Anatomy of nose and paranasal sinuses
... infraorbital nerve • Floor is formed by alveolar process and hard palate. In children it lies at or above the level of floor of nasal fossa.In adults it lies one cm. below the nasal fossa floor. The roots of many teeth may be related to floor. ...
... infraorbital nerve • Floor is formed by alveolar process and hard palate. In children it lies at or above the level of floor of nasal fossa.In adults it lies one cm. below the nasal fossa floor. The roots of many teeth may be related to floor. ...
I. Bone Structure
... 1. A human skull usually consists of ____________________________________ 2. The moveable bone in the skull is the _________________________________ 3. Some cranial and skull bones together form the ________________ of the eye. B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects ________________________ ...
... 1. A human skull usually consists of ____________________________________ 2. The moveable bone in the skull is the _________________________________ 3. Some cranial and skull bones together form the ________________ of the eye. B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects ________________________ ...
I. Bone Structure
... 1. A human skull usually consists of ____________________________________ 2. The moveable bone in the skull is the _________________________________ 3. Some cranial and skull bones together form the ________________ of the eye. B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects ________________________ ...
... 1. A human skull usually consists of ____________________________________ 2. The moveable bone in the skull is the _________________________________ 3. Some cranial and skull bones together form the ________________ of the eye. B. Cranium 1. The cranium encloses and protects ________________________ ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... The clavicles (2) are slender, curved long bones lying across the superior thorax The acromial (lateral) end articulates with the scapula, and the sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum They provide attachment points for numerous muscles, and act as braces to hold the scapulae and a ...
... The clavicles (2) are slender, curved long bones lying across the superior thorax The acromial (lateral) end articulates with the scapula, and the sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum They provide attachment points for numerous muscles, and act as braces to hold the scapulae and a ...
handout_8
... It is responsible for closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowing, and also for closing off the airway. During sneezing, it protects the nasal passage by diverting a portion of the excreted substance to the mouth. The soft palate also retracts and elevates during speech to sepa ...
... It is responsible for closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowing, and also for closing off the airway. During sneezing, it protects the nasal passage by diverting a portion of the excreted substance to the mouth. The soft palate also retracts and elevates during speech to sepa ...
THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
... position, the radius is lateral (thumb side); with pronation the palm faces posteriorly and the bones cross Prone: body lying face down Suppine: body lying face up (you can remember prone if you think about how you would fall forward onto your face if you passed out) ...
... position, the radius is lateral (thumb side); with pronation the palm faces posteriorly and the bones cross Prone: body lying face down Suppine: body lying face up (you can remember prone if you think about how you would fall forward onto your face if you passed out) ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... The cervical region of the spinal column contains two unique vertebrae, the Atlas C1 and the Axis C2. The occipital bone of the skull rests on and communicates with the first cervical vertebra C1. The arrangement of these first two vertebrae allows the rotation of the head on the spinal column. The ...
... The cervical region of the spinal column contains two unique vertebrae, the Atlas C1 and the Axis C2. The occipital bone of the skull rests on and communicates with the first cervical vertebra C1. The arrangement of these first two vertebrae allows the rotation of the head on the spinal column. The ...
Pathology Codes - Museum of London
... T9-11 consistent with DISH (Ortner 2003,559). T9-10 show similar fusion of the left side. The disk spaces remain intact and the facets are unfused. Discussion The above described changes to the skeleton are found to be consistent with the changes described by Ortner (2003,378) for multiple myeloma. ...
... T9-11 consistent with DISH (Ortner 2003,559). T9-10 show similar fusion of the left side. The disk spaces remain intact and the facets are unfused. Discussion The above described changes to the skeleton are found to be consistent with the changes described by Ortner (2003,378) for multiple myeloma. ...
Part D - Pearson
... • Mucosa-lined, air-filled sacs found in five skull bones – the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and paired maxillary bones • Air enters the paranasal sinuses from the nasal cavity and mucus drains into the nasal cavity from the sinuses • Lighten the skull and enhance the resonance of the voice ...
