Ch. 5
... • Severe, persistent, and unreasonable fears of social or performance situations in which embarrassment may occur • Behavioral treatments – ______________________________ – social skills & __________________ • Cognitive therapies ...
... • Severe, persistent, and unreasonable fears of social or performance situations in which embarrassment may occur • Behavioral treatments – ______________________________ – social skills & __________________ • Cognitive therapies ...
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
... • Severe, persistent, and unreasonable fears of social or performance situations in which embarrassment may occur • Behavioral treatments – ______________________________ – social skills & __________________ • Cognitive therapies ...
... • Severe, persistent, and unreasonable fears of social or performance situations in which embarrassment may occur • Behavioral treatments – ______________________________ – social skills & __________________ • Cognitive therapies ...
Slide 1
... COMPULSIONS – acts that are irresistible and carried out in a repetitive or ritualistic manner ...
... COMPULSIONS – acts that are irresistible and carried out in a repetitive or ritualistic manner ...
Anxiety, anxiety disorders, somatoform disorders
... Panic disorder, Agoraphobia • lifetime prevalence: 1.5-5% • Panic attacks (20-30 minutes - extreme fear, fear of dying, palpitations, sweating, trembling, short of breath, chest pain, nausea, dizziness, etc. ) • Anticipatory anxiety • Agoraphobia: fear of being alone in public places ...
... Panic disorder, Agoraphobia • lifetime prevalence: 1.5-5% • Panic attacks (20-30 minutes - extreme fear, fear of dying, palpitations, sweating, trembling, short of breath, chest pain, nausea, dizziness, etc. ) • Anticipatory anxiety • Agoraphobia: fear of being alone in public places ...
Mental Disorder Notes File
... Psychiatrist: Medical doctor that diagnoses and treats mental disorders. Can treat and prescribe medication. Neurologist: a doctor that treats organic disorders of the brain and nervous system. (Alzheimer’s ,ADD, tumor). Clinical Psychologist: treats abnormal behavior. Can’t prescribe medication, bu ...
... Psychiatrist: Medical doctor that diagnoses and treats mental disorders. Can treat and prescribe medication. Neurologist: a doctor that treats organic disorders of the brain and nervous system. (Alzheimer’s ,ADD, tumor). Clinical Psychologist: treats abnormal behavior. Can’t prescribe medication, bu ...
The DSM-V
... disorders and problems. Anxiety isn’t limited to anxiety disorders. • Somatoform disorders are physical symptoms with psychological origins. • Hypochondriasis is a preoccupation that you have a serious physical disease despite no evidence. ...
... disorders and problems. Anxiety isn’t limited to anxiety disorders. • Somatoform disorders are physical symptoms with psychological origins. • Hypochondriasis is a preoccupation that you have a serious physical disease despite no evidence. ...
SYSTEMATIC ASSESSMENT OF CO
... important to try to distinguish generalized anxiety from situational anxiety in response to having ADHD. Individuals with ADHD may become anxious as they repeatedly encounter frustration, failure and peer rejection, and this situational anxiety is likely to improve with successful management of thei ...
... important to try to distinguish generalized anxiety from situational anxiety in response to having ADHD. Individuals with ADHD may become anxious as they repeatedly encounter frustration, failure and peer rejection, and this situational anxiety is likely to improve with successful management of thei ...
Anxiety Disorder
... • OCD is not usually curable, but it is highly treatable, in that effective treatment can greatly reduce the occurrence of obsessive thoughts and compulsive rituals. • A combination of behavior therapy and medication seems to offer the best long-term improvement. ...
... • OCD is not usually curable, but it is highly treatable, in that effective treatment can greatly reduce the occurrence of obsessive thoughts and compulsive rituals. • A combination of behavior therapy and medication seems to offer the best long-term improvement. ...
