Assessment of Substance Use Disorders
... activities are given up or reduced because of alcohol use. 8. Recurrent alcohol use in situations in which it is ...
... activities are given up or reduced because of alcohol use. 8. Recurrent alcohol use in situations in which it is ...
t\bnormal Practice Test
... and worrying about whether his business would still be open next week despite the fact that his business was evidencing its highest profit ever. Jim's condition would most likely be diagnosed as a. major depression b. a phobic disorder c. generalized anxiety disorder d. a minor psychotic break 33. C ...
... and worrying about whether his business would still be open next week despite the fact that his business was evidencing its highest profit ever. Jim's condition would most likely be diagnosed as a. major depression b. a phobic disorder c. generalized anxiety disorder d. a minor psychotic break 33. C ...
General adult psychiatry
... she is no longer able to continue with her job. About a month ago, she started having episodes of dizziness and palpitations, coupled with the thought that she was ‘going to die’. These ...
... she is no longer able to continue with her job. About a month ago, she started having episodes of dizziness and palpitations, coupled with the thought that she was ‘going to die’. These ...
AP PP Meyers disorders - Unit 12
... – Anxiety gene, some are predisposed to anxiety (twins reared apart have similar phobias) – Glutamate, neurotransmitter, regulated by genes; too much glutamate leads to over activity in brain’s alarm centers • The Brain – Anterior cingulate cortex that monitors actions and checks for errors, hyperac ...
... – Anxiety gene, some are predisposed to anxiety (twins reared apart have similar phobias) – Glutamate, neurotransmitter, regulated by genes; too much glutamate leads to over activity in brain’s alarm centers • The Brain – Anterior cingulate cortex that monitors actions and checks for errors, hyperac ...
MOOD DISORDERS
... occurring more days than not for at least 2 years No more than 2 months in which s/s not present No manic or depressive episode Important because of chronic nature ...
... occurring more days than not for at least 2 years No more than 2 months in which s/s not present No manic or depressive episode Important because of chronic nature ...
Prof. Millie Roqueta - ISS 1161 Chapter 15 Summary
... loss of physical function, with no apparent organic basis, usually in a single organ system. Common symptoms include loss of vision, hearing, paralysis, seizures, vomiting, and loss of feeling or function in limbs. People with conversion disorders are usually troubled by more severe ailments than pe ...
... loss of physical function, with no apparent organic basis, usually in a single organ system. Common symptoms include loss of vision, hearing, paralysis, seizures, vomiting, and loss of feeling or function in limbs. People with conversion disorders are usually troubled by more severe ailments than pe ...
Overview of Psychopathologies and Their Treatments
... like they have taken a stimulant like cocaine or amphetamine. Taking the medication makes them feel normal. ...
... like they have taken a stimulant like cocaine or amphetamine. Taking the medication makes them feel normal. ...
ppt: bipolar disorder
... Associated Impairments Etiology, Prevalence & Prognosis Treatment Best Practices for the School Psychologists ...
... Associated Impairments Etiology, Prevalence & Prognosis Treatment Best Practices for the School Psychologists ...
eating disorders in the younger child: is it really an ed?
... weight or significant loss of weight over at least 1 mo. B. The disturbance is not because of an associated gastrointestinal or other general medical condition (e.g. esophageal reflux). C. The disturbance is not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g. Rumination Disorder) or by lac ...
... weight or significant loss of weight over at least 1 mo. B. The disturbance is not because of an associated gastrointestinal or other general medical condition (e.g. esophageal reflux). C. The disturbance is not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g. Rumination Disorder) or by lac ...
Chapter009 - Wolters Kluwer Health
... Copyright © 2011 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Copyright © 2011 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
Depression Dictionary - Mood Disorders Association of Manitoba
... phenomenon similar to the female menopause, called andropause. Unlike women, men do not have a clear-cut signpost such as the cessation of menstruation to mark this transition. Both, however, are distinguished by a drop in hormone levels: estrogen in the female and testosterone in the male. The bodi ...
... phenomenon similar to the female menopause, called andropause. Unlike women, men do not have a clear-cut signpost such as the cessation of menstruation to mark this transition. Both, however, are distinguished by a drop in hormone levels: estrogen in the female and testosterone in the male. The bodi ...
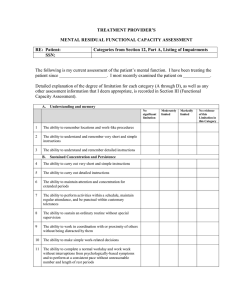
TREATMENT PROVIDER`S MENTAL RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL
... * Note: Items 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 correspond to listings 12.09A, 12.09B, 12.09C, 12.09D, 12.09E, 12.09F, 12.09G, 12.09H and 12.09I, respectively. If items 1, 2, 3 or 4 are checked, only the numbered items in subsections IIA, IIC, IIE or IIG of the form need be checked. The first block under ...
... * Note: Items 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 correspond to listings 12.09A, 12.09B, 12.09C, 12.09D, 12.09E, 12.09F, 12.09G, 12.09H and 12.09I, respectively. If items 1, 2, 3 or 4 are checked, only the numbered items in subsections IIA, IIC, IIE or IIG of the form need be checked. The first block under ...
Understanding anxiety and depression
... rituals. For example, a fear of germs and contamination can lead to constant washing of hands and clothes. ...
... rituals. For example, a fear of germs and contamination can lead to constant washing of hands and clothes. ...
