Distributed measurement-based quantum computation
... a formal language for distributed quantum computation is lacking. While some endeavors have been made into using techniques from classical process calculi [LJ04, GN04], these have remained rather descriptive and are, to our opinion, not very well-suited to really get a grip on the low-level quantum ...
... a formal language for distributed quantum computation is lacking. While some endeavors have been made into using techniques from classical process calculi [LJ04, GN04], these have remained rather descriptive and are, to our opinion, not very well-suited to really get a grip on the low-level quantum ...
Sections 4 - Columbia Physics
... 5. In this problem, please measure energies in M eV (mega-electron volts), velocities in units of the speed of light c and rest mass in units of M eV /c2 . Consider a collision between two particles, each of rest mass m = 0.5M eV /c2 . In this problem you are asked to compare two reference frames: ...
... 5. In this problem, please measure energies in M eV (mega-electron volts), velocities in units of the speed of light c and rest mass in units of M eV /c2 . Consider a collision between two particles, each of rest mass m = 0.5M eV /c2 . In this problem you are asked to compare two reference frames: ...
Chapter 8 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Electron Configurations and
... This chapter deals with atoms that have more than one electron … we will look at the ways in which electrons are arranged in the rest of the elements and introduce the concept of an orbital energy diagram. These diagrams show the electron occupancy of energy levels for shells, subshells and orbitals ...
... This chapter deals with atoms that have more than one electron … we will look at the ways in which electrons are arranged in the rest of the elements and introduce the concept of an orbital energy diagram. These diagrams show the electron occupancy of energy levels for shells, subshells and orbitals ...
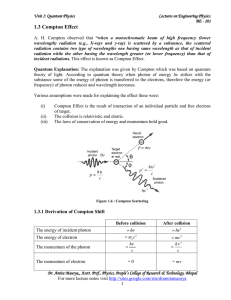
1.3 Compton Effect - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... A. H. Compton observed that “when a monochromatic beam of high frequency (lower wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wav ...
... A. H. Compton observed that “when a monochromatic beam of high frequency (lower wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wav ...
Document
... Radial part of hydrogen wave function Rnl(r) Radial part of the wave function for n=1, n=2, n=3. x-axis is in units of the Bohr radius aB. Number of radial nodes (R(r) crosses x-axis or |R(r)|2 goes to 0) is equal to n−ℓ-1 Quantum number m has no affect on the radial part of the wave function. ...
... Radial part of hydrogen wave function Rnl(r) Radial part of the wave function for n=1, n=2, n=3. x-axis is in units of the Bohr radius aB. Number of radial nodes (R(r) crosses x-axis or |R(r)|2 goes to 0) is equal to n−ℓ-1 Quantum number m has no affect on the radial part of the wave function. ...
Modern IV - Wappingers Central School District
... of electrons as particles, but they also act like waves and spend part of the time inside the nucleus! Electrons act like waves that move in specific resonant frequencies. There is a “fundamental state” (ground state) that is close to the atom. As energy is added to the electron, it is added in disc ...
... of electrons as particles, but they also act like waves and spend part of the time inside the nucleus! Electrons act like waves that move in specific resonant frequencies. There is a “fundamental state” (ground state) that is close to the atom. As energy is added to the electron, it is added in disc ...
Chapter 3 de Broglie`s postulate: wavelike properties of particles
... (1) Wave and particle is made to display either face at will but not both simultaneously. Dirac’s relativistic of electron: E ofc 2radiation; p 2 m02c 4 (2) We can observequantum either themechanics wave or the particle behavior ...
... (1) Wave and particle is made to display either face at will but not both simultaneously. Dirac’s relativistic of electron: E ofc 2radiation; p 2 m02c 4 (2) We can observequantum either themechanics wave or the particle behavior ...
6 - Rutgers Physics
... α is the called the “fine-structure constant”. Notice that it is dimensionless. The fine-structure constant will show up in various places and has an important role in fundamental physics. ...
