be the most prevalent DD in general population and clinical studies with a prevalence rates up to 8.3% in the community reviewed in [23]. Across general population studies, the most severe DD, dissociative identity disorder (DID) has a prevalence of approximately 1% and has been f ...
Factitious disorders refer to those conditions that
... cases of factitious disorder. Then, as it is now, the term "Munchausen" was associated with extreme, chronic forms of factitious behavior in which ex treme and routine lying and purposeful wandering or traveling (also de scribed as peregrination) in order to prevent detection from medical profes ...
... cases of factitious disorder. Then, as it is now, the term "Munchausen" was associated with extreme, chronic forms of factitious behavior in which ex treme and routine lying and purposeful wandering or traveling (also de scribed as peregrination) in order to prevent detection from medical profes ...
Birthplace
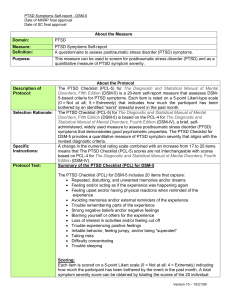
... A provisional PTSD diagnosis can be made by counting each item rated as 2 ("Moderately") or higher as a symptom endorsement, then following the DSM-5 diagnostic rule, which requires at least 1 item from cluster B (questions 1–5), 1 item from cluster C (questions 6–7), 2 items from cluster D (questio ...
... A provisional PTSD diagnosis can be made by counting each item rated as 2 ("Moderately") or higher as a symptom endorsement, then following the DSM-5 diagnostic rule, which requires at least 1 item from cluster B (questions 1–5), 1 item from cluster C (questions 6–7), 2 items from cluster D (questio ...
Deconstructing the DSM-5 By Jason H. King The DSM
... individuals must present with a minimum of two criteria. And to avoid overdiagnosing substance abuse solely on legal involvement (as happened with the DSM-IV-TR), the DSM-5 replaced this criterion with craving. In diagnosing schizophrenia, counselors will notice an important conceptual change from D ...
... individuals must present with a minimum of two criteria. And to avoid overdiagnosing substance abuse solely on legal involvement (as happened with the DSM-IV-TR), the DSM-5 replaced this criterion with craving. In diagnosing schizophrenia, counselors will notice an important conceptual change from D ...
the continuity of psychotic experiences in the general population
... interpret in the absence of associations with third aetiological, social impairment, or treatment variables. Therefore, as far as the prevalence argument is concerned, studies assessing the prevalence of psychotic symptoms themselves, rather than variably-defined attenuated experiences, may be more ...
... interpret in the absence of associations with third aetiological, social impairment, or treatment variables. Therefore, as far as the prevalence argument is concerned, studies assessing the prevalence of psychotic symptoms themselves, rather than variably-defined attenuated experiences, may be more ...
Eating Disorders - Intermountain Healthcare
... For adults: • Mild: BMI ≥ 17 kg/m2 • Moderate: BMI 16–16.99 kg/m2 • Severe: BMI 15–15.99 kg/m2 • Extreme: BMI < 15 kg/m2 For children and adolescents, corresponding BMI percentiles should be used. Note: The level of severity may be increased to reflect clinical symptoms, degree of functional dis ...
... For adults: • Mild: BMI ≥ 17 kg/m2 • Moderate: BMI 16–16.99 kg/m2 • Severe: BMI 15–15.99 kg/m2 • Extreme: BMI < 15 kg/m2 For children and adolescents, corresponding BMI percentiles should be used. Note: The level of severity may be increased to reflect clinical symptoms, degree of functional dis ...
Brand et al. Personality Differences Rorschach DID
... (American Psychiatric Association, 2004). Regarding the symptom overlap between DID and PSD, Schneiderian first-rank symptoms such as hearing voices and experiencing “made” thoughts and feelings are more commonly reported in patients with DID than in patients with schizophrenia, even though firstran ...
... (American Psychiatric Association, 2004). Regarding the symptom overlap between DID and PSD, Schneiderian first-rank symptoms such as hearing voices and experiencing “made” thoughts and feelings are more commonly reported in patients with DID than in patients with schizophrenia, even though firstran ...
Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders
... It thus seems that unconscious processes control the underlying mechanism that results in dissociation, or splitting off of awareness. There may even be “interpersonality rivalry” in which one personality aspires to do away with another, usually in ignorance of the fact that murdering an alternate w ...
... It thus seems that unconscious processes control the underlying mechanism that results in dissociation, or splitting off of awareness. There may even be “interpersonality rivalry” in which one personality aspires to do away with another, usually in ignorance of the fact that murdering an alternate w ...
Between 1 and 2% of adults have avoidant personality disorder
... The behaviors of people with these disorders are so dramatic, emotional, or erratic that it is almost impossible for them to have relationships that are truly giving and satisfying These personality disorders are more commonly diagnosed than the others ...
... The behaviors of people with these disorders are so dramatic, emotional, or erratic that it is almost impossible for them to have relationships that are truly giving and satisfying These personality disorders are more commonly diagnosed than the others ...
Giedd 2000
... for ADHD, are similarly ineffective in the treatment of bipolar disorder and may in fact induce mania in some individuals. Clinically, nonresponsiveness or an atypical response to pharmacologic management of a disorder should raise suspicions of an incorrect diagnosis. Selective serotonin reuptake i ...
... for ADHD, are similarly ineffective in the treatment of bipolar disorder and may in fact induce mania in some individuals. Clinically, nonresponsiveness or an atypical response to pharmacologic management of a disorder should raise suspicions of an incorrect diagnosis. Selective serotonin reuptake i ...
Borderline personality disorder in adolescents
... a mentally unstable mother who was financially unable to care for her. She was two years below the legal age when she married her first husband. She took numerous overdoses and had many passionate relationships. She underwent several psychological treatments and psychiatric hospitalizations. ...
... a mentally unstable mother who was financially unable to care for her. She was two years below the legal age when she married her first husband. She took numerous overdoses and had many passionate relationships. She underwent several psychological treatments and psychiatric hospitalizations. ...
ASD and pscyhosis the overlap - Royal College of Psychiatrists
... disturbance’ to describe 11 children that would alternatively be known as having ‘childhood schizophrenia’ • Asperger (1944) used the term ‘autistic psychopathy’ ...
... disturbance’ to describe 11 children that would alternatively be known as having ‘childhood schizophrenia’ • Asperger (1944) used the term ‘autistic psychopathy’ ...
Anxiety Disorders in Children and Adolescents
... Prevalence: The 12-month prevalence estimate of social anxiety disorder for the United States is approximately 7%. The 12-month prevalence rates in children and adolescents are comparable to those in adults. Prevalence rates decrease with age. The 12-month prevalence for older adults ranges from 2% ...
... Prevalence: The 12-month prevalence estimate of social anxiety disorder for the United States is approximately 7%. The 12-month prevalence rates in children and adolescents are comparable to those in adults. Prevalence rates decrease with age. The 12-month prevalence for older adults ranges from 2% ...
Bipolar Disorder - Psychiatric Services, PC
... disorder maintain good quality of life. Can Children and Adolescents Have Bipolar Disorder? Both children and adolescents can develop bipolar disorder. It is more likely to affect the children of parents who have the illness. Unlike many adults with bipolar disorder, whose episodes tend to be more c ...
... disorder maintain good quality of life. Can Children and Adolescents Have Bipolar Disorder? Both children and adolescents can develop bipolar disorder. It is more likely to affect the children of parents who have the illness. Unlike many adults with bipolar disorder, whose episodes tend to be more c ...
Short communication: State-related differences in heart rate
... Algra, A., Tijssen, J.G., Roelandt, J.R., Pool, J., and Lubsen, J. (1993). Contribution of the 24 hour electrocardiogram to the prediction of sudden coronary death. Br. Heart J. 70, 421–427. ...
... Algra, A., Tijssen, J.G., Roelandt, J.R., Pool, J., and Lubsen, J. (1993). Contribution of the 24 hour electrocardiogram to the prediction of sudden coronary death. Br. Heart J. 70, 421–427. ...
