Psycho-flexed Hand Associated with Conversion Reaction: A Case
... Revision (DSM-IV-TR) criteria defines conversion disorders characterized by the presence of one or more neurological symptoms such as paralysis, blindness, etc. that are not explained by known neurological or medical disorders. It gives a range from as low as 11 to as high as 500 cases per 100,000 ...
... Revision (DSM-IV-TR) criteria defines conversion disorders characterized by the presence of one or more neurological symptoms such as paralysis, blindness, etc. that are not explained by known neurological or medical disorders. It gives a range from as low as 11 to as high as 500 cases per 100,000 ...
Psychological Disorders
... Psychoanalytic: repressed feelings during childhood symbolized by trigger. Behavioral: learned fear, which has been reinforced, or social learning, imitating others who have fear, like parents. May be generalized from other learned experiences: one dog to all dogs. Biological: predisposed geneticall ...
... Psychoanalytic: repressed feelings during childhood symbolized by trigger. Behavioral: learned fear, which has been reinforced, or social learning, imitating others who have fear, like parents. May be generalized from other learned experiences: one dog to all dogs. Biological: predisposed geneticall ...
Disorders - Tipp City Schools
... • Behavior Therapy – systemic application of the principles of learning to the direct modification of a client’s problem behaviors (conditioning and observational learning) • Systemic desensitization – reducing fears by associating images of fear-evoking stimuli with muscle relaxation (for phobias) ...
... • Behavior Therapy – systemic application of the principles of learning to the direct modification of a client’s problem behaviors (conditioning and observational learning) • Systemic desensitization – reducing fears by associating images of fear-evoking stimuli with muscle relaxation (for phobias) ...
Psychological Disorders PPT
... identical Genain sisters suffer from schizophrenia. Two more than others, thus there are contributing environmental factors. ...
... identical Genain sisters suffer from schizophrenia. Two more than others, thus there are contributing environmental factors. ...
WHAT IS “PSEUDO” ABOUT PSEUDOSEIZURES A REVIEW OF CONVERSION DISORDER
... – Emotional issues in conversion disorder can result in real chemical changes in the body that have been measurable in research studies – This diagnosis will only be made after a thorough medical and psychiatric assessment has been completed – Symptoms can change significantly over time into other a ...
... – Emotional issues in conversion disorder can result in real chemical changes in the body that have been measurable in research studies – This diagnosis will only be made after a thorough medical and psychiatric assessment has been completed – Symptoms can change significantly over time into other a ...
Please answer all questions on your Scantron
... When psychologists talk about the control of abnormal behavior, they mean that they: a. seek to understand the underlying cause of that behavior. b. restrict the freedom of dangerous clients. c. try to anticipate the future behaviors of clients. d. take charge of the client’s life. e. use therapy to ...
... When psychologists talk about the control of abnormal behavior, they mean that they: a. seek to understand the underlying cause of that behavior. b. restrict the freedom of dangerous clients. c. try to anticipate the future behaviors of clients. d. take charge of the client’s life. e. use therapy to ...
W03 - Psychology
... When psychologists talk about the control of abnormal behavior, they mean that they: a. seek to understand the underlying cause of that behavior. b. restrict the freedom of dangerous clients. c. try to anticipate the future behaviors of clients. d. take charge of the client’s life. e. use therapy to ...
... When psychologists talk about the control of abnormal behavior, they mean that they: a. seek to understand the underlying cause of that behavior. b. restrict the freedom of dangerous clients. c. try to anticipate the future behaviors of clients. d. take charge of the client’s life. e. use therapy to ...
Ch. 18 Section 4: Somatoform Disorders
... somatoform disorders may go undiagnosed because of the focus on physical, as opposed to psychological, symptoms. ...
... somatoform disorders may go undiagnosed because of the focus on physical, as opposed to psychological, symptoms. ...
Are the DSM Disorders Universal Across Cultures?
... A series of curious incidents at a Veterans Administration psychiatric facility in the US, the National Center for the Treatment of PTSD, whereby wielders of the adopted psychodynamic theory into practice took form in a way that created an ideology-centric interaction between the cultural expectatio ...
... A series of curious incidents at a Veterans Administration psychiatric facility in the US, the National Center for the Treatment of PTSD, whereby wielders of the adopted psychodynamic theory into practice took form in a way that created an ideology-centric interaction between the cultural expectatio ...
Chapter 16 Test Review - DeForest Area School District
... • When people’s symptoms of psychological distress are at their worst, whatever they do to try to alleviate the condition is likely to be followed by improvement rather than further deterioration. This is best explained in terms of: a. systematic desensitization. b. the therapeutic alliance. ...
... • When people’s symptoms of psychological distress are at their worst, whatever they do to try to alleviate the condition is likely to be followed by improvement rather than further deterioration. This is best explained in terms of: a. systematic desensitization. b. the therapeutic alliance. ...
actual neurosis and ptsd
... associative way, it is not a trauma in the PTSD sense of the word. As we will see, the psychological processing of stressful events happens in early development through the mediation by the Other.1 If this Other, for one reason or another, is not able to provide this mediation, then the processing b ...
... associative way, it is not a trauma in the PTSD sense of the word. As we will see, the psychological processing of stressful events happens in early development through the mediation by the Other.1 If this Other, for one reason or another, is not able to provide this mediation, then the processing b ...
Schizotypal (Personality) Disorder Delusional Disorder
... In erotomanic type, the central theme of the delusion is that another person is in love with the individual. The person about whom this conviction is held is usually of higher status (e.g., a famous individual or a superior at work) but can be a complete stranger. Efforts to contact the object of th ...
