What is a maladaptive behavior? Are all personality disorders
... In the Categorical approach, some disorders are defined similarly to mental illnesses through the use of diagnostic criteria. Though purely clinical, this approach has its advantages; like being consistent with the approach used by psychiatrists (DSM) to describe all other mental disorders. This app ...
... In the Categorical approach, some disorders are defined similarly to mental illnesses through the use of diagnostic criteria. Though purely clinical, this approach has its advantages; like being consistent with the approach used by psychiatrists (DSM) to describe all other mental disorders. This app ...
An Overview of Mood Disorders Major Depression: An Overview
... Bipolar II Disorder: An Overview • Overview and Defining Features – Alternations between major depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes • Facts and Statistics – Average age on onset is 22 years, but can begin in childhood – Only 10 to 13% of cases progress to full bipolar I disorder – Tends to be ...
... Bipolar II Disorder: An Overview • Overview and Defining Features – Alternations between major depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes • Facts and Statistics – Average age on onset is 22 years, but can begin in childhood – Only 10 to 13% of cases progress to full bipolar I disorder – Tends to be ...
Module 22
... contribute to the development of mental disorders including deficits in cognitive processes, such as having unusual thoughts and beliefs deficits in processing emotional stimuli, such as under-or-overreacting to ...
... contribute to the development of mental disorders including deficits in cognitive processes, such as having unusual thoughts and beliefs deficits in processing emotional stimuli, such as under-or-overreacting to ...
Introduction to Psychological Disorders
... American Psychiatric Association • Lists and describes all the currently accepted categories of mental disorders ...
... American Psychiatric Association • Lists and describes all the currently accepted categories of mental disorders ...
A New Diagnosis in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... manual lists mental diseases, conditions and disorders and also lists the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... manual lists mental diseases, conditions and disorders and also lists the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
Memory
... are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions. •“BTK Killer” ...
... are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions. •“BTK Killer” ...
Psychological Disorders
... Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to stigmatize people? ...
... Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to stigmatize people? ...
depressive disorders
... Axis IV: Rates the severity of psychosocial stressors such as school or housing issues in the individual’s life during the past year Axis V: Assess the level of adaptive functioning currently and during the past year on Global Assessment of Functioning Scale (GAF) 0-100. ...
... Axis IV: Rates the severity of psychosocial stressors such as school or housing issues in the individual’s life during the past year Axis V: Assess the level of adaptive functioning currently and during the past year on Global Assessment of Functioning Scale (GAF) 0-100. ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Often attributable to a life stressor or trauma Only abnormal if the trance is considered undesirable/pathological by the culture ...
... Often attributable to a life stressor or trauma Only abnormal if the trance is considered undesirable/pathological by the culture ...
Types of Mood Disorders
... their usual activities and pursuits, have difficulty concentrating and making decisions, have pressing thoughts of death, and attempt suicide. They even show impaired driving skills in driving simulation tests (Bulmash et al., 2006). ...
... their usual activities and pursuits, have difficulty concentrating and making decisions, have pressing thoughts of death, and attempt suicide. They even show impaired driving skills in driving simulation tests (Bulmash et al., 2006). ...
somatoform disorders
... slight physical anomaly is present, the person’s concern is markedly excessive. B. The preoccupation causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. C. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g ...
... slight physical anomaly is present, the person’s concern is markedly excessive. B. The preoccupation causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. C. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g ...
Exploring 9e
... Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to stigmatize people? ...
... Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to stigmatize people? ...
DSM-5 Released: The Big Changes
... for this change: “(1) Opportunity for early detection. The earlier the better for patients with these symptoms. (2) It also encourages an early effective treatment plan, ” before dementia sets in. Other New & Notable Disorders Both binge eating disorder and premenstrual dysphoric disorder and now of ...
... for this change: “(1) Opportunity for early detection. The earlier the better for patients with these symptoms. (2) It also encourages an early effective treatment plan, ” before dementia sets in. Other New & Notable Disorders Both binge eating disorder and premenstrual dysphoric disorder and now of ...
- Bepress
... • Clinical Case Formulation – Making diagnoses requires clinical judgment, not just checking off the symptoms in the criteria. – The client’s cultural and social context must be considered. – The DSM-5 does not include all possible mental disorders. ...
... • Clinical Case Formulation – Making diagnoses requires clinical judgment, not just checking off the symptoms in the criteria. – The client’s cultural and social context must be considered. – The DSM-5 does not include all possible mental disorders. ...
Ch. 18 S. 4
... do not intentionally fake their illnesses. They honestly feel ____________ or believe they cannot move their limbs. Reliable _____________________ on the incidence of somatoform disorders are not available. Many diagnoses of somatoform illness later prove to be incorrect when patients are found to h ...
