Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Case Presentation
... Psychostimulant medications generally have the same effect: stimulation of the central nervous system in the areas of the brain that control impulses, self-regulation of behavior, and attention. Although these medications often facilitate remarkable changes in behavior, they are not without their do ...
... Psychostimulant medications generally have the same effect: stimulation of the central nervous system in the areas of the brain that control impulses, self-regulation of behavior, and attention. Although these medications often facilitate remarkable changes in behavior, they are not without their do ...
Dissociative identity disorder.
... Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) or previously known as multiple personality disorder (Spanos, 1994), is frequently known when there is a coexistence of two or more personalities (also known as alters) that existence in one body. (webmd,2015) ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) or previously known as multiple personality disorder (Spanos, 1994), is frequently known when there is a coexistence of two or more personalities (also known as alters) that existence in one body. (webmd,2015) ...
File
... Each of the personality states that the individual experiences has its own distinct personal history, self-image, and identity, including different age, different gender, and also a different name. There usually exists a main, primary identity which carries the individual’s given name. When this pri ...
... Each of the personality states that the individual experiences has its own distinct personal history, self-image, and identity, including different age, different gender, and also a different name. There usually exists a main, primary identity which carries the individual’s given name. When this pri ...
Module 23
... continually being in a bad mood, having no interest in anything, and getting no pleasure from activities – Four of the following symptoms: problems eating, sleeping, thinking, concentrating, or making decisions; lacking energy; thinking about suicide; feeling worthless or guilty ...
... continually being in a bad mood, having no interest in anything, and getting no pleasure from activities – Four of the following symptoms: problems eating, sleeping, thinking, concentrating, or making decisions; lacking energy; thinking about suicide; feeling worthless or guilty ...
Day 7
... Often avoid social situations or endure them with great distress Generalized subtype – Social phobia across numerous social situations ...
... Often avoid social situations or endure them with great distress Generalized subtype – Social phobia across numerous social situations ...
Ciccarelli Chapter 14 - Psychological Disorders
... 1) Recognize the seriousness of the situation – Don’t fall for the myth of thinking that people who talk about suicide are not truly serious; 2) Take implied threats seriously – Some suicidal people don’t come right out and say they are planning to kill themselves; 3) Express understanding – Engag ...
... 1) Recognize the seriousness of the situation – Don’t fall for the myth of thinking that people who talk about suicide are not truly serious; 2) Take implied threats seriously – Some suicidal people don’t come right out and say they are planning to kill themselves; 3) Express understanding – Engag ...
Unit 1 Notes: Psychological Disorders
... Biochemical factors involve overreactivity or overabundance of dopamine levels in the brain The brain does not have more dopamine, rather schizophrenia patients seem to have more dopamine receptors and these may be overly sensitive Excess dopamine promotes hallucinations and delusional thinking Anti ...
... Biochemical factors involve overreactivity or overabundance of dopamine levels in the brain The brain does not have more dopamine, rather schizophrenia patients seem to have more dopamine receptors and these may be overly sensitive Excess dopamine promotes hallucinations and delusional thinking Anti ...
An Overview of the DSM-5 - Chapman University Digital Commons
... Mental Illness as Defined -- DSM-5 “A mental illness is a condition characterized by dysfunction in thought, mood or behaviors which cause distress – The condition should not be a result of social deviance or conflict with society” ...
... Mental Illness as Defined -- DSM-5 “A mental illness is a condition characterized by dysfunction in thought, mood or behaviors which cause distress – The condition should not be a result of social deviance or conflict with society” ...
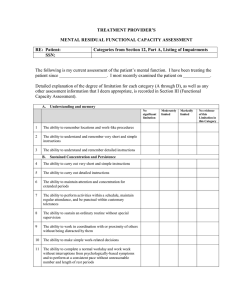
TREATMENT PROVIDER`S MENTAL RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL
... 1. Mental incapacity evidenced by dependence upon others for personal needs (e.g., toileting, eating, dressing, or bathing) and inability to follow instructions such that the use of standardized measures of intellectual functioning is precluded* 2. A valid verbal, performance, or full scale IQ of 59 ...
... 1. Mental incapacity evidenced by dependence upon others for personal needs (e.g., toileting, eating, dressing, or bathing) and inability to follow instructions such that the use of standardized measures of intellectual functioning is precluded* 2. A valid verbal, performance, or full scale IQ of 59 ...
SPED and Psychology Terms
... notice that their infant doesn’t cuddle or want to be held and may even cry when touched or may appear excessively agitated and cry for a large portion of his/her waking hours. As time passes, the child appears to withdraw into his/her own world and usually doesn’t develop language skills at a norma ...
... notice that their infant doesn’t cuddle or want to be held and may even cry when touched or may appear excessively agitated and cry for a large portion of his/her waking hours. As time passes, the child appears to withdraw into his/her own world and usually doesn’t develop language skills at a norma ...
Psychobabble 101: Mental Health Professions, Diagnoses, Terminology, and Methods April 17, 2007
... Characterized by a stable, enduring pattern of behavior that deviates from the expectations of a person’s culture, is pervasive and inflexible, has an onset in adolescence or early adulthood, and causes distress or impairment ...
... Characterized by a stable, enduring pattern of behavior that deviates from the expectations of a person’s culture, is pervasive and inflexible, has an onset in adolescence or early adulthood, and causes distress or impairment ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... Research indicates that in the United States there are more prison inmates with severe mental disorders than there are psychiatric inpatients in all the country's hospitals. True ...
... Research indicates that in the United States there are more prison inmates with severe mental disorders than there are psychiatric inpatients in all the country's hospitals. True ...
