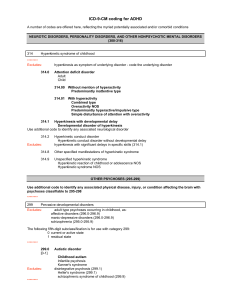
ICD-9-CM coding for ADHD
... Excludes: long-term (current) use of aspirin (V58.66) V58.62 Long-term (current) use of antibiotics V58.63 Long-term (current) use of antiplatelets/antithrombotics Excludes: long-term (current) use of aspirin (V58.66) V58.64 Long-term (current) use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAID) Exclud ...
... Excludes: long-term (current) use of aspirin (V58.66) V58.62 Long-term (current) use of antibiotics V58.63 Long-term (current) use of antiplatelets/antithrombotics Excludes: long-term (current) use of aspirin (V58.66) V58.64 Long-term (current) use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAID) Exclud ...
Emotional Disorders - Cherokee County Schools
... In MPD or DDI there are 2 or more intact personalities. ...
... In MPD or DDI there are 2 or more intact personalities. ...
Chapter 7
... Handout 65: How Are Dissociative Disorders Treated? How do therapists help individuals with DID? • Therapists usually try to help the client by: Integrating the subpersonalities The final goal of therapy is to merge the different subpersonalities into a single, integrated entity Integration is a c ...
... Handout 65: How Are Dissociative Disorders Treated? How do therapists help individuals with DID? • Therapists usually try to help the client by: Integrating the subpersonalities The final goal of therapy is to merge the different subpersonalities into a single, integrated entity Integration is a c ...
Anxiety disorder specificity of anxiety sensitivity in a community
... large community sample (N = 1867) of young German women, were used to investigate whether AS possesses specificity to anxiety-related psychopathology versus depression-related psychopathology when specific disorders were utilized as dependent variables. Participants completed a diagnostic interview ...
... large community sample (N = 1867) of young German women, were used to investigate whether AS possesses specificity to anxiety-related psychopathology versus depression-related psychopathology when specific disorders were utilized as dependent variables. Participants completed a diagnostic interview ...
področja: posameznik in travma
... mistreated by someone close as adults (approximately 40% compared to less than 12% of men) and as children (approximately 30% compared to less than 14%). Women also reported more sexual abuse in adulthood and in childhood than did men. However, men were much more likely to report having witnessed so ...
... mistreated by someone close as adults (approximately 40% compared to less than 12% of men) and as children (approximately 30% compared to less than 14%). Women also reported more sexual abuse in adulthood and in childhood than did men. However, men were much more likely to report having witnessed so ...
Impact of Traumatic Brain Injury Among Recently Returned
... normal healthy individuals All symptoms/problems overlap with one or more other conditions (PTSD, Depression, Anxiety, Chronic Pain, Somatoform Disorder, chronic health conditions) ...
... normal healthy individuals All symptoms/problems overlap with one or more other conditions (PTSD, Depression, Anxiety, Chronic Pain, Somatoform Disorder, chronic health conditions) ...
Document
... Children’s Global Assessment of Functioning Scale: Ages 6-17 100-91 Superior functioning in all areas (at home, at school and with peers); involved in a wide range of activities and has many interests (e.g., has hobbies or participates in extracurricular activities or belongs to an organized group ...
... Children’s Global Assessment of Functioning Scale: Ages 6-17 100-91 Superior functioning in all areas (at home, at school and with peers); involved in a wide range of activities and has many interests (e.g., has hobbies or participates in extracurricular activities or belongs to an organized group ...
Conversion Disorder in Childhood
... despite her marked chronic psychosocial stresses. Other traumatized children who experience psychosocial stress develop psychotic symptoms (Andrade and Srinath, 1986; Brašic and Perry, 1997a, b). Children with brain injury have particular vulnerability to develop a variety of neurological and psycho ...
