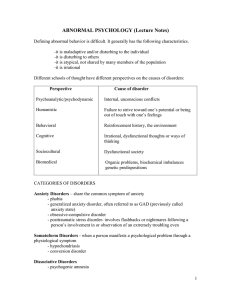
Roadmap for Diagnosis
... R. Typical feature of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis; in the presence of nontypical features, look for alternatives (p.47) S. Previous typical response to treatment for a disorder increases its likelihood as your diagnosis (p.48) T. Use the word undiagnosed whenever you cannot ...
... R. Typical feature of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis; in the presence of nontypical features, look for alternatives (p.47) S. Previous typical response to treatment for a disorder increases its likelihood as your diagnosis (p.48) T. Use the word undiagnosed whenever you cannot ...
Renfrew perspective 12-03
... comfortable pace (assuming she is eating adequate calories). Moreover, it is still possible to move forward with other Intuitive Eating principles within this framework—such as working on permission to eat any food. Patients often express feeling safer trying new food challenges within the framework ...
... comfortable pace (assuming she is eating adequate calories). Moreover, it is still possible to move forward with other Intuitive Eating principles within this framework—such as working on permission to eat any food. Patients often express feeling safer trying new food challenges within the framework ...
document
... A desire to withdraw from other people Sleeplessness and a loss of appetite and sexual desire Change in activity level to laziness, or agitation ...
... A desire to withdraw from other people Sleeplessness and a loss of appetite and sexual desire Change in activity level to laziness, or agitation ...
General Classification of Psychiatric Disorders
... of sexual fantasies and desire for sexual activity), Sexual Aversion Disorder (persistent or recurring aversion to or avoidance of sexual activity), Sexual Arousal and Male Erectile Disorder (Inability to attain or maintain until completion of sexual activity adequate lubrication (in women) or erect ...
... of sexual fantasies and desire for sexual activity), Sexual Aversion Disorder (persistent or recurring aversion to or avoidance of sexual activity), Sexual Arousal and Male Erectile Disorder (Inability to attain or maintain until completion of sexual activity adequate lubrication (in women) or erect ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, be ...
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, be ...
Frequency of Eating Disorders
... • Eating disorders are severe disturbances in eating behavior that result from the sufferer’s obsessive fear of gaining weight. • DSM-IV-TR lists two major types of eating disorders: anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. • The most obvious characteristic of anorexia nervosa is extreme emaciation, or ...
... • Eating disorders are severe disturbances in eating behavior that result from the sufferer’s obsessive fear of gaining weight. • DSM-IV-TR lists two major types of eating disorders: anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. • The most obvious characteristic of anorexia nervosa is extreme emaciation, or ...
Eating Disorders
... Anorexia nervosa is a syndrome in which the individual maintains a low weight as a result of a pre-occupation with body weight, construed either as a fear of fatness or pursuit of thinness. In anorexia nervosa, weight is maintained at least 15 per cent below that expected, or in adults body mass ind ...
... Anorexia nervosa is a syndrome in which the individual maintains a low weight as a result of a pre-occupation with body weight, construed either as a fear of fatness or pursuit of thinness. In anorexia nervosa, weight is maintained at least 15 per cent below that expected, or in adults body mass ind ...
Abnormal Psychology - Courses and Syllabi
... 4. The frequency and distribution of these problems in the United States and elsewhere (i.e., epidemiology). Gender differences and cultural factors will be considered with regard to certain forms of psychological disorder. 5. Causal models, especially those involving multiple systems (biological, p ...
... 4. The frequency and distribution of these problems in the United States and elsewhere (i.e., epidemiology). Gender differences and cultural factors will be considered with regard to certain forms of psychological disorder. 5. Causal models, especially those involving multiple systems (biological, p ...
McKenna - Rutgers Psychology
... Please Note: In past semesters there have been bogus notes posted on the doors of classrooms stating that the assigned classroom has been reassigned to a different location. Please ignore these notes..You will receive an email from myself or the psychology department if any changes in classroom assi ...
... Please Note: In past semesters there have been bogus notes posted on the doors of classrooms stating that the assigned classroom has been reassigned to a different location. Please ignore these notes..You will receive an email from myself or the psychology department if any changes in classroom assi ...
Navigating the Kraepelinian Vortex2
... American Psychiatric Association DSM IV and IV-TR DSM 5 The Selling of DSM, The Rhetoric of Science in Psychiatry Various other websites and publications ...
... American Psychiatric Association DSM IV and IV-TR DSM 5 The Selling of DSM, The Rhetoric of Science in Psychiatry Various other websites and publications ...
Ch 17 Mental Disorders
... psychological trauma is changed into a symbolic physical dysfunction (ex. hysterical blindness or hysterical paralysis). Conversion disorders are quite rare – C. Hypochondrias – Disorders characterized by feeling excessive concern about one’s health and exaggerating the seriousness of minor physical ...
... psychological trauma is changed into a symbolic physical dysfunction (ex. hysterical blindness or hysterical paralysis). Conversion disorders are quite rare – C. Hypochondrias – Disorders characterized by feeling excessive concern about one’s health and exaggerating the seriousness of minor physical ...
Mental Disorders, Basic Concepts
... directedness – feels that there is meaning to present and past life and holds beliefs that give life purpose Personal Growth – see themselves as growing and expanding – open to new experiences – have a sense ...
