Lecture 10
... A system [also called a closed system] is a quantity of matter of fixed identity. No mass can cross a system boundary. A control volume [also called an open system] is a region in space chosen for study. Mass can cross a control surface (the surface of the control volume). The fundamental cons ...
... A system [also called a closed system] is a quantity of matter of fixed identity. No mass can cross a system boundary. A control volume [also called an open system] is a region in space chosen for study. Mass can cross a control surface (the surface of the control volume). The fundamental cons ...
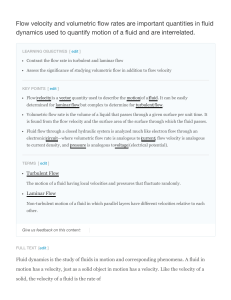
Flow velocity and volumetric flow rates are important quantities in
... thus hard to predict; it must be analyzed on a system per system basis. In the case of Laminar flow, however, fluid flow is much simpler and flow velocity can be accurately calculated using ...
... thus hard to predict; it must be analyzed on a system per system basis. In the case of Laminar flow, however, fluid flow is much simpler and flow velocity can be accurately calculated using ...
Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
... (c) For each y in 0 < y ≤ K, show that dy/dt as given by the Gompertz equation is never less than dy/dt as given by the logistic equation. 17. (a) Solve the Gompertz equation dy/dt = ry ln(K/y), subject to the initial condition y(0) = y0 . Hint: You may wish to let u = ln(y/K). (b) For the data give ...
... (c) For each y in 0 < y ≤ K, show that dy/dt as given by the Gompertz equation is never less than dy/dt as given by the logistic equation. 17. (a) Solve the Gompertz equation dy/dt = ry ln(K/y), subject to the initial condition y(0) = y0 . Hint: You may wish to let u = ln(y/K). (b) For the data give ...
Divide both sides by 8 to undo the multiplication
... California Standards AF1.1 Write and solve one-step linear equations in one variable. ...
... California Standards AF1.1 Write and solve one-step linear equations in one variable. ...
The No-Slip Boundary Condition in Fluid Mechanics
... that flow velocity in the channel is sufficiently small. This is a brave conclusion in spite of the cautious qualification. It is quite possible he was influenced by the model of a rolling ball (see Box 1 in Part 1) which may roll without slipping at low velocities but may slip at higher velocities. ...
... that flow velocity in the channel is sufficiently small. This is a brave conclusion in spite of the cautious qualification. It is quite possible he was influenced by the model of a rolling ball (see Box 1 in Part 1) which may roll without slipping at low velocities but may slip at higher velocities. ...
Biosketch of Peter Read (April 2017)
... between global eigenstates that may be stimulated by interactions with the diurnal cycle and thermal tide. This line of work has demonstrated clearly ways in which the circulation and climate of Mars differs from that of the Earth. Recent work within the group has explored possible applications of a ...
... between global eigenstates that may be stimulated by interactions with the diurnal cycle and thermal tide. This line of work has demonstrated clearly ways in which the circulation and climate of Mars differs from that of the Earth. Recent work within the group has explored possible applications of a ...
Resume Wizard - COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
... 5. Rabia Azia (2011) Similarity Transformation s for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations 6. Javeria Ahmed (2011) A Stagnation Point Flow of a Second Grade Fluid with Suction 7. Maria Munir (2011) Unsteady Flows Due to Non-Coaxial Rotations of a Disk and a Fluid at Infinity. 8. Humayoun Shahid ( ...
... 5. Rabia Azia (2011) Similarity Transformation s for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations 6. Javeria Ahmed (2011) A Stagnation Point Flow of a Second Grade Fluid with Suction 7. Maria Munir (2011) Unsteady Flows Due to Non-Coaxial Rotations of a Disk and a Fluid at Infinity. 8. Humayoun Shahid ( ...
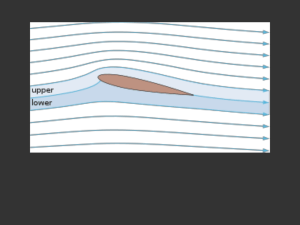
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.