... despite her marked chronic psychosocial stresses. Other traumatized children who experience psychosocial stress develop psychotic symptoms (Andrade and Srinath, 1986; Brašic and Perry, 1997a, b). Children with brain injury have particular vulnerability to develop a variety of neurological and psycho ...
Dissociative Symptoms in Filipino College Students
... Depersonalization. "Detachment from one's self, e.g., a sense of looking at one's self as if one is an outsider" (Steinberg, 1994, p. 19). Some participants felt as though they were watching themselves from a point outside of their bodies. Marcial described walking somewhere, but also seeing himself ...
... Depersonalization. "Detachment from one's self, e.g., a sense of looking at one's self as if one is an outsider" (Steinberg, 1994, p. 19). Some participants felt as though they were watching themselves from a point outside of their bodies. Marcial described walking somewhere, but also seeing himself ...
Anxiety - Lifeline
... – Face your Fears! People with anxiety may use substances such as alcohol and other drugs to cope with their symptoms. They may also exhibit other unhelpful coping strategies (such as avoidance techniques) which serve to provide short-term relief, however exacerbate their anxiety in the long-term. I ...
... – Face your Fears! People with anxiety may use substances such as alcohol and other drugs to cope with their symptoms. They may also exhibit other unhelpful coping strategies (such as avoidance techniques) which serve to provide short-term relief, however exacerbate their anxiety in the long-term. I ...
Services aux enfants et adultes - Brant Family and Children`s Services
... According to the author, the coping theorists have as one of their premises that “people act on their environments to shape and select their experience. They develop models rather than just react… People are both affected by their environments and in turn affect their environments” (p. 10). Thus per ...
... According to the author, the coping theorists have as one of their premises that “people act on their environments to shape and select their experience. They develop models rather than just react… People are both affected by their environments and in turn affect their environments” (p. 10). Thus per ...
Durand and Barlow Chapter 4: Anxiety Disorders
... • Next revision of the DSM will likely see major changes like we have never seen before. – Focus of NIMH research in the future will be on underlying genetic/neurobiological causes that are common among psychological disorders. This is known as the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) project. ...
... • Next revision of the DSM will likely see major changes like we have never seen before. – Focus of NIMH research in the future will be on underlying genetic/neurobiological causes that are common among psychological disorders. This is known as the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) project. ...
assessment criteria for community and specialist camhs
... Emergency Department. The jointly agreed protocol for the management of self-harm will be followed. Deliberate self-harm that requires within 24 hours ...
... Emergency Department. The jointly agreed protocol for the management of self-harm will be followed. Deliberate self-harm that requires within 24 hours ...
Lecture_2
... himself as the subject of life relationships and his behavior. High self-attitude of the individual is a condition of maximum activity, productivity in it, realization of creative potential and also impacts on freedom of feelings expression, the level of selfdisclosure in communication. Positive and ...
... himself as the subject of life relationships and his behavior. High self-attitude of the individual is a condition of maximum activity, productivity in it, realization of creative potential and also impacts on freedom of feelings expression, the level of selfdisclosure in communication. Positive and ...
t\bnormal Practice Test
... d. a histology 10. Diagnosis is to prognosis as a. why is to what b. what is to outcome c. outcome is to etiology d. ontogeny is to phylogeny 11. Prognosis is to etiology as a. outcome is to why b. why is to outcome c. what is to why d. why is to what 12. Behavior that does not coincide with cultura ...
... d. a histology 10. Diagnosis is to prognosis as a. why is to what b. what is to outcome c. outcome is to etiology d. ontogeny is to phylogeny 11. Prognosis is to etiology as a. outcome is to why b. why is to outcome c. what is to why d. why is to what 12. Behavior that does not coincide with cultura ...
Generalized dissociative amnesia
... details about her childhood from a cousin in Israel who witnessed her childhood hardships. She was born in Hungary, an only child to a Jewish couple. When she was 8 years old, the Germans first took her father, then a few months later, arrested her mother. She was left with her grandmother who died ...