Dyslexia and Learning Disorders
... presented themselves prior to age seven. They should be present for greater than six months, causing mal-adaptation. They should also be presenting in more than one setting (i.e. home, and school). Symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity are listed in table # 2. Squirming with fidgeting, running a ...
... presented themselves prior to age seven. They should be present for greater than six months, causing mal-adaptation. They should also be presenting in more than one setting (i.e. home, and school). Symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity are listed in table # 2. Squirming with fidgeting, running a ...
Defining Psychological Disorders
... – a developmental behavior disorder characterized by problems with focus, difficulty maintaining attention, and inability to concentrate, in which symptoms start before 7 years of age ADHD can persist in adulthood, and up to 7% of college students are diagnosed with it. In adults the symptoms of ADH ...
... – a developmental behavior disorder characterized by problems with focus, difficulty maintaining attention, and inability to concentrate, in which symptoms start before 7 years of age ADHD can persist in adulthood, and up to 7% of college students are diagnosed with it. In adults the symptoms of ADH ...
Panic Disorders
... misperceptions of underlying causes) on the one hand and physiological reactions on the other. Perceiving these bodily sensations as dire threats induces anxiety, which is accompanied by activation of the sympathetic nervous system. The changes in bodily sensations that trigger a panic attack may re ...
... misperceptions of underlying causes) on the one hand and physiological reactions on the other. Perceiving these bodily sensations as dire threats induces anxiety, which is accompanied by activation of the sympathetic nervous system. The changes in bodily sensations that trigger a panic attack may re ...
Sample Student Informative Speech Outline
... a) They give too much attention to trivial things, which makes their normal routines difficult to follow. b) For example, some people affected by OCPD feel the need to be obsessively clean and organized. c) While many are indeed clean and orderly; even those who aren’t feel the need to set up system ...
... a) They give too much attention to trivial things, which makes their normal routines difficult to follow. b) For example, some people affected by OCPD feel the need to be obsessively clean and organized. c) While many are indeed clean and orderly; even those who aren’t feel the need to set up system ...
- Colorado Respite Coalition
... Hyperarousal symptoms are usually constant, instead of being triggered by things that remind one of the traumatic event. They can make the person feel stressed and angry. These symptoms may make it hard to do daily tasks, such as sleeping, eating, or concentrating. It is normal to experience these s ...
... Hyperarousal symptoms are usually constant, instead of being triggered by things that remind one of the traumatic event. They can make the person feel stressed and angry. These symptoms may make it hard to do daily tasks, such as sleeping, eating, or concentrating. It is normal to experience these s ...
PERSONALITY DISORDER
... B. The individual is at least age 18 years. C. There is evidence of conduct disorder with onset before age 15 years. D. The occurrence of antisocial behavior is not exclusively during the course of schizophrenia or a manic episode. Narcissistic Personality Disorder: The hallmarks of narcissistic per ...
... B. The individual is at least age 18 years. C. There is evidence of conduct disorder with onset before age 15 years. D. The occurrence of antisocial behavior is not exclusively during the course of schizophrenia or a manic episode. Narcissistic Personality Disorder: The hallmarks of narcissistic per ...
Chapter 18—Psychological Disorders
... two-chair dental office, installing 20 booths so that he could simultaneously attend to 20 patients. That same day he drew up plans for this arrangement, telephoned a number of remodelers, and invited bids for the work. Later that day, impatient to get rolling on his remodeling, he rolled up his sle ...
... two-chair dental office, installing 20 booths so that he could simultaneously attend to 20 patients. That same day he drew up plans for this arrangement, telephoned a number of remodelers, and invited bids for the work. Later that day, impatient to get rolling on his remodeling, he rolled up his sle ...
psychotic disorders
... Schizoaffective disorder: People with this illness have symptoms of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder such as depression or bi-polar disorder. Brief psychotic disorder: People with this illness experience a sudden but short onset of psychotic behaviour that is often linked to a stressful ev ...
... Schizoaffective disorder: People with this illness have symptoms of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder such as depression or bi-polar disorder. Brief psychotic disorder: People with this illness experience a sudden but short onset of psychotic behaviour that is often linked to a stressful ev ...
update on the etiology and treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar
... Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are two debilitating mental health disorders, both of which manifest early in adulthood and are associated with severe impairment as well as increased suicide risk. In addition, factors affecting disease severity, such as substance abuse, are often prevalent in the ...
... Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are two debilitating mental health disorders, both of which manifest early in adulthood and are associated with severe impairment as well as increased suicide risk. In addition, factors affecting disease severity, such as substance abuse, are often prevalent in the ...
Chapter 18 - PsychChapter18Psych
... having an addiction. For example, just because Sara smoked weed a few times doesn't mean that she has an addiction, but it does mean that she's abusing a drug — and that could lead to an ...
... having an addiction. For example, just because Sara smoked weed a few times doesn't mean that she has an addiction, but it does mean that she's abusing a drug — and that could lead to an ...
Abnormal Quiz Overivew
... 45. In obsessive-compulsive disorder the obsessive thoughts ________, and the compulsive behaviors are performed to ________. A) increase anxiety; reduce it B) decrease anxiety; reduce it C) trigger panic attacks; decrease anxiety D) trigger panic attacks; increase anxiety ...
... 45. In obsessive-compulsive disorder the obsessive thoughts ________, and the compulsive behaviors are performed to ________. A) increase anxiety; reduce it B) decrease anxiety; reduce it C) trigger panic attacks; decrease anxiety D) trigger panic attacks; increase anxiety ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.