Anxiety Disorders
... • Fear of embarrassment, and social interaction • Some people have very strong fears of being watched or evaluated by others. Do you worry that you might do or way something that would embarrass you in front of others, or that other people might think badly of you? • …what about the situation bother ...
... • Fear of embarrassment, and social interaction • Some people have very strong fears of being watched or evaluated by others. Do you worry that you might do or way something that would embarrass you in front of others, or that other people might think badly of you? • …what about the situation bother ...
Memory
... Explaining Mood Disorders Since depression is so prevalent worldwide, investigators want to develop a theory of depression that will suggest ways to treat it. Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1995) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes, including ...
... Explaining Mood Disorders Since depression is so prevalent worldwide, investigators want to develop a theory of depression that will suggest ways to treat it. Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1995) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes, including ...
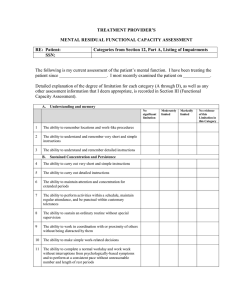
TREATMENT PROVIDER`S MENTAL RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL
... Complete this section if 12.02 (Organic Mental), 12.03 (Schizophrenic, etc.), or 12.04 (Affective) applies and the requirements in paragraph B of the appropriate listings are not satisfied. ...
... Complete this section if 12.02 (Organic Mental), 12.03 (Schizophrenic, etc.), or 12.04 (Affective) applies and the requirements in paragraph B of the appropriate listings are not satisfied. ...
Chapter 16
... the person’s current interpretation of events, or in the person’s bad habits and poor social skills. ...
... the person’s current interpretation of events, or in the person’s bad habits and poor social skills. ...
Structured Interview of Personality Organization
... from a unit specializing in personality disorders at a universitybased psychiatric hospital in the New York metropolitan area. Data from this site also include 24 outpatients being seen in clinics and private practices of clinicians associated with the same hospital. Unit staff and therapists workin ...
... from a unit specializing in personality disorders at a universitybased psychiatric hospital in the New York metropolitan area. Data from this site also include 24 outpatients being seen in clinics and private practices of clinicians associated with the same hospital. Unit staff and therapists workin ...
Mood Disorders - School District of Cambridge
... over which they have little or no control. As they acquire this feeling of helplessness, they give up and no longer try to improve their situation, because they learned in the past that efforts to improve the situation will not work. This, by itself, can produce depression. Learned helplessness may ...
... over which they have little or no control. As they acquire this feeling of helplessness, they give up and no longer try to improve their situation, because they learned in the past that efforts to improve the situation will not work. This, by itself, can produce depression. Learned helplessness may ...
Mood Disorders PPT
... over which they have little or no control. As they acquire this feeling of helplessness, they give up and no longer try to improve their situation, because they learned in the past that efforts to improve the situation will not work. This, by itself, can produce depression. Learned helplessness may ...
... over which they have little or no control. As they acquire this feeling of helplessness, they give up and no longer try to improve their situation, because they learned in the past that efforts to improve the situation will not work. This, by itself, can produce depression. Learned helplessness may ...
Figure 6-2 Multipath Model for Somatic Symptom Disorders
... Etiology of Dissociative Disorders (cont’d.) • Diagnosis depends on self-report, making it difficult to differentiate between genuine and faked cases • Two most influential models, post-traumatic and sociocognitive, are not sufficient to explain why only some develop disorders – Must look at vulner ...
... Etiology of Dissociative Disorders (cont’d.) • Diagnosis depends on self-report, making it difficult to differentiate between genuine and faked cases • Two most influential models, post-traumatic and sociocognitive, are not sufficient to explain why only some develop disorders – Must look at vulner ...
Psychology 373A
... Attendance: More than one unexcused absence will constitute a reduction worth 10% of the overall grade. Due to concerns about a possible flu epidemic, absences as a result of having (or recovering) from the flu with be considered excused absences. Participation: You are expected to have read the ass ...
... Attendance: More than one unexcused absence will constitute a reduction worth 10% of the overall grade. Due to concerns about a possible flu epidemic, absences as a result of having (or recovering) from the flu with be considered excused absences. Participation: You are expected to have read the ass ...
4468 ANXIETY DISORDERS - PANIC DISORDER
... c. invariably leads to agoraphobia if not treated with medications 14. The behavior portion of cognitive-behavioral therapy for panic disorder may involve: a. analyzing one’s thought process b. psychodynamic approaches c. systematic training in relaxation techniques ...
... c. invariably leads to agoraphobia if not treated with medications 14. The behavior portion of cognitive-behavioral therapy for panic disorder may involve: a. analyzing one’s thought process b. psychodynamic approaches c. systematic training in relaxation techniques ...
Personality Disorders
... who have antisocial personalities such as Bundy’s can maintain a facade of coolness and charm, but behind it lies a long-standing core of aggressiveness and deceit with no regard or empathy for the rights of others. The degree of damage associated with a personality disorder can be as severe as Bund ...
... who have antisocial personalities such as Bundy’s can maintain a facade of coolness and charm, but behind it lies a long-standing core of aggressiveness and deceit with no regard or empathy for the rights of others. The degree of damage associated with a personality disorder can be as severe as Bund ...
Mental Health and Substance Abuse
... ₋Emotional disorders ₋Pervasive developmental disorders ₋Schizophrenia ₋Separation anxiety ₋Failure to thrive ₋Growth retardation ₋Asperger’s syndrome ₋Tic disorders with specific type ...
... ₋Emotional disorders ₋Pervasive developmental disorders ₋Schizophrenia ₋Separation anxiety ₋Failure to thrive ₋Growth retardation ₋Asperger’s syndrome ₋Tic disorders with specific type ...