... directedness – feels that there is meaning to present and past life and holds beliefs that give life purpose Personal Growth – see themselves as growing and expanding – open to new experiences – have a sense ...
Anxiety and Mood Disorders
... becomes a problem when it is irrational, uncontrollable, and disruptive ...
... becomes a problem when it is irrational, uncontrollable, and disruptive ...
The DSM-5
... reason, after the end of the current comment period, the content of DSM-5 will be under strict embargo until publication. This policy applies to all uses and parties, including for those who wish to produce DSM-5 educational materials, diagnostic instruments, or computer-assisted applications of the ...
... reason, after the end of the current comment period, the content of DSM-5 will be under strict embargo until publication. This policy applies to all uses and parties, including for those who wish to produce DSM-5 educational materials, diagnostic instruments, or computer-assisted applications of the ...
Topic 22
... excessive feelings of anxiety and/or fear, where anxiety is worry about future events and fear is a reaction to current events. • Common Anxiety Disorders: – Panic disorder - characterized by recurring severe panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month ...
... excessive feelings of anxiety and/or fear, where anxiety is worry about future events and fear is a reaction to current events. • Common Anxiety Disorders: – Panic disorder - characterized by recurring severe panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month ...
File
... silly, bizarre, or obscene behavior. Social impairment is usually extreme. Catatonic schizophrenia is associated with stupor, mutism and odd postures. Sometimes violent and agitated behavior also occurs. In paranoid schizophrenia (the most common type), outlandish delusions of grandeur and perse ...
... silly, bizarre, or obscene behavior. Social impairment is usually extreme. Catatonic schizophrenia is associated with stupor, mutism and odd postures. Sometimes violent and agitated behavior also occurs. In paranoid schizophrenia (the most common type), outlandish delusions of grandeur and perse ...
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY - Thomas Jefferson High School for …
... Repeated attacks of intense fear involving physical symptoms such as faintness, dizziness, and nausea. ...
... Repeated attacks of intense fear involving physical symptoms such as faintness, dizziness, and nausea. ...
Chapter 16 PowerPoint Notes
... Schizophrenia has also been observed in individuals who contracted a __________________ (flu) during the middle of their fetal development. Genetic Factors The likelihood of an individual suffering from schizophrenia is _________ if their identical twin has the disease (Gottesman, 1991). Psychologic ...
... Schizophrenia has also been observed in individuals who contracted a __________________ (flu) during the middle of their fetal development. Genetic Factors The likelihood of an individual suffering from schizophrenia is _________ if their identical twin has the disease (Gottesman, 1991). Psychologic ...
Psychological Disorders
... unrealistic body image and extreme body ideal. a desire to control food and the body when one’s situation can’t be controlled. cycles of depression. health problems. ...
... unrealistic body image and extreme body ideal. a desire to control food and the body when one’s situation can’t be controlled. cycles of depression. health problems. ...
Somatic Symptom Disorder - DSM-5
... Comprehensive assessment of patients requires the recognition that psychiatric problems often cooccur in patients with medical problems. While DSM-IV was organized centrally around the concept of medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s though ...
... Comprehensive assessment of patients requires the recognition that psychiatric problems often cooccur in patients with medical problems. While DSM-IV was organized centrally around the concept of medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s though ...
SOSC 103 FALL 2012 BERNSTEIN ET AL. PSYCHOLOGICAL
... People with weaker diathesis may not show signs of a disorder until stress becomes extreme or prolonged Classifying Psychological Disorders How many psychological disorders have been identified? ...
... People with weaker diathesis may not show signs of a disorder until stress becomes extreme or prolonged Classifying Psychological Disorders How many psychological disorders have been identified? ...
Personality Disorder
... more distinct and alternating personalities, formerly called multiple personality disorder. ...
... more distinct and alternating personalities, formerly called multiple personality disorder. ...
MPHLECTURE6 - health and wellness
... Psychotherapy (a type of counseling) addresses the emotional response to mental illness. It is a process in which trained mental health professionals help people by talking through strategies for understanding and dealing with their disorder. Cognitive-behavioral therapy: People suffering from anxie ...
... Psychotherapy (a type of counseling) addresses the emotional response to mental illness. It is a process in which trained mental health professionals help people by talking through strategies for understanding and dealing with their disorder. Cognitive-behavioral therapy: People suffering from anxie ...
Anxiety Disorders - Mental Health Association of East Tennessee
... patterns so they can react differently to the situations that cause them anxiety. Is it Possible for Anxiety Disorders to Coexist with Other Physical or Mental Disorders? It is common for an anxiety disorder to accompany another anxiety disorder, or in some cases depression, eating disorders or subs ...
... patterns so they can react differently to the situations that cause them anxiety. Is it Possible for Anxiety Disorders to Coexist with Other Physical or Mental Disorders? It is common for an anxiety disorder to accompany another anxiety disorder, or in some cases depression, eating disorders or subs ...
Unit 8: Study Guide Stress and Abnormal Psychology
... A way to introduce the study of abnormal psychology is with a discussion of the definition of stress. Researchers in this area focus on the impact of life changes, daily stress, and emergency situations on physiological and psychological well-being. Personality characteristics as they relate to phys ...
... A way to introduce the study of abnormal psychology is with a discussion of the definition of stress. Researchers in this area focus on the impact of life changes, daily stress, and emergency situations on physiological and psychological well-being. Personality characteristics as they relate to phys ...