... In erotomanic type, the central theme of the delusion is that another person is in love with the individual. The person about whom this conviction is held is usually of higher status (e.g., a famous individual or a superior at work) but can be a complete stranger. Efforts to contact the object of th ...
click here - Whole Health Solutions
... tension, sweating, loose stools, disturbed sleep and irregular sleep patterns. Some of the behavior patterns associated with stress include anger outbursts, an increase in smoking, crying, irritability, relationship problems, overeating or eating when you're not hungry. Stress has many damaging effe ...
... tension, sweating, loose stools, disturbed sleep and irregular sleep patterns. Some of the behavior patterns associated with stress include anger outbursts, an increase in smoking, crying, irritability, relationship problems, overeating or eating when you're not hungry. Stress has many damaging effe ...
Stress - Ch 10
... Hans Selye (1930 – 1940) Described an universal and predictablee response pattern to all stressors Recognized that stressors can be either pleasant (eustress) or unpleasant (distress). The sequence of physical responses occurs in three stages: ...
... Hans Selye (1930 – 1940) Described an universal and predictablee response pattern to all stressors Recognized that stressors can be either pleasant (eustress) or unpleasant (distress). The sequence of physical responses occurs in three stages: ...
Glossary Of Terms Related To The Psychological Evaluation Pain
... an emotion. The meaning of the word pain is learned in childhood and is associated with injury, illness, and emotional distress. Although pain is generally associated with nociception, it may occur without any physical cause. The perception of pain involves both cognitive judgments and affective rea ...
... an emotion. The meaning of the word pain is learned in childhood and is associated with injury, illness, and emotional distress. Although pain is generally associated with nociception, it may occur without any physical cause. The perception of pain involves both cognitive judgments and affective rea ...
Memory Fragmentation in Dissociative Identity Disorder
... Participants chose emotionally significant but non-traumatic experiences such as a vacation or trip, receiving a compliment from an adult, contact with a friendly adult, birth of twin-sisters, experiencing something pleasant, winning a prize in a lottery. Many participants experienced difficulties i ...
... Participants chose emotionally significant but non-traumatic experiences such as a vacation or trip, receiving a compliment from an adult, contact with a friendly adult, birth of twin-sisters, experiencing something pleasant, winning a prize in a lottery. Many participants experienced difficulties i ...
Psychological Disorders
... Dissociative Identity Disorder (D.I.D.) • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • Rare & controversial disorder where the person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities. • Number of cases increased dramatically during the 1980’s (popular book “Sybil”). • Claims of c ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder (D.I.D.) • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • Rare & controversial disorder where the person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities. • Number of cases increased dramatically during the 1980’s (popular book “Sybil”). • Claims of c ...
psychogenic myopia - Journal of Research in Medical Sciences
... boy who had been under the supervision of different ophthalmologists for 4 years. During this period, the patient had undergone various ophthalmologic and neurological examines. However, no noticeable organic reason was put forth for the disorder. Finally, with the possibility of a psychological rea ...
... boy who had been under the supervision of different ophthalmologists for 4 years. During this period, the patient had undergone various ophthalmologic and neurological examines. However, no noticeable organic reason was put forth for the disorder. Finally, with the possibility of a psychological rea ...
Somatoform disorders
... Pain disorder - diagnostic criteria • Pain in one or more anatomical sites causing clinical significant distress • Psychological factors have an important role in the onset • The symptom or deficit is not intentionaly produced • The pain is not better accounted for by a mood, anxiety or psychotic d ...
... Pain disorder - diagnostic criteria • Pain in one or more anatomical sites causing clinical significant distress • Psychological factors have an important role in the onset • The symptom or deficit is not intentionaly produced • The pain is not better accounted for by a mood, anxiety or psychotic d ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... •Measures the extent to which individuals become apprehensive in response to their bodily sensations. •Developed by Peterson & Reiss (1987) •High scorers on the ASI were more likely than low scorers to experience panic attacks, especially if they had been told they would feel relaxed instead of arou ...
... •Measures the extent to which individuals become apprehensive in response to their bodily sensations. •Developed by Peterson & Reiss (1987) •High scorers on the ASI were more likely than low scorers to experience panic attacks, especially if they had been told they would feel relaxed instead of arou ...
ACF-Support-document-abstracts-of-papers
... data relevant to AS experience in the RDP were collected using self-report measures to assess posttraumatic stress (Harvard Trauma Questionnaire–Revised) and depressive and anxiety symptoms (25-item Hopkins Symptom Checklist), and the Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview 6.0 psychiatric int ...
... data relevant to AS experience in the RDP were collected using self-report measures to assess posttraumatic stress (Harvard Trauma Questionnaire–Revised) and depressive and anxiety symptoms (25-item Hopkins Symptom Checklist), and the Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview 6.0 psychiatric int ...
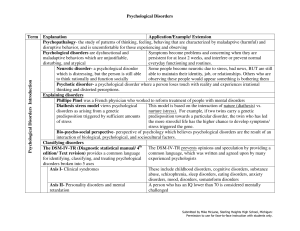
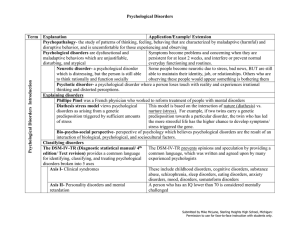
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
13A-Psychdisorder-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
Psychiatric Classification
... Symptoms are preceded by stressors Symptoms are not intentionally feigned or produced No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...
... Symptoms are preceded by stressors Symptoms are not intentionally feigned or produced No neuro, medical, substance abuse or cultural explanation Must cause marked distress ...