Coolidge Correctional Inventory (CCI)
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) published by the American Psychiatric Association. It was created (a) to be a cost-effective measure of psychological problems, (b) to be a DSM-IV-TR aligned measure of Axis I clinical syndromes and Axis II personality disorders , (c) ...
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) published by the American Psychiatric Association. It was created (a) to be a cost-effective measure of psychological problems, (b) to be a DSM-IV-TR aligned measure of Axis I clinical syndromes and Axis II personality disorders , (c) ...
Assessment and Diagnosis of DSM-5 Substance
... desire to continue use of substance to reduce unpleasant symptoms has physiological/cognitive consequences significant distress in social and occupational functioning symptoms are not attributed to another medical or mental disorder ...
... desire to continue use of substance to reduce unpleasant symptoms has physiological/cognitive consequences significant distress in social and occupational functioning symptoms are not attributed to another medical or mental disorder ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in
... disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
... disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
General diagnostic criteria for a Anxiety Disorders
... are excessive or unreasonable. Note: This does not apply to children. C. The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time consuming (take more than 1 hour a day), or significantly interfere with the person's normal routine, occupational (or academic) functioning, or usual social activit ...
... are excessive or unreasonable. Note: This does not apply to children. C. The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time consuming (take more than 1 hour a day), or significantly interfere with the person's normal routine, occupational (or academic) functioning, or usual social activit ...
Chapter 18 Section 1 Psychological Disorders
... Psychological disorders are behavior patterns or mental processes that cause serious personal suffering or interfere with a person’s ability to cope with everyday life. Many people believe that psychological disorders are uncommon, affecting relatively few individuals. It is true that the great majo ...
... Psychological disorders are behavior patterns or mental processes that cause serious personal suffering or interfere with a person’s ability to cope with everyday life. Many people believe that psychological disorders are uncommon, affecting relatively few individuals. It is true that the great majo ...
myers ap – unit 12
... – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take the user directly to the beginning of that subsection. This allows teachers quick acces ...
... – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take the user directly to the beginning of that subsection. This allows teachers quick acces ...
A Measure of Conduct Disorder for Incarcerated
... • The MACI Unrulyy scale was the onlyy significant g predictor p of conduct disorder based on K-SADS-PL ratings. • These results suggest that additional clinical attention is warranted for those individuals who endorse items on the MACI unruly scale given its item content as well as its meaningful r ...
... • The MACI Unrulyy scale was the onlyy significant g predictor p of conduct disorder based on K-SADS-PL ratings. • These results suggest that additional clinical attention is warranted for those individuals who endorse items on the MACI unruly scale given its item content as well as its meaningful r ...
Personality Disorders in Older Adults: Emerging Research Issues
... assessing adaptive personality traits among older adults in the general population, although the NEO-PI-R also seems to assess maladaptive traits [18]. Nonetheless, psychometric data of the NEO-PI-R for clinical populations of older adults are lacking. An example of an informant-report questionnaire ...
... assessing adaptive personality traits among older adults in the general population, although the NEO-PI-R also seems to assess maladaptive traits [18]. Nonetheless, psychometric data of the NEO-PI-R for clinical populations of older adults are lacking. An example of an informant-report questionnaire ...
Irritable mood and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... a variety of different categories in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). More precise diagnostic terms and concepts are needed. Methods: A concise critical historical review of DSM categories characterized by irritability, anger, and aggression is presented followed by r ...
... a variety of different categories in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). More precise diagnostic terms and concepts are needed. Methods: A concise critical historical review of DSM categories characterized by irritability, anger, and aggression is presented followed by r ...
( “Autistic Spectrum”) Disorders
... ?? A 9 year old third grade boy is brought to your office by his mother who is distraught about his report card. He is below average in reading and spelling and his teacher states that he does not complete assignments and is distractible in class. He is not a management problem at home other than w ...
... ?? A 9 year old third grade boy is brought to your office by his mother who is distraught about his report card. He is below average in reading and spelling and his teacher states that he does not complete assignments and is distractible in class. He is not a management problem at home other than w ...
Immigrants and borderline personality disorder at a psychiatric
... antecedents and less previous contact with out-patient mental health services. There were no differences between immigrant and indigenous groups with respect to substance use disorder. Hospitalisation was higher for immigrants than for the indigenous group. Immigrants were more frequently brought to ...
... antecedents and less previous contact with out-patient mental health services. There were no differences between immigrant and indigenous groups with respect to substance use disorder. Hospitalisation was higher for immigrants than for the indigenous group. Immigrants were more frequently brought to ...
DSM 5
... DSM - 5 replaces DSM IV on all the ASWB license exams on July 1, 2015. DSM - 5 is organized across the life span. Diagnoses that begin during childhood are not separated. Emphasis is on the impact on functioning. More than one diagnosis can occur at the same time. Listed here are the basic changes i ...
... DSM - 5 replaces DSM IV on all the ASWB license exams on July 1, 2015. DSM - 5 is organized across the life span. Diagnoses that begin during childhood are not separated. Emphasis is on the impact on functioning. More than one diagnosis can occur at the same time. Listed here are the basic changes i ...
Disorders of Personality
... All of the personality disorders refer to symptoms that cause problems with relationships, work, or both Personality disorders refer to enduring patterns of experience and behavior that differ greatly from the norms and expectations of a person’s culture Copyright © 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, I ...
... All of the personality disorders refer to symptoms that cause problems with relationships, work, or both Personality disorders refer to enduring patterns of experience and behavior that differ greatly from the norms and expectations of a person’s culture Copyright © 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, I ...