Appendix 2
... over a long period that the individual’s health and life are threatened. It is different from dieting, or deliberate starvation, in that the sufferer usually thinks their diet is adequate, and often has a very distorted image of what they look like, i.e. their body weight falls to a level where thei ...
... over a long period that the individual’s health and life are threatened. It is different from dieting, or deliberate starvation, in that the sufferer usually thinks their diet is adequate, and often has a very distorted image of what they look like, i.e. their body weight falls to a level where thei ...
DisordersMultipleChoice - Homework due date to be
... c. statistical conformity d. diagnostic validity 5. _____ Anxiety disorders are characterized by all of the following symptoms except a. panic attacks b. free-floating anxiety c. worry d. hallucinations 6. _____ A man breaks out in a cold sweat when he sees the color orange and takes great pains to ...
... c. statistical conformity d. diagnostic validity 5. _____ Anxiety disorders are characterized by all of the following symptoms except a. panic attacks b. free-floating anxiety c. worry d. hallucinations 6. _____ A man breaks out in a cold sweat when he sees the color orange and takes great pains to ...
psych mod 22 terms
... Labeling: identifying and naming differences among individuals, the label, which places individuals into specific categories, may have either positive or negative associations. Generalized anxiety disorder: characterized by excessive or unrealistic worry about almost everything or feeling that somet ...
... Labeling: identifying and naming differences among individuals, the label, which places individuals into specific categories, may have either positive or negative associations. Generalized anxiety disorder: characterized by excessive or unrealistic worry about almost everything or feeling that somet ...
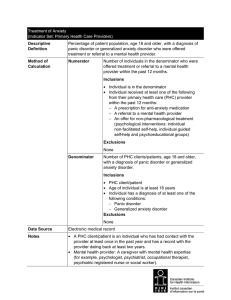
Treatment of Anxiety
... • A high rate for this indicator can be interpreted as a positive result. ...
... • A high rate for this indicator can be interpreted as a positive result. ...
Anxiety Disorders
... • In extreme cases, inability to leave house or even room • Begins after a panic attack, but can continue ...
... • In extreme cases, inability to leave house or even room • Begins after a panic attack, but can continue ...
Abnormal Psychology Overview
... Men and women were found to have an equal chance of developing a mental disorder although women suffered proportionately more from depression and men from antisocial personality. ...
... Men and women were found to have an equal chance of developing a mental disorder although women suffered proportionately more from depression and men from antisocial personality. ...
File - Pharmacology (HOME)
... In OCD and PTSD changes in amygdala Increase in lactic acid levels in some people before a panic attack Involves changes in 5HT, Gaba, Glutamate, Norepi, and Cortisol Cortisol balance: o Hypocortisolism: depression, motivation problems o Hypercortisolism: OCD, panic disorders, atrophy of the ...
... In OCD and PTSD changes in amygdala Increase in lactic acid levels in some people before a panic attack Involves changes in 5HT, Gaba, Glutamate, Norepi, and Cortisol Cortisol balance: o Hypocortisolism: depression, motivation problems o Hypercortisolism: OCD, panic disorders, atrophy of the ...
Depression and Mental Disorders PP
... adjust to change, or to get along with others. Some causes of mental disorders: Physical factors Heredity Early Experiences Recent Experiences ...
... adjust to change, or to get along with others. Some causes of mental disorders: Physical factors Heredity Early Experiences Recent Experiences ...
No Slide Title
... Relapse and avoidance SSRIs Preferred drugs Relapse rates are high following medication discontinuation Psychological and Combined Treatments Cognitive-behavior therapies seem highly effective Panic Control Treatment Graded Exposure plus Coping Skills Combined treatments do well in ...
... Relapse and avoidance SSRIs Preferred drugs Relapse rates are high following medication discontinuation Psychological and Combined Treatments Cognitive-behavior therapies seem highly effective Panic Control Treatment Graded Exposure plus Coping Skills Combined treatments do well in ...