... and conditions of the study and asked to sign a consent form and complete anonymous questionnaires. They received no type of incentive for taking part in the study. The measurement instruments were always completed under the supervision of a researcher. This study is part of a broader research initi ...
Prevention and early intervention for borderline personality disorder
... emotional instability, interpersonal dysfunction and disturbed self-image.1 It affects 0.7–2.7% of the general adult population,2,3 9.3–22.5% of people receiving psychiatric out-patient treatment, and in some settings over 40% of in-patients.4 The outcome of this disorder in adulthood is now reliabl ...
... emotional instability, interpersonal dysfunction and disturbed self-image.1 It affects 0.7–2.7% of the general adult population,2,3 9.3–22.5% of people receiving psychiatric out-patient treatment, and in some settings over 40% of in-patients.4 The outcome of this disorder in adulthood is now reliabl ...
DSM-5: Implications for Social Work Practice Latino Social Work Organization October 16, 2014
... manifested until social demands exceed capabilities; milder forms may not be identified until early adolescence. – Trajectory is variable with some experiencing substantial improvement over time while others continue with problems through adult years. ...
... manifested until social demands exceed capabilities; milder forms may not be identified until early adolescence. – Trajectory is variable with some experiencing substantial improvement over time while others continue with problems through adult years. ...
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Fact Sheet
... abuse during pregnancy, poor maternal nutrition, and chemical poison ingestion during pregnancy may contribute to ADHD.12 ...
... abuse during pregnancy, poor maternal nutrition, and chemical poison ingestion during pregnancy may contribute to ADHD.12 ...
Cotard`s Syndrome
... As described earlier, nihilistic delusions concerning the individual’s body are the central features of Cotard’s syndrome. In an analysis of 100 cases, the most prominent symptoms in Cotard’s syndrome are: depressive mood (89%), nihilistic delusions concerning one’s own existence (69%), anxiety (65% ...
... As described earlier, nihilistic delusions concerning the individual’s body are the central features of Cotard’s syndrome. In an analysis of 100 cases, the most prominent symptoms in Cotard’s syndrome are: depressive mood (89%), nihilistic delusions concerning one’s own existence (69%), anxiety (65% ...
Multi-Disciplinary Team Training
... One of the more common disorders that is characterised by: Overwhelming anxiety and excessive self-consciousness in ...
... One of the more common disorders that is characterised by: Overwhelming anxiety and excessive self-consciousness in ...
Rumination syndrome

Rumination syndrome, or Merycism, is an under-diagnosed chronic motility disorder characterized by effortless regurgitation of most meals following consumption, due to the involuntary contraction of the muscles around the abdomen. There is no retching, nausea, heartburn, odour, or abdominal pain associated with the regurgitation, as there is with typical vomiting. The disorder has been historically documented as affecting only infants, young children, and people with cognitive disabilities (the prevalence is as high as 10% in institutionalized patients with various mental disabilities).Today it is being diagnosed in increasing numbers of otherwise healthy adolescents and adults, though there is a lack of awareness of the condition by doctors, patients and the general public.Rumination syndrome presents itself in a variety of ways, with especially high contrast existing between the presentation of the typical adult sufferer without a mental disability and the presentation of an infant and/or mentally impaired sufferer. Like related gastrointestinal disorders, rumination can adversely affect normal functioning and the social lives of individuals. It has been linked with depression.Little comprehensive data regarding rumination syndrome in otherwise healthy individuals exists because most sufferers are private about their illness and are often misdiagnosed due to the number of symptoms and the clinical similarities between rumination syndrome and other disorders of the stomach and esophagus, such as gastroparesis and bulimia nervosa. These symptoms include the acid-induced erosion of the esophagus and enamel, halitosis, malnutrition, severe weight loss and an unquenchable appetite. Individuals may begin regurgitating within a minute following ingestion, and the full cycle of ingestion and regurgitation can mimic the binging and purging of bulimia.Diagnosis of rumination syndrome is non-invasive and based on a history of the individual. Treatment is promising, with upwards of 85% of individuals responding positively to treatment, including infants and the mentally handicapped.