... do not intentionally fake their illnesses. They honestly feel ____________ or believe they cannot move their limbs. Reliable _____________________ on the incidence of somatoform disorders are not available. Many diagnoses of somatoform illness later prove to be incorrect when patients are found to h ...
Schizophrenia Disorder Diagnostic Tool
... catatonic behavior—a marked decrease in reactivity to the environment which reaches the extreme in catatonic stupor. Other examples are catatonic rigidity, catatonic negativism, catatonic posturing, or catatonic excitement. The clinician must be aware that catatonic symptoms are non-specific and may ...
... catatonic behavior—a marked decrease in reactivity to the environment which reaches the extreme in catatonic stupor. Other examples are catatonic rigidity, catatonic negativism, catatonic posturing, or catatonic excitement. The clinician must be aware that catatonic symptoms are non-specific and may ...
ch._9-1
... 20 percent of the U.S. population—54 million people—are affected by some form of mental disorder. Fewer than 8 million people with mental disorders actually A mental disorder is seek treatment. an illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, Of the 20 percent of children and adolescents who suf ...
... 20 percent of the U.S. population—54 million people—are affected by some form of mental disorder. Fewer than 8 million people with mental disorders actually A mental disorder is seek treatment. an illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, Of the 20 percent of children and adolescents who suf ...
Abnormal Behavior
... medically possible Somatoform pain disorders – primary symptom is pain with no physical cause ...
... medically possible Somatoform pain disorders – primary symptom is pain with no physical cause ...
Theories of personality
... (1) causes a person to suffer, is self-destructive; (2) seriously impairs the person’s ability to work or get along with others; (3) or endangers others or the community. ...
... (1) causes a person to suffer, is self-destructive; (2) seriously impairs the person’s ability to work or get along with others; (3) or endangers others or the community. ...
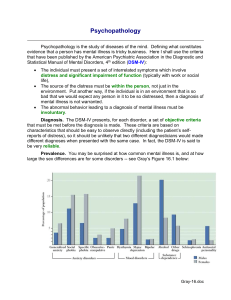
Psychopathology
... histories was written to include information that was consistent with the criteria for a diagnosis of antisocial personality, a disorder in which the individual has no sense of guilt and no respect for others’ rights. The other case history included information consistent with a diagnosis of histrio ...
... histories was written to include information that was consistent with the criteria for a diagnosis of antisocial personality, a disorder in which the individual has no sense of guilt and no respect for others’ rights. The other case history included information consistent with a diagnosis of histrio ...
What personality disorders are recognized by the DSM-IV-TR?
... 2. The enduring pattern is inflexible and pervasive across a broad range of personal and social situations. 3. The enduring pattern leads to clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. 4. The enduring pattern is stable and of long ...
... 2. The enduring pattern is inflexible and pervasive across a broad range of personal and social situations. 3. The enduring pattern leads to clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. 4. The enduring pattern is stable and of long ...
The Nervous System
... – Low compliance with drug treatment because manic phases are often pleasant for the individual – Untreated bipolar disorder is associated with suicide risk and other maladaptive behaviors ...
... – Low compliance with drug treatment because manic phases are often pleasant for the individual – Untreated bipolar disorder is associated with suicide risk and other maladaptive behaviors ...
Chapter 16 – Psychological Disorders
... anxiety on a specific object, activity, or situation. It is an irrational fear that disrupts behavior. Social phobia – an intense fear of being scrutinized by others. The anxious person may avoid speaking up, eating out, or going to parties or will sweat and tremble when doing so. Obsessive Compulsi ...
... anxiety on a specific object, activity, or situation. It is an irrational fear that disrupts behavior. Social phobia – an intense fear of being scrutinized by others. The anxious person may avoid speaking up, eating out, or going to parties or will sweat and tremble when doing so. Obsessive Compulsi ...
Unit 12 Practice-No Answers
... intelligence, and quite charming. He has swindled several older people out of their life savings, and he seems to have little feeling for his victims, nor does he fear the consequences of getting caught. His behavior is evidence of a. bipolar disorder. b. schizophrenia. c. obsessive-compulsive disor ...
... intelligence, and quite charming. He has swindled several older people out of their life savings, and he seems to have little feeling for his victims, nor does he fear the consequences of getting caught. His behavior is evidence of a. bipolar disorder. b. schizophrenia. c. obsessive-compulsive disor ...
No Slide Title
... Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Either obsessions or compulsions • At some point during course of disorder, symptoms are recognized as excessive and unreasonable • Symptoms cause marked distress • If Another Axis I Disorder is present, the content of the obsessions or compulsions is not restricted ...
... Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Either obsessions or compulsions • At some point during course of disorder, symptoms are recognized as excessive and unreasonable • Symptoms cause marked distress • If Another Axis I Disorder is present, the content of the obsessions or compulsions is not restricted ...