Semmelweis University School of Doctoral Studies for
... that round window niche fairly completes within a week. Walls of the round window niche are established by both membranous and enchondral ossification, however, to different degrees, which results in the great variability in the phenotype of the round window niche. The posterior and lower walls ossi ...
... that round window niche fairly completes within a week. Walls of the round window niche are established by both membranous and enchondral ossification, however, to different degrees, which results in the great variability in the phenotype of the round window niche. The posterior and lower walls ossi ...
Anatomy and Anatomical Terms Quiz Knowledge/Understanding
... 2. Place the words from the bank below into the appropriate places on the diagram. (10 Marks – K) Scapula ...
... 2. Place the words from the bank below into the appropriate places on the diagram. (10 Marks – K) Scapula ...
“Suppliers of advanced neuro embolisation coils” Foramen magnum
... Hand wasting in foramen magnum compression This intriguing sign has yet to be satisfactorily explained. The most plausible suggestions are ischaemia of the anterior horns following compression of the anterior spinal artery or venous congestion from obstruction of the vertebral veins. This axial sect ...
... Hand wasting in foramen magnum compression This intriguing sign has yet to be satisfactorily explained. The most plausible suggestions are ischaemia of the anterior horns following compression of the anterior spinal artery or venous congestion from obstruction of the vertebral veins. This axial sect ...
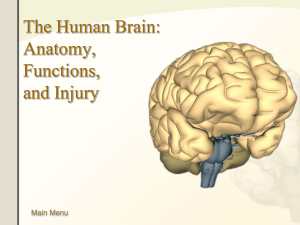
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
... complex brain function. The emotional core of the brain is the limbic system. This is where senses and awareness are first processed in the brain. Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and ...
... complex brain function. The emotional core of the brain is the limbic system. This is where senses and awareness are first processed in the brain. Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and ...
Amatomy of Nose
... - Postero-superior part Medial posterior superