Plant Adaptations WebQuest-key
... quickly due to trees being coniferous Needle-like leaves lose less water and shed snow Dark colored needles to absorb more sunlight Low growing plants to keep them from freezing Dark colored plants to absorb more solar heat Clumps of plants to protect from wind and cold Flexible stems and leaves to ...
... quickly due to trees being coniferous Needle-like leaves lose less water and shed snow Dark colored needles to absorb more sunlight Low growing plants to keep them from freezing Dark colored plants to absorb more solar heat Clumps of plants to protect from wind and cold Flexible stems and leaves to ...
Liriomyza Leaf Miners
... not native to the UK. They are notifiable to Defra whenever found. They are all highly polyphagous, feeding on a wide range of plant species, including economically important vegetable and ornamental plants. The tomato leaf miner (L. bryoniae) is closely related to the South American leaf miner, but ...
... not native to the UK. They are notifiable to Defra whenever found. They are all highly polyphagous, feeding on a wide range of plant species, including economically important vegetable and ornamental plants. The tomato leaf miner (L. bryoniae) is closely related to the South American leaf miner, but ...
Name
... association with the seedlings' roots. E) The dirt from the Southwest probably contained eggs of worms and other soil animals. 27) Which one of the following statements about mycorrhizae is false? A) The fungus benefits by receiving a steady supply of sugar from the host plant. B) The fungus increa ...
... association with the seedlings' roots. E) The dirt from the Southwest probably contained eggs of worms and other soil animals. 27) Which one of the following statements about mycorrhizae is false? A) The fungus benefits by receiving a steady supply of sugar from the host plant. B) The fungus increa ...
100 - Central Lyon CSD
... Once on the stigma, the pollen grains grow a tube from the stigma to the ovary. What part of the pistol allows the male gamete to swimming down to fertilize the egg? ...
... Once on the stigma, the pollen grains grow a tube from the stigma to the ovary. What part of the pistol allows the male gamete to swimming down to fertilize the egg? ...
Cranberry hibiscus (Hibiscus acetosella, false roselle, African
... Cranberry hibiscus (Hibiscus acetosella, false roselle, African rosemallow) It is a striking and colorful plant with red leaves that resemble a maple leaf. It tends to grow so tall it straggles all over the place because its slender branches bend right over from the weight of its leaves. Prune it wh ...
... Cranberry hibiscus (Hibiscus acetosella, false roselle, African rosemallow) It is a striking and colorful plant with red leaves that resemble a maple leaf. It tends to grow so tall it straggles all over the place because its slender branches bend right over from the weight of its leaves. Prune it wh ...
Maple Syrup in the Classroom by Pete Barnum
... Chloroplasts are the ultimate energy factories of the tree. Chloroplasts convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar) and oxygen in the process of photosynthesis. ...
... Chloroplasts are the ultimate energy factories of the tree. Chloroplasts convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar) and oxygen in the process of photosynthesis. ...
to file.
... live oak trees have also been planted and will provide some shady areas in just a few years. The garden is an excellent place to get good ideas for plants that will survive well in the sometimes harsh environment of South Texas. All of these plants have adapted different types of leaves. The goal of ...
... live oak trees have also been planted and will provide some shady areas in just a few years. The garden is an excellent place to get good ideas for plants that will survive well in the sometimes harsh environment of South Texas. All of these plants have adapted different types of leaves. The goal of ...
Seed Plants
... • Many produce fruit = a wall of tissue surrounding a seed • The seed leaves of plant embryos are called cotyledons • Flowers that complete an entire life cycle within one growing season are called –annuals ...
... • Many produce fruit = a wall of tissue surrounding a seed • The seed leaves of plant embryos are called cotyledons • Flowers that complete an entire life cycle within one growing season are called –annuals ...
Name - Humble ISD
... 1) Which type of angiosperm has tap roots? Dicot 2) Which type of angiosperm has fibrous roots? Monocot 3) Which type of root is more efficient at erosion control? Fibrous Why? Because they are closer to the soil and there are lots of them. 4) Which type of root is harder to pull out of the ground? ...
... 1) Which type of angiosperm has tap roots? Dicot 2) Which type of angiosperm has fibrous roots? Monocot 3) Which type of root is more efficient at erosion control? Fibrous Why? Because they are closer to the soil and there are lots of them. 4) Which type of root is harder to pull out of the ground? ...
PlantClassification Word Splash
... instead of flowers. The flowering plants can be further classified according to their leaf and seed structure. Plants with branching veins in their leaves are called _________________ and plants with parallel veins in their leaves are called _________________. Maple trees are dicots . You can see th ...
... instead of flowers. The flowering plants can be further classified according to their leaf and seed structure. Plants with branching veins in their leaves are called _________________ and plants with parallel veins in their leaves are called _________________. Maple trees are dicots . You can see th ...
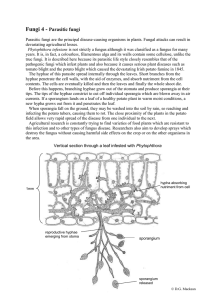
Parasitic fungi - Biology Resources
... hyphae penetrate the cell walls, with the aid of enzymes, and absorb nutriment from the cell contents. The cells are eventually killed and then the leaves and finally the whole shoot die. Before this happens, branching hyphae grow out of the stomata and produce sporangia at their tips. The tips of t ...