Anxiety Disorders - Home
... – Affects about 2.7% (in a year) & 4.7% (in a lifetime) of the general population – Onset is often acute, median between 20 and 24 years of age – 75% of individuals with agoraphobia are female • Causes of panic disorder - Combination of psychological, biological, & social ...
... – Affects about 2.7% (in a year) & 4.7% (in a lifetime) of the general population – Onset is often acute, median between 20 and 24 years of age – 75% of individuals with agoraphobia are female • Causes of panic disorder - Combination of psychological, biological, & social ...
Mental Illness pwrpt
... • Anxiety can be constant over a long time or it may occur in short bursts ...
... • Anxiety can be constant over a long time or it may occur in short bursts ...
PSY 111 Practice Quiz Psychological Disorders Answers will be
... (6) Describe the medical model of psychological disorders. The medical model suggests that disorders can be cured like a disease. This idea is tied to the discovery of underlying biological causes for many disorders and the description of symptoms for the disorders. ...
... (6) Describe the medical model of psychological disorders. The medical model suggests that disorders can be cured like a disease. This idea is tied to the discovery of underlying biological causes for many disorders and the description of symptoms for the disorders. ...
Mutts and Manic Man-eating Moggies
... Can the animal learn to be good? NO YES How is the behaviour best managed? Does the pet need to be calmed with pheromones, homeopathics or ...
... Can the animal learn to be good? NO YES How is the behaviour best managed? Does the pet need to be calmed with pheromones, homeopathics or ...
Jeopardy - Stritch School of Medicine
... Fear that help may not be available or escape may be difficult in situations such as using public transportation, being in an open or enclosed space, standing in line, or being in a crowd is this ...
... Fear that help may not be available or escape may be difficult in situations such as using public transportation, being in an open or enclosed space, standing in line, or being in a crowd is this ...
Document
... Acute Stress disorder occurs within one month of event, while PTSD requires at least one month of symptoms. Thus, PTSD cannot be diagnosed within one month of traumatic event, but should be considered if symptoms persist beyond one month. ...
... Acute Stress disorder occurs within one month of event, while PTSD requires at least one month of symptoms. Thus, PTSD cannot be diagnosed within one month of traumatic event, but should be considered if symptoms persist beyond one month. ...
Panic Disorder - Montville.net
... numbness of extremities, accompanied by an inexplicable terror, usually of a physical disaster such as death. ...
... numbness of extremities, accompanied by an inexplicable terror, usually of a physical disaster such as death. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... to adopt socially adaptive personality traits. e.g., psychosis, multiple personality disorder 4. Schizophrenia ...
... to adopt socially adaptive personality traits. e.g., psychosis, multiple personality disorder 4. Schizophrenia ...
Anxiety disorder

Anxiety disorders are a category of mental disorders characterized by feelings of anxiety and fear, where anxiety is a worry about future events and fear is a reaction to current events. These feelings may cause physical symptoms, such as a racing heart and shakiness. There are a number of anxiety disorders: including generalized anxiety disorder, a specific phobia, social anxiety disorder, separation anxiety disorder, agoraphobia, and panic disorder among others. While each has its own characteristics and symptoms, they all include symptoms of anxiety.Anxiety disorders are partly genetic but may also be due to drug use including alcohol and caffeine, as well as withdrawal from certain drugs. They often occur with other mental disorders, particularly major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, certain personality disorders, and eating disorders. The term anxiety covers four aspects of experiences that an individual may have: mental apprehension, physical tension, physical symptoms and dissociative anxiety. The emotions present in anxiety disorders range from simple nervousness to bouts of terror. There are other psychiatric and medical problems that may mimic the symptoms of an anxiety disorder, such as hyperthyroidism.Common treatment options include lifestyle changes, therapy, and medications. Medications are typically recommended only if other measures are not effective. Anxiety disorders occur about twice as often in females as males, and generally begin during childhood. As many as 18% of Americans and 14% of Europeans may be affected by one or more anxiety disorders.