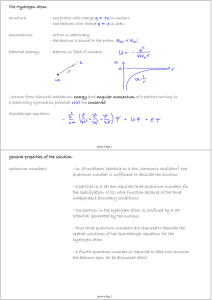
general properties of the solution: quantum numbers:
... - the quantization axis can be determined by an external magnetic field B pointing in the z-direction for example - ml can take 2 l + 1 different values from -l, …, 0, …, l - note that Lz is never equal to L and therefore can never be pointing in the direction of the quantization axis - physical int ...
... - the quantization axis can be determined by an external magnetic field B pointing in the z-direction for example - ml can take 2 l + 1 different values from -l, …, 0, …, l - note that Lz is never equal to L and therefore can never be pointing in the direction of the quantization axis - physical int ...
Strings in the Quantum World. - Queen Mary University of London
... annihilation operators for electrons, positrons and photons. At the same time this new language captures thewave properties of electrons, photons. ...
... annihilation operators for electrons, positrons and photons. At the same time this new language captures thewave properties of electrons, photons. ...
4. One mole of a monatomic ideal gas initially at temperature 0 T
... a. (20) Show using conservation of energy and momentum that it is not possible for a free electron moving through vacuum to emit a photon. b. (20) Now consider the related problem of an electron moving through superfluid helium. Show that in this case the electron can emit a phonon as long as it mov ...
... a. (20) Show using conservation of energy and momentum that it is not possible for a free electron moving through vacuum to emit a photon. b. (20) Now consider the related problem of an electron moving through superfluid helium. Show that in this case the electron can emit a phonon as long as it mov ...
Spacetime structures of continuous
... for our understanding of physics. In quantum mechanics, next to the harmonic oscillator, the particle in a box provides much insight into the quantum world 共e.g. 关1兴兲. Recently, the problem of a quantum mechanical particle initially characterized by a Gaussian wave packet and moving in an infinite b ...
... for our understanding of physics. In quantum mechanics, next to the harmonic oscillator, the particle in a box provides much insight into the quantum world 共e.g. 关1兴兲. Recently, the problem of a quantum mechanical particle initially characterized by a Gaussian wave packet and moving in an infinite b ...
Many problems that take long time to solve on a deterministic Turing
... To a PTM a state has multiple legitimate successors states available The choice of which state is the one ultimately determined by the outcome of a random choice Models are certainly fine as mathematical abstractions but are they consistent with known physics? ...
... To a PTM a state has multiple legitimate successors states available The choice of which state is the one ultimately determined by the outcome of a random choice Models are certainly fine as mathematical abstractions but are they consistent with known physics? ...
PX408: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
... Q15 At what energies/lengths are the following relativistic: (i) photons; (ii) electrons; (iii) protons? Q16 If light can be treated as particles, why don’t these particles collide when two beams of light are shone at each other? Q17 Using a non-relativistic approximation, estimate the threshold Z f ...
... Q15 At what energies/lengths are the following relativistic: (i) photons; (ii) electrons; (iii) protons? Q16 If light can be treated as particles, why don’t these particles collide when two beams of light are shone at each other? Q17 Using a non-relativistic approximation, estimate the threshold Z f ...
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... MODEL OF THE ATOM ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IS THE CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM? ...
... MODEL OF THE ATOM ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IS THE CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM? ...
QUANTUM DOTS
... In the case of the high barrier potential the tunnelling is forbidden between dots (no evolution in time). In the low barrier potential spins will be subject to a transient Heisenberg coupling (Hubbard model). The equation obtained with this model gives a good description of a quantum dot system if ...
... In the case of the high barrier potential the tunnelling is forbidden between dots (no evolution in time). In the low barrier potential spins will be subject to a transient Heisenberg coupling (Hubbard model). The equation obtained with this model gives a good description of a quantum dot system if ...
Quantum Computing
... As computers get smaller and smaller, limitations in the hardware restrict our ability to build faster and faster solid state computers. Quantum computers are an attempt to design more powerful computers using the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum computers rely on quantum entanglement and qu ...