... • Mucosa-lined, air-filled sacs found in five skull bones – the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and paired maxillary bones • Air enters the paranasal sinuses from the nasal cavity and mucus drains into the nasal cavity from the sinuses • Lighten the skull and enhance the resonance of the voice ...
Head and Neck
... The frontal bone formed the forehead the two halves fail to fuse leaving a midline metopic suture, and forms the upper margins of the orbits and formed the supraorbital ridge. The supraorbital notch or foramen can be recognized medially. There are two zygomatic process of frontal bone and suture lat ...
... The frontal bone formed the forehead the two halves fail to fuse leaving a midline metopic suture, and forms the upper margins of the orbits and formed the supraorbital ridge. The supraorbital notch or foramen can be recognized medially. There are two zygomatic process of frontal bone and suture lat ...
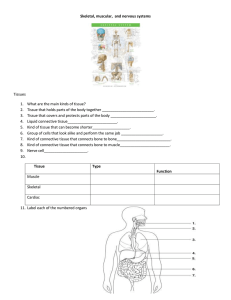
Skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems
... 30. The human skeleton is made up of about (106 / 206) bones. 31. There are three small bones located in the (nose / ears). 32. The largest bone in the body is located in the (thighs / arms). 33. The outer covering of a bone is called the (compact bone / periosteum). 34. The hardest part of a bone i ...
... 30. The human skeleton is made up of about (106 / 206) bones. 31. There are three small bones located in the (nose / ears). 32. The largest bone in the body is located in the (thighs / arms). 33. The outer covering of a bone is called the (compact bone / periosteum). 34. The hardest part of a bone i ...
R. Barsbold THE BONY CREST AND HELMET ON THE SKULL OF
... skulls of predatory dinosaurs. Among these are the development of horns in one case and of paired plate-like crests in other cases (Welles, 1970), respectively, in two species of North American carnosaurs. It may be that the paired crests were the foundation of a wall of the dome-shaped projection t ...
... skulls of predatory dinosaurs. Among these are the development of horns in one case and of paired plate-like crests in other cases (Welles, 1970), respectively, in two species of North American carnosaurs. It may be that the paired crests were the foundation of a wall of the dome-shaped projection t ...
Slide ()
... Normal axial CT scans of the brain, orbits, and lumbar spine from a young healthy man. A. Image through the cerebral hemispheres at the level of the corona radiata. The dense bone of the calvarium is white. Gray matter appears denser than white matter. The triangular shape of the sagittal sinus in a ...
... Normal axial CT scans of the brain, orbits, and lumbar spine from a young healthy man. A. Image through the cerebral hemispheres at the level of the corona radiata. The dense bone of the calvarium is white. Gray matter appears denser than white matter. The triangular shape of the sagittal sinus in a ...
The Nasal Bones
... sutures (joints with teeth-like protrusions). They envelop and protect the brain. The frontal bone forms the forehead and portions of the eye sockets (or orbits). The occipital bone, at the base of the skull contains a large opening, called the foramen magnum, through which the spinal cord passes. O ...
... sutures (joints with teeth-like protrusions). They envelop and protect the brain. The frontal bone forms the forehead and portions of the eye sockets (or orbits). The occipital bone, at the base of the skull contains a large opening, called the foramen magnum, through which the spinal cord passes. O ...
zygomatic bone
... • http://www.uiowa.edu/~acadtech/phonetics/# • See articulation anatomy on the website above. ...
... • http://www.uiowa.edu/~acadtech/phonetics/# • See articulation anatomy on the website above. ...
the orbit - havilahedutool
... directed anterolaterally and their apices directed posteromedially. The orbit contain the eyeballs and their muscles, nerves and vessels together with most of the lacrimal apparatus. The space not occupied by structures contain orbital fat. Conditions resulting in increased overall volume of the orb ...