Personality Disorders - Life Christian Counseling Network
... Differential Diagnosis of Obsessive-Compulsive Personality • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCPD) tends to be ego-sytonic whereas OCD is ego-dystonic and includes intrusive obsessional thoughts that result in some type of ritual/compelled behavior) • Rule out other Personality Disorders such as Nar ...
... Differential Diagnosis of Obsessive-Compulsive Personality • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCPD) tends to be ego-sytonic whereas OCD is ego-dystonic and includes intrusive obsessional thoughts that result in some type of ritual/compelled behavior) • Rule out other Personality Disorders such as Nar ...
ADHD and the DSM 5 - ADHD Awareness Month
... officially be diagnosed with ADHD. The DSM-5 has changed this; adults and teens can now be officially diagnosed with the disorder. The diagnostic criteria mentions and gives examples of how the disorder appears in adults and teens. ...
... officially be diagnosed with ADHD. The DSM-5 has changed this; adults and teens can now be officially diagnosed with the disorder. The diagnostic criteria mentions and gives examples of how the disorder appears in adults and teens. ...
DSM * 5 and Trauma Related Diagnosis
... PTSD in DSM IV Criterion C: 3 or more avoidance symptoms • Avoid thoughts, feelings, conversations about the trauma. • Avoid places or people that remind you of the trauma. • Have difficult time remembering important parts of the trauma. • A loss of interest in important, once positive, activities. ...
... PTSD in DSM IV Criterion C: 3 or more avoidance symptoms • Avoid thoughts, feelings, conversations about the trauma. • Avoid places or people that remind you of the trauma. • Have difficult time remembering important parts of the trauma. • A loss of interest in important, once positive, activities. ...
Did you know that... Psychology works for Obsessive Compulsive
... another person, or of doubting whether you acted correctly in a particular situation. Have you had an irresistible urge to do something that you know is entirely senseless, like checking the door even though you know it is locked, or washing your hands even though they are clean? Most people experie ...
... another person, or of doubting whether you acted correctly in a particular situation. Have you had an irresistible urge to do something that you know is entirely senseless, like checking the door even though you know it is locked, or washing your hands even though they are clean? Most people experie ...
Link to PowerPoint
... consist of dieting, binging, and purging. •Persons who diets and then binge eats after becoming hungry • Feels out of control while eating • Tries to “undo” binge by vomiting, laxatives, exercise or fasting •Weight may be normal to slightly below normal ...
... consist of dieting, binging, and purging. •Persons who diets and then binge eats after becoming hungry • Feels out of control while eating • Tries to “undo” binge by vomiting, laxatives, exercise or fasting •Weight may be normal to slightly below normal ...
Personality Disorders
... Differential Diagnosis of Obsessive-Compulsive Personality • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCPD) tends to be ego-sytonic whereas OCD is ego-dystonic and includes intrusive obsessional thoughts that result in some type of ritual/compelled behavior) • Rule out other Personality Disorders such as Nar ...
... Differential Diagnosis of Obsessive-Compulsive Personality • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCPD) tends to be ego-sytonic whereas OCD is ego-dystonic and includes intrusive obsessional thoughts that result in some type of ritual/compelled behavior) • Rule out other Personality Disorders such as Nar ...
Chapter 2: Psychology As a Science
... Disregards and violates the rights of others, impulsive, reckless, self-centred; linked to criminal behaviour Explanations: Modelling, operant conditioning; low serotonin activity, deficient functioning in the frontal lobes, lower arousal to stress and less anxiety Borderline personality disorde ...
... Disregards and violates the rights of others, impulsive, reckless, self-centred; linked to criminal behaviour Explanations: Modelling, operant conditioning; low serotonin activity, deficient functioning in the frontal lobes, lower arousal to stress and less anxiety Borderline personality disorde ...
Mood Stabilizers in the Treatment of Bipolar Disorder: High Yield
... ◦ Can cause a life-threatening thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, and aplastic anemia in 0.0005%. ◦ Signs of bleeding abnl +/- infx? CBC immediately! ◦ D/c if WBC < 3,000, ANC <1500, or platelets <100,000. ...
... ◦ Can cause a life-threatening thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, and aplastic anemia in 0.0005%. ◦ Signs of bleeding abnl +/- infx? CBC immediately! ◦ D/c if WBC < 3,000, ANC <1500, or platelets <100,000. ...
Mental Disorders
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder • A person with this disorder displays intense worry, fears, or anxiety most days for at least six months. ...
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder • A person with this disorder displays intense worry, fears, or anxiety most days for at least six months. ...
Schizophrenia
... • High expressed emotion in the family is associated with relapse Substance abuse (cannabis etc..) • May activate underlying vulnerability and/or increase risk of relapse ...
... • High expressed emotion in the family is associated with relapse Substance abuse (cannabis etc..) • May activate underlying vulnerability and/or increase risk of relapse ...
Negative Generalization and Symptoms of
... array of cognitive risk factors for depression, including negative generalization, or interpreting a single failure as reflecting upon one’s entire self-worth. This variable has emerged in a series of studies as a correlate and predictor of depression. Initial studies found that negative generalizat ...
... array of cognitive risk factors for depression, including negative generalization, or interpreting a single failure as reflecting upon one’s entire self-worth. This variable has emerged in a series of studies as a correlate and predictor of depression. Initial studies found that negative generalizat ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.