LOTL NW plants Sp12
... Douglas Fir 1 of 3 dominant trees, needles go all around the stem, cones with ‘rat tails’, pointed buds ...
... Douglas Fir 1 of 3 dominant trees, needles go all around the stem, cones with ‘rat tails’, pointed buds ...
Plants - cayugascience
... Leaves came next Increased surface area of plant allowed better exchange of gases involved in photosynthesis and ...
... Leaves came next Increased surface area of plant allowed better exchange of gases involved in photosynthesis and ...
Chapter 28-31 Plants 28.1 Overview of Plants 28.1 Overview of
... – Schlerenchyma – used for support (in non-growing regions) – Thick and even ...
... – Schlerenchyma – used for support (in non-growing regions) – Thick and even ...
Kingdom Plantae
... protects them from damage and water loss • Seeds contain a food source for the plant embryo called the cotyledon ...
... protects them from damage and water loss • Seeds contain a food source for the plant embryo called the cotyledon ...
2013 Training Handout
... Collecting Leaves 1. Only collect leaves on a sunny day and after dew has dried. 2. Collect good leaves, leaves that have not been damaged by insects, diseases or the sun. 3. Always collect more than one leaf. Collect a small branch full. That way, you will be sure to get a good representative of th ...
... Collecting Leaves 1. Only collect leaves on a sunny day and after dew has dried. 2. Collect good leaves, leaves that have not been damaged by insects, diseases or the sun. 3. Always collect more than one leaf. Collect a small branch full. That way, you will be sure to get a good representative of th ...
2012 Training Handout
... Collecting Leaves 1. Only collect leaves on a sunny day and after dew has dried. 2. Collect good leaves, leaves that have not been damaged by insects, diseases or the sun. 3. Always collect more than one leaf. Collect a small branch full. That way, you will be sure to get a good representative of th ...
... Collecting Leaves 1. Only collect leaves on a sunny day and after dew has dried. 2. Collect good leaves, leaves that have not been damaged by insects, diseases or the sun. 3. Always collect more than one leaf. Collect a small branch full. That way, you will be sure to get a good representative of th ...
Urban Herbology – River of Herbs Project Stinging Nettle (Urtica
... Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) Echte Valeriaan ...
... Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) Echte Valeriaan ...
Structure Review Part 2
... C. are mainly to increase absorption D. always have a symbiotic relationship with bacteria E. grow in the air, not in soil 6. The function of the casparian strip is to__. A. channel water into vascular tissue B. increase surface area for absorption C. form a symbiotic relationship with fungi D. abso ...
... C. are mainly to increase absorption D. always have a symbiotic relationship with bacteria E. grow in the air, not in soil 6. The function of the casparian strip is to__. A. channel water into vascular tissue B. increase surface area for absorption C. form a symbiotic relationship with fungi D. abso ...
Plants – Characteristics and Function --
... primary food reserve • Have cellulose in their cell walls • Use chlorophyll a and b for photosynthesis ...
... primary food reserve • Have cellulose in their cell walls • Use chlorophyll a and b for photosynthesis ...
Flower Dissection Lab (Part 1)
... and "peeling" the fingernail polish off the leaf. This is the leaf impression you will examine. (Only make one leaf impression on each side of the leaf, especially if the leaf is going to be left on a live plant.) 6. Tape your peeled impression to a very clean microscope slide. Use scissors to trim ...
... and "peeling" the fingernail polish off the leaf. This is the leaf impression you will examine. (Only make one leaf impression on each side of the leaf, especially if the leaf is going to be left on a live plant.) 6. Tape your peeled impression to a very clean microscope slide. Use scissors to trim ...
weed control guidelines
... Nodding Saltbush (Einadia nutans) has lighter, smaller and sparser leaves with thinner stems. Berry Saltbush (Atriplex semibaccata) also has lighter, smaller and sparser leaves with thinner stems. Further Information If you would like help to identify or control weeds on your property, contact the S ...
... Nodding Saltbush (Einadia nutans) has lighter, smaller and sparser leaves with thinner stems. Berry Saltbush (Atriplex semibaccata) also has lighter, smaller and sparser leaves with thinner stems. Further Information If you would like help to identify or control weeds on your property, contact the S ...
Common Name: AMERICAN LILY-OF-THE
... ½ the length of the leaves, rising from the base of the plant. Flower clusters with 5 - 15 white, nodding flowers. Flowers ¼ - ⅜ inch (6 - 10 mm) long, bell-shaped with 6 upturned tips, fragrant. Fruit a round, reddish-orange berry about ¼ inch (7 - 9 mm) wide. Similar Species: European lily-of-the- ...
... ½ the length of the leaves, rising from the base of the plant. Flower clusters with 5 - 15 white, nodding flowers. Flowers ¼ - ⅜ inch (6 - 10 mm) long, bell-shaped with 6 upturned tips, fragrant. Fruit a round, reddish-orange berry about ¼ inch (7 - 9 mm) wide. Similar Species: European lily-of-the- ...
Plants Overview
... area of growth at the top end of stem – Axillary Buds – area of growth located in the V area between the leaf and the stem (branches) ...
... area of growth at the top end of stem – Axillary Buds – area of growth located in the V area between the leaf and the stem (branches) ...
Salvia clevelandii `Allen Chickering`
... spaced whorls along 1½-2-ft. stems in early summer Deliciously aromatic, wrinkled graygreen 2-in.-long leaves California (Hybrid) ...
... spaced whorls along 1½-2-ft. stems in early summer Deliciously aromatic, wrinkled graygreen 2-in.-long leaves California (Hybrid) ...
Roots
... • Stems that support upright growth • Photosynthetic leaves • Reproductive shoots (flowers) ...
... • Stems that support upright growth • Photosynthetic leaves • Reproductive shoots (flowers) ...
Chapter 31 - Mason Gmu
... have cell wall, roots, stems, leaves, and gametangia to produce gametes, reproduce sexually. Some of the oldest organisms on earth. Ex: redwood over 100 feet, and giant sequoia or general Sherman is 84 meters tall and 10 m in diameter, 1700 years old. Plants are divided into 2 major groups: Gymnos ...
... have cell wall, roots, stems, leaves, and gametangia to produce gametes, reproduce sexually. Some of the oldest organisms on earth. Ex: redwood over 100 feet, and giant sequoia or general Sherman is 84 meters tall and 10 m in diameter, 1700 years old. Plants are divided into 2 major groups: Gymnos ...
Photosynthesis and Plant Canopies
... pigments in photosynthesizers absorb the energy of photons, initiating a chain of photochemical and chemical events. Where does this energy and material exchange occur? In plant canopies. The amount of photosynthesis that occurs in canopies depends on the amount of photosynthetically active radiatio ...
... pigments in photosynthesizers absorb the energy of photons, initiating a chain of photochemical and chemical events. Where does this energy and material exchange occur? In plant canopies. The amount of photosynthesis that occurs in canopies depends on the amount of photosynthetically active radiatio ...
Plant Science HL
... • The central region of a root used for storage and support. • A plant’s growth in response to light. • Open and close the stomata. • A plants that produces flowers with petals in multiples of threes. • The transfer of yellow grains from anther to carpel. Buzz Buzz. • Surround the vascular tissue in ...
... • The central region of a root used for storage and support. • A plant’s growth in response to light. • Open and close the stomata. • A plants that produces flowers with petals in multiples of threes. • The transfer of yellow grains from anther to carpel. Buzz Buzz. • Surround the vascular tissue in ...
5799 Cover.qxd
... Plant. Perennial ascending-to-upright leguminous forb, 3 to 6 feet (1 to 2 m) in height, with one-to-many leafy slender stems often branching at midplant, threeleaflet leaves, and tiny whitish flowers. Plant arising from a woody rootcrown. Dormant brown plants remaining upright during most of the wi ...
... Plant. Perennial ascending-to-upright leguminous forb, 3 to 6 feet (1 to 2 m) in height, with one-to-many leafy slender stems often branching at midplant, threeleaflet leaves, and tiny whitish flowers. Plant arising from a woody rootcrown. Dormant brown plants remaining upright during most of the wi ...
Slide 1
... C. Gas exchange—plants must exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) to perform photosynthesis D. Movement of water and nutrients— plants take up water and minerals with their roots, but make food in their leaves. ...
... C. Gas exchange—plants must exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) to perform photosynthesis D. Movement of water and nutrients— plants take up water and minerals with their roots, but make food in their leaves. ...
Plant_powerpoint - District 128 Moodle
... Stems – support and transportation • Vascular tissue – tubular cells used for transporting materials (like human veins) • Two Types – – Xylem – transports water and dissolved minerals upward from roots into the shoots – Phloem – transports food (glucose) made in the leaves down to the parts that do ...
... Stems – support and transportation • Vascular tissue – tubular cells used for transporting materials (like human veins) • Two Types – – Xylem – transports water and dissolved minerals upward from roots into the shoots – Phloem – transports food (glucose) made in the leaves down to the parts that do ...
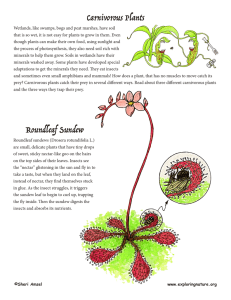
Carnivorous Plants Roundleaf Sundew
... Wetlands, like swamps, bogs and peat marshes, have soil that is so wet, it is not easy for plants to grow in them. Even though plants can make their own food, using sunlight and the process of photosynthesis, they also need soil rich with minerals to help them grow. Soils in wetlands have their mine ...
... Wetlands, like swamps, bogs and peat marshes, have soil that is so wet, it is not easy for plants to grow in them. Even though plants can make their own food, using sunlight and the process of photosynthesis, they also need soil rich with minerals to help them grow. Soils in wetlands have their mine ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.