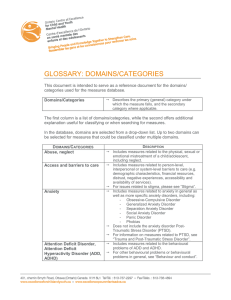
Glossary of domains/categories - Ontario Centre of Excellence for
... Includes measures relating to various aspects of parenting, including parent-child relationship, parenting efficacy and parenting style. Includes measures related to: - Antisocial personality disorder - Avoidant personality disorder - Borderline personality disorder - Dependent personality disor ...
... Includes measures relating to various aspects of parenting, including parent-child relationship, parenting efficacy and parenting style. Includes measures related to: - Antisocial personality disorder - Avoidant personality disorder - Borderline personality disorder - Dependent personality disor ...
Understanding The DSM-5 Implications for Juvenile
... substance use disorders. Individuals whose symptoms meet criteria for both disruptive mood dysregulation disorder and oppositional defiant disorder should only be given the diagnosis of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder. If an individual has ever experienced a manic or hypomanic episode, the di ...
... substance use disorders. Individuals whose symptoms meet criteria for both disruptive mood dysregulation disorder and oppositional defiant disorder should only be given the diagnosis of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder. If an individual has ever experienced a manic or hypomanic episode, the di ...
Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 8th edition
... • The impact of biological processes on these disorders can be understood through research on placebos and the placebo effect • Placebos: substances with no known medicinal value • Treatment with placebos has been shown to bring improvement to many – possibly through the power of suggestion but like ...
... • The impact of biological processes on these disorders can be understood through research on placebos and the placebo effect • Placebos: substances with no known medicinal value • Treatment with placebos has been shown to bring improvement to many – possibly through the power of suggestion but like ...
ICD - Mental and Behavioral Disorders
... F3 Mood (affective) disorders F4 Neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders F5 Behavioral syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors F6 Disorders of adult personality and behavior F7 Mental retardation F8 Disorders of psychological development F9 Behavioral and ...
... F3 Mood (affective) disorders F4 Neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders F5 Behavioral syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors F6 Disorders of adult personality and behavior F7 Mental retardation F8 Disorders of psychological development F9 Behavioral and ...
Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 8th edition
... – Personality is a unique and long-term pattern of inner experience and outward behavior – Personality tends to be consistent and is often described in terms of “traits” ...
... – Personality is a unique and long-term pattern of inner experience and outward behavior – Personality tends to be consistent and is often described in terms of “traits” ...
DMH Adult Clinical Service Authorization
... Determining Service Authorization for Children Adolescents and Adults, December 2009 (Revised December 1, 2011) ...
... Determining Service Authorization for Children Adolescents and Adults, December 2009 (Revised December 1, 2011) ...
Chapter 13 Understanding Psychological Disorders
... • How do you know if you suffer from an anxiety disorder? • Three features distinguish normal anxiety from pathological anxiety. • Pathological anxiety is: • a. irrational—it is provoked by perceived threats that are exaggerated or nonexistent, and the anxiety response is out of proportion to the ac ...
... • How do you know if you suffer from an anxiety disorder? • Three features distinguish normal anxiety from pathological anxiety. • Pathological anxiety is: • a. irrational—it is provoked by perceived threats that are exaggerated or nonexistent, and the anxiety response is out of proportion to the ac ...
13 Mood Disorders
... episodes that do not meet criteria for major depression or mania • criteria include duration of at least 2 years with recurrent periods of mild depression alternating with hypomania ...
... episodes that do not meet criteria for major depression or mania • criteria include duration of at least 2 years with recurrent periods of mild depression alternating with hypomania ...
psychological disorders.notebook
... many people do not like the DSM because it diagnoses people's problems in terms of their symptoms which says that it is a mental illness they do however still see it as a very practical tool when diagnosing and treating people with disorders health insurance companies require a DSMIV diag ...
... many people do not like the DSM because it diagnoses people's problems in terms of their symptoms which says that it is a mental illness they do however still see it as a very practical tool when diagnosing and treating people with disorders health insurance companies require a DSMIV diag ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... • Most other forms of mental disorder, such as anxiety disorders and mood disorders, are ego-dystonic; that is, people with these disorders are distressed by their symptoms and uncomfortable with their situations. • Personality disorders are usually ego-syntonic—the ideas or impulses with which they ...
... • Most other forms of mental disorder, such as anxiety disorders and mood disorders, are ego-dystonic; that is, people with these disorders are distressed by their symptoms and uncomfortable with their situations. • Personality disorders are usually ego-syntonic—the ideas or impulses with which they ...
From DSM-IV-TR to DSM-5
... From DSM-IV-TR to DSM-5: Analysis of some changes with another specification or unspecified, with diagnostic codes, with specification of severity, etc. In any case, to the contrary of what is often published, the number of diagnoses (with criteria) is slightly lower. The new DSM diagnostic classificat ...
... From DSM-IV-TR to DSM-5: Analysis of some changes with another specification or unspecified, with diagnostic codes, with specification of severity, etc. In any case, to the contrary of what is often published, the number of diagnoses (with criteria) is slightly lower. The new DSM diagnostic classificat ...
axis i - School-Based Health Alliance
... school and peers (e.g., destructive behavior, self harming behavior, severe psychosomatic complaints, compulsive behavior, obsessions, anxiety, somatic delusions, major developmental delays, refusal to attend school, withdrawal and isolation, hallucinations). ...