... hyphae penetrate the cell walls, with the aid of enzymes, and absorb nutriment from the cell contents. The cells are eventually killed and then the leaves and finally the whole shoot die. Before this happens, branching hyphae grow out of the stomata and produce sporangia at their tips. The tips of t ...
Type Variety Description Broccoli Marathon As an industry standard
... eighteenth century. Bluegreen strap-like leaves are 3" wide by 10-18" long with a heavily savoyed texture. Excellent flavor that is enhanced by frost. Best eaten when leaves are small and tender. ...
... eighteenth century. Bluegreen strap-like leaves are 3" wide by 10-18" long with a heavily savoyed texture. Excellent flavor that is enhanced by frost. Best eaten when leaves are small and tender. ...
Kingdom Plantae: Types of Plants and Their Characteristics
... a. Leaves consist of 2 parts—the stalk (connects the leaf to the stem) and the blade (the thin, flat part). 1. Leaves that have only one blade are called simple leaves, while those made up of 2 or more blades are called compound leaves. b. Leaves are responsible for carrying out photosynthesis by ca ...
... a. Leaves consist of 2 parts—the stalk (connects the leaf to the stem) and the blade (the thin, flat part). 1. Leaves that have only one blade are called simple leaves, while those made up of 2 or more blades are called compound leaves. b. Leaves are responsible for carrying out photosynthesis by ca ...
PASS Review—Plants Name: All living organisms share the
... study of how scientists classify organisms; Scientists use a series of levels to group organisms—the more levels they share with each other, the more characteristics they have in common. Biggest to smallest: Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species (King Phillip came over for good spagh ...
... study of how scientists classify organisms; Scientists use a series of levels to group organisms—the more levels they share with each other, the more characteristics they have in common. Biggest to smallest: Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species (King Phillip came over for good spagh ...
garden disease problems
... Leaves turn yellow, wilt, and die. Brown spots on petals or red-pink spots on lighter colored flower buds. Brown dieback of cut canes, brown fuzzy mold on debris around the plant. In severe cases, the entire flower bud rots. Botrytis. This disease is caused by a fungus that is commonly found on dead ...
... Leaves turn yellow, wilt, and die. Brown spots on petals or red-pink spots on lighter colored flower buds. Brown dieback of cut canes, brown fuzzy mold on debris around the plant. In severe cases, the entire flower bud rots. Botrytis. This disease is caused by a fungus that is commonly found on dead ...
Wildflower Stories by Wendy E. Jones, Head Naturalist
... anthers (pollen sacs) that point out from the blossom like the tongue of a snake; and dogtooth violet, a reference to the white, tooth-shaped bulb, despite the fact that trout lily is not a violet at all. The lily is common in many different folklore traditions. It is the sacred flower of motherhood ...
... anthers (pollen sacs) that point out from the blossom like the tongue of a snake; and dogtooth violet, a reference to the white, tooth-shaped bulb, despite the fact that trout lily is not a violet at all. The lily is common in many different folklore traditions. It is the sacred flower of motherhood ...
A Closer Look at
... C. Roots anchor the plant, absorb water and minerals from the soil, and transport these materials to the stem. Some plants also store food in their roots. Each root has root hairs, tiny extensions of epidermal cells that increase surface area for water absorption. *Water is absorbed into the plant b ...
... C. Roots anchor the plant, absorb water and minerals from the soil, and transport these materials to the stem. Some plants also store food in their roots. Each root has root hairs, tiny extensions of epidermal cells that increase surface area for water absorption. *Water is absorbed into the plant b ...
Plantae: Divisions 1. Mosses and liverworts :Division Bryophyte
... Plantae: Divisions 1. Mosses and liverworts :Division Bryophyte (bryophytes) -No vascular tissue and therefore no roots or stems -restricted to moist environments because they absorb water directly through the surface of the plant Ferns and Fern Allies: 2. Division Psilophyta: Whisk Ferns Psilotum - ...
... Plantae: Divisions 1. Mosses and liverworts :Division Bryophyte (bryophytes) -No vascular tissue and therefore no roots or stems -restricted to moist environments because they absorb water directly through the surface of the plant Ferns and Fern Allies: 2. Division Psilophyta: Whisk Ferns Psilotum - ...
Kingdom Plantae The Diversity of Plants - Biology102-104
... Moss exhibiting gametophyte and sporophyte stages. ...
... Moss exhibiting gametophyte and sporophyte stages. ...
Weed fact sheet
... moisture, nutrients and light in tropical and subtropical crops. The burrs can reduce wool value and make shearing hazardous. The spines of burrs penetrate hides decreasing the value. ...
... moisture, nutrients and light in tropical and subtropical crops. The burrs can reduce wool value and make shearing hazardous. The spines of burrs penetrate hides decreasing the value. ...
Plant Identification
... and seed Stems are short-jointed Leaves are flat and spreading Leaves may be hairy or smooth Seedhead = two rows of spikelets on finger-like spikes White collar region with sparse, relatively long hairs ...
... and seed Stems are short-jointed Leaves are flat and spreading Leaves may be hairy or smooth Seedhead = two rows of spikelets on finger-like spikes White collar region with sparse, relatively long hairs ...
Kingdom Plantae
... balance between allowing for gas exchange without losing too much water. “Plant sweat” is known as transpiration. ...
... balance between allowing for gas exchange without losing too much water. “Plant sweat” is known as transpiration. ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.