... As computers get smaller and smaller, limitations in the hardware restrict our ability to build faster and faster solid state computers. Quantum computers are an attempt to design more powerful computers using the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum computers rely on quantum entanglement and qu ...
PHOTON AS A QUANTUM PARTICLE ∗
... molecule, and in such a way that the momentum is directed along the direction of propagation of the ray if the energy is absorbed, and directed in the opposite direction, if the energy is emitted.” Compton was probably unaware of the Einstein paper. As a matter of fact, he does not refer to any theo ...
... molecule, and in such a way that the momentum is directed along the direction of propagation of the ray if the energy is absorbed, and directed in the opposite direction, if the energy is emitted.” Compton was probably unaware of the Einstein paper. As a matter of fact, he does not refer to any theo ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... the spin of one electron in an orbital is “clockwise”, what is the spin of the other electron in that orbital? What is the approximate energy of a photon having a frequency of 4 x 107 Hz? (h = 6.6 x 10-34 J . s) Which of the following would be most stable: a) 4d55s1, or b) 4d45s2 ...
... the spin of one electron in an orbital is “clockwise”, what is the spin of the other electron in that orbital? What is the approximate energy of a photon having a frequency of 4 x 107 Hz? (h = 6.6 x 10-34 J . s) Which of the following would be most stable: a) 4d55s1, or b) 4d45s2 ...
The statistical interpretation of quantum mechanics
... in the limiting case where the numbers of the stationary states, the so-called quantum numbers, are very large (that is to say, far to the right and to the lower part in the above array) and the energy changes relatively little from place to place, in fact practically continuously. Theoretical physi ...
... in the limiting case where the numbers of the stationary states, the so-called quantum numbers, are very large (that is to say, far to the right and to the lower part in the above array) and the energy changes relatively little from place to place, in fact practically continuously. Theoretical physi ...
Modern Physics 342
... It was believed that different atoms in the ground states have all their electrons dropped down in the 1s state. This means they all must have the same physical properties. This is not the case, in fact. A conclusion was drawn by Pauli that states that: No two electrons in a single atom can have the ...
... It was believed that different atoms in the ground states have all their electrons dropped down in the 1s state. This means they all must have the same physical properties. This is not the case, in fact. A conclusion was drawn by Pauli that states that: No two electrons in a single atom can have the ...
The Dual Nature of the Electron
... Contrary to Feynman’s conjecture, the experimental results of the double-slit interferometer experiment can be explained in a classical way. The electron is a classical electromagnetic object, not a quantum object. Gauss’s classical law of electric fields recognizes that the distribution of charge i ...
... Contrary to Feynman’s conjecture, the experimental results of the double-slit interferometer experiment can be explained in a classical way. The electron is a classical electromagnetic object, not a quantum object. Gauss’s classical law of electric fields recognizes that the distribution of charge i ...
review
... impossible, as it violated the local realist view of causality (Einstein referred to it as "spooky action at a distance"),[4] and argued that the accepted formulation of quantum mechanics must therefore be incomplete. Later, however, the counterintuitive predictions of quantum mechanics were verifie ...
... impossible, as it violated the local realist view of causality (Einstein referred to it as "spooky action at a distance"),[4] and argued that the accepted formulation of quantum mechanics must therefore be incomplete. Later, however, the counterintuitive predictions of quantum mechanics were verifie ...
Electric Field Control of Magnetic Coupling in a Double Quantum
... Kittel–Kasuya–Yosida (RKKY) interaction and voltage operated double-exchange (DE) interaction. We point out that switching off magnetic interaction by an electric field induces parasitic instantaneous electric dipoles. We prove that the dissipation of the energy during logic operations due to these ...
... Kittel–Kasuya–Yosida (RKKY) interaction and voltage operated double-exchange (DE) interaction. We point out that switching off magnetic interaction by an electric field induces parasitic instantaneous electric dipoles. We prove that the dissipation of the energy during logic operations due to these ...
The true nature of the atom?
... emitting energy like radio signals; & • As energy is emitted it is lost, and the electron would spiral in and crash. ...
... emitting energy like radio signals; & • As energy is emitted it is lost, and the electron would spiral in and crash. ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.