... directed anterolaterally and their apices directed posteromedially. The orbit contain the eyeballs and their muscles, nerves and vessels together with most of the lacrimal apparatus. The space not occupied by structures contain orbital fat. Conditions resulting in increased overall volume of the orb ...
Study Guide (II)
... (2). What purpose do the trochanters serve? ___________________________________________________________ (3). On the posterior part of the femur, you find a roughened line called the _______________ and this diverges into the medial and lateral _____________________ lines. These sites serve as points ...
... (2). What purpose do the trochanters serve? ___________________________________________________________ (3). On the posterior part of the femur, you find a roughened line called the _______________ and this diverges into the medial and lateral _____________________ lines. These sites serve as points ...
practice quiz chapters7, 8,9
... The unique compromise of the articulations in the appendicular skeleton is: the weaker the joint, the more restricted the range of motion the stronger the joint, the less restricted the range of motion the strength of the joint and range of motion are unrelated the stronger the joint, the more restr ...
... The unique compromise of the articulations in the appendicular skeleton is: the weaker the joint, the more restricted the range of motion the stronger the joint, the less restricted the range of motion the strength of the joint and range of motion are unrelated the stronger the joint, the more restr ...
Chapter 5 - Lisle CUSD 202
... Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity Functions of paranasal sinuses Lighten the skull Give resonance and amplification to voice ...
... Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity Functions of paranasal sinuses Lighten the skull Give resonance and amplification to voice ...
Anatomy and Physiology Part I
... An arm-like branch off the body of a bone. A cavity within a cranial bone. A relatively long, thin projection or bump. Articulation between cranial bones. ...
... An arm-like branch off the body of a bone. A cavity within a cranial bone. A relatively long, thin projection or bump. Articulation between cranial bones. ...
Anatomy Chp 5 Notes
... 2. Protection: protect soft body organs (skull) 3. Movement: attach to skeletal muscle form movement 4. Storage: Fat is stored in internal cavities, and bone itself is a storehouse for minerals (Ca) 5. Blood Cell Formation: Hematopoiesis occurs in the marrow cavities of certain bones B. Classificati ...
... 2. Protection: protect soft body organs (skull) 3. Movement: attach to skeletal muscle form movement 4. Storage: Fat is stored in internal cavities, and bone itself is a storehouse for minerals (Ca) 5. Blood Cell Formation: Hematopoiesis occurs in the marrow cavities of certain bones B. Classificati ...
Summary: Femur, tibia and fibula are the long bones of legs of lower
... Femur, tibia and fibula are the long bones of legs of lower extremity. Femur is the bone of the thigh, while tibia and fibula are the bones of lower leg. Being long bones, all the three bones are characterized by the presence of two ends (epiphyses) and one shaft (diaphysis) which connects the upper ...
... Femur, tibia and fibula are the long bones of legs of lower extremity. Femur is the bone of the thigh, while tibia and fibula are the bones of lower leg. Being long bones, all the three bones are characterized by the presence of two ends (epiphyses) and one shaft (diaphysis) which connects the upper ...
midterm review packet _2 skeletal and muscular systems student
... -What happens to the sarcomere during muscle contraction? ______________________________________________________ - What makes up a motor unit? ______________________________________________________________ -Why are you out of breath after a hard workout? Why do your muscles burn? How does this help ...
... -What happens to the sarcomere during muscle contraction? ______________________________________________________ - What makes up a motor unit? ______________________________________________________________ -Why are you out of breath after a hard workout? Why do your muscles burn? How does this help ...
Anatomy: Skeletal System
... • Moderate to severe pain, swelling, and joint stiffness are present • Partial tear of the lateral ligament(s) • Moderate loss of function with difficulty on toe raises and walking • Takes up to 2-3 months before regaining close to full strength and stability in the joint ...
... • Moderate to severe pain, swelling, and joint stiffness are present • Partial tear of the lateral ligament(s) • Moderate loss of function with difficulty on toe raises and walking • Takes up to 2-3 months before regaining close to full strength and stability in the joint ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.