... school and peers (e.g., destructive behavior, self harming behavior, severe psychosomatic complaints, compulsive behavior, obsessions, anxiety, somatic delusions, major developmental delays, refusal to attend school, withdrawal and isolation, hallucinations). ...
Chapter 6
... – Removal of Chronic Specifier – Addition of Mixed Features and Catatonic Features Specifiers Major Depressive Disorder, Recurrent – Same as MDD, Single Episode Dysthymic Disorder: Renamed to Chronic Depressive Disorder Depressive Disorder NOS: Renamed Depressive Conditions Not ...
... – Removal of Chronic Specifier – Addition of Mixed Features and Catatonic Features Specifiers Major Depressive Disorder, Recurrent – Same as MDD, Single Episode Dysthymic Disorder: Renamed to Chronic Depressive Disorder Depressive Disorder NOS: Renamed Depressive Conditions Not ...
Disorders
... Gender-Identity Disorders Disorders that involve the desire to become, or the insistence that one really is, a member of the other biological sex. • gender-identity disorder in children: Rejection of one’s biological gender in childhood, along with the clothing and behavior society considers approp ...
... Gender-Identity Disorders Disorders that involve the desire to become, or the insistence that one really is, a member of the other biological sex. • gender-identity disorder in children: Rejection of one’s biological gender in childhood, along with the clothing and behavior society considers approp ...
Psychological Disorders and Therapy What are they? • Behavior
... but Bulimia was not. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder was not added until after ______________. In the original there were only 60 disorder categories while the current edition has over 400. • The DSM ONLY contains the symptoms of currently considered disorders. It does NOT discuss causes or ...
... but Bulimia was not. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder was not added until after ______________. In the original there were only 60 disorder categories while the current edition has over 400. • The DSM ONLY contains the symptoms of currently considered disorders. It does NOT discuss causes or ...
Generalized anxiety disorder
... effective for short-term management of generalized anxiety disorder and is less likely to cause dependency, but has a slower onset of action . The SNRIs venlafaxine XR and duloxetine were demonstrated efficacious, Pregabalin, a GABA analogue that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitt ...
... effective for short-term management of generalized anxiety disorder and is less likely to cause dependency, but has a slower onset of action . The SNRIs venlafaxine XR and duloxetine were demonstrated efficacious, Pregabalin, a GABA analogue that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitt ...
Lundbeck Institute Campus Slide deck library
... highest number of days away from work of any physical or mental disorder1 ...
... highest number of days away from work of any physical or mental disorder1 ...
Document
... 2. Subscription to more obvious symptoms of widely publicized disorders in the face of denial of more subtle features 3. Refusal to comply with recommended diagnostic or treatment procedures; avoidance of direct examination 4. Traits common to antisocial, narcissistic, borderline, or histrionic pers ...
... 2. Subscription to more obvious symptoms of widely publicized disorders in the face of denial of more subtle features 3. Refusal to comply with recommended diagnostic or treatment procedures; avoidance of direct examination 4. Traits common to antisocial, narcissistic, borderline, or histrionic pers ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... • Malfunction of the emotional centres (the limbic system, especially the amygdala); in combination with the malfunction of the narrative centre; reflect respectively, the high emotional loading of the content of the traumatic material, and the difficulty in accurate recall and the ability to constr ...
... • Malfunction of the emotional centres (the limbic system, especially the amygdala); in combination with the malfunction of the narrative centre; reflect respectively, the high emotional loading of the content of the traumatic material, and the difficulty in accurate recall and the ability to constr ...
Dysfunctional_Behavior_web_notes_2
... • Women attempt suicide 2-3x as often as men; BUT 4x a many men as women die by suicide • Evidence suggests prevalence is increasing, particularly in certain age cohorts • Often co-occurs with anxiety disorders and substance abuse ...
... • Women attempt suicide 2-3x as often as men; BUT 4x a many men as women die by suicide • Evidence suggests prevalence is increasing, particularly in certain age cohorts • Often co-occurs with anxiety disorders and substance abuse ...
The Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT
... There are numerous studies reporting the rates of comorbid personality disorders (PDs) in patients with mood disorders. PDs appear to be highly prevalent among patients with chronic depression,1-11 with up to 50% of patients with dysthymic disorder reported to have a comorbid PD.4,12,13 Rates of PDs ...
... There are numerous studies reporting the rates of comorbid personality disorders (PDs) in patients with mood disorders. PDs appear to be highly prevalent among patients with chronic depression,1-11 with up to 50% of patients with dysthymic disorder reported to have a comorbid PD.4,12,13 Rates of PDs ...
Chapter 8
... • Much of what we know is based on studies using criteria the predate DSM-5 • Anxiety disorders are prevalent and quite debilitating • In the United States, almost one-third of individuals will meet criteria for at least one anxiety disorder in their lifetimes – Prevalence rate is secondary only to ...
... • Much of what we know is based on studies using criteria the predate DSM-5 • Anxiety disorders are prevalent and quite debilitating • In the United States, almost one-third of individuals will meet criteria for at least one anxiety disorder in their lifetimes – Prevalence rate is secondary only to ...
Should Borderline Personality Disorder be added to the MA Parity
... sample of 633 patients, those diagnosed with BPD were significantly more likely than patients with major depressive disorder to use most types of treatment. [32] Similarly the McLean Study of Adult Development showed that borderline patients were far heavier utilizers of treatment than patients with ...
... sample of 633 patients, those diagnosed with BPD were significantly more likely than patients with major depressive disorder to use most types of treatment. [32] Similarly the McLean Study of Adult Development showed that borderline patients were far heavier utilizers of treatment than patients with ...