... α is the called the “fine-structure constant”. Notice that it is dimensionless. The fine-structure constant will show up in various places and has an important role in fundamental physics. ...
EXPERIMENT 2-10 ABSORPTION OF BETA AND GAMMA RAYS
... Objective: To study the behavior of gamma and beta rays passing through matter; to measure the range of beta-particles from a given source and hence to determine the endpoint energy of decay; to determine the absorption coefficient in lead of the gamma radiation from a given source. Safety Note: The ...
... Objective: To study the behavior of gamma and beta rays passing through matter; to measure the range of beta-particles from a given source and hence to determine the endpoint energy of decay; to determine the absorption coefficient in lead of the gamma radiation from a given source. Safety Note: The ...
4– Quantum Mechanical Description of NMR 4.1 Mathematical Tools∗
... Since changing the representation of an operator into matrix form should not change its properties, the commutation relations given in equation 4.28 should still be valid, i.e. ...
... Since changing the representation of an operator into matrix form should not change its properties, the commutation relations given in equation 4.28 should still be valid, i.e. ...
Learning station V: Predicting the hydrogen emission lines with a
... particles like the electron are seen as quanta of a field, a matter field. The hypothesis of De Broglie, that lives on into quantum field theory, is indeed that some kind of quantum matter field must be connected to a matter particle. Matter particles arise from this matter field. Light particles - ...
... particles like the electron are seen as quanta of a field, a matter field. The hypothesis of De Broglie, that lives on into quantum field theory, is indeed that some kind of quantum matter field must be connected to a matter particle. Matter particles arise from this matter field. Light particles - ...
1 Chem. 152 Term Symbols for Atoms with Equivalent Electrons Prof
... Equivalent electrons have the same n and l values, so the possiblity exists that they might end up with all four quantum numbers the same, which is forbidden by the Pauli Principle. In this case you have to look at all allowable combinations of ML and MS values, and from those values infer the L and ...
... Equivalent electrons have the same n and l values, so the possiblity exists that they might end up with all four quantum numbers the same, which is forbidden by the Pauli Principle. In this case you have to look at all allowable combinations of ML and MS values, and from those values infer the L and ...
Quantum telescopes
... William Herschel and his sister Caroline in the late 18th century. Its aperture diameter of 1.2 m was gigantic for the time. Accordingly, the costs greatly exceeded the initial estimates – a familiar tale in modern telescope construction. But Herschel had discovered a planet in 1781 and had called i ...
... William Herschel and his sister Caroline in the late 18th century. Its aperture diameter of 1.2 m was gigantic for the time. Accordingly, the costs greatly exceeded the initial estimates – a familiar tale in modern telescope construction. But Herschel had discovered a planet in 1781 and had called i ...
The beauty of string theory - Institute for Advanced Study
... space, it also can vibrate in the new fermionic dimensions. This new kind of vibration produces a cousin or “superpartner” for every elementary particle that has the same electric charge but differs in other properties such as spin. Supersymmetric theories make detailed predictions about how superpa ...
... space, it also can vibrate in the new fermionic dimensions. This new kind of vibration produces a cousin or “superpartner” for every elementary particle that has the same electric charge but differs in other properties such as spin. Supersymmetric theories make detailed predictions about how superpa ...
Bohmian Mechanics
... quantum mechanics, it is probably because they think that, contrary to the official doctrine, physical systems do have quantitative properties (like energy, momentum, spin, etc.) and that properly designed experiments reveal their numerical values. In that view, let us call it the naive one, the mea ...
... quantum mechanics, it is probably because they think that, contrary to the official doctrine, physical systems do have quantitative properties (like energy, momentum, spin, etc.) and that properly designed experiments reveal their numerical values. In that view, let us call it the naive one, the mea ...
p Well - Purdue Physics
... Will the boundary be total transparent to the electrons going across the pixel boundaries? ...
... Will the boundary be total transparent to the electrons going across the pixel boundaries? ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.