... details about her childhood from a cousin in Israel who witnessed her childhood hardships. She was born in Hungary, an only child to a Jewish couple. When she was 8 years old, the Germans first took her father, then a few months later, arrested her mother. She was left with her grandmother who died ...
Tourette Syndrome - Canadian Psychological Association
... Future tic severity can be predicted by severity and degree of psychosocial stress and depression in childhood, as well as by fine motor skill deficits in childhood (Bloch et al., 2006). Individuals can sometimes suppress (i.e. hold in) their tics for short periods of time. The ability to suppress d ...
... Future tic severity can be predicted by severity and degree of psychosocial stress and depression in childhood, as well as by fine motor skill deficits in childhood (Bloch et al., 2006). Individuals can sometimes suppress (i.e. hold in) their tics for short periods of time. The ability to suppress d ...
- Bepress
... characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. There is usually significant distress or disability in social or o ...
... characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes underlying mental functioning. There is usually significant distress or disability in social or o ...
Chapter 12 Psychological Disorders
... diseases that, like ordinary physical diseases, have objective physical causes and require specific treatments. • Mental disorders are best treated with drug therapy. ...
... diseases that, like ordinary physical diseases, have objective physical causes and require specific treatments. • Mental disorders are best treated with drug therapy. ...
Overview of DSM Changes
... Sex: q Male q Female Date: If the measure is being completed by an informant, what is your relationship with the individual receiving care? In a typical week, approximately how much time do you spend with the individual receiving care? hours/week Instructions: On the DSM-5 Level 1 cross-cutting ques ...
... Sex: q Male q Female Date: If the measure is being completed by an informant, what is your relationship with the individual receiving care? In a typical week, approximately how much time do you spend with the individual receiving care? hours/week Instructions: On the DSM-5 Level 1 cross-cutting ques ...
psychological evaluation of torture allegations
... than physical disability. Several aspects of psychological functioning may continue to be impaired in long-term; if not treated victims may suffer from the psychological consequences of torture even months or years following the event, sometimes for life, with varying degrees of severity. (Carlsson ...
... than physical disability. Several aspects of psychological functioning may continue to be impaired in long-term; if not treated victims may suffer from the psychological consequences of torture even months or years following the event, sometimes for life, with varying degrees of severity. (Carlsson ...
[1] - mrsjanis
... Somatoform Disorders 3 types: somatization, coversion, hypochondriasis Marked by a pattern of recurring, multiple and significant bodily (somatic) symptoms that extend over several years These symptoms (pain, vomiting, paralysis, etc) are not under voluntary control & have no known physical cau ...
... Somatoform Disorders 3 types: somatization, coversion, hypochondriasis Marked by a pattern of recurring, multiple and significant bodily (somatic) symptoms that extend over several years These symptoms (pain, vomiting, paralysis, etc) are not under voluntary control & have no known physical cau ...
University of Southampton Research Repository ePrints Soton
... Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) is a complex and often poorly understood dissociative disorder, characterised by disruption of identity with the presence of two or more distinct personality states (APA, 2013). Several theoretical models have been proposed to provide a framework within which to ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) is a complex and often poorly understood dissociative disorder, characterised by disruption of identity with the presence of two or more distinct personality states (APA, 2013). Several theoretical models have been proposed to provide a framework within which to ...
A brief note on the terms Neurosis and Psychoneurosis Bill Tillier
... In other words, the individual unconsciously struggles to repress certain elements of the Id. These thoughts, conflicts, desires, memories, etc. often focus on unacceptable sexual desires, or memories of intense, inappropriate (e.g. murderous) feelings toward a parent or other loved one. If these id ...
... In other words, the individual unconsciously struggles to repress certain elements of the Id. These thoughts, conflicts, desires, memories, etc. often focus on unacceptable sexual desires, or memories of intense, inappropriate (e.g. murderous) feelings toward a parent or other loved one. If these id ...




















![[1] - mrsjanis](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008646871_1-e695c0d664a7c853a981eb87ee41bc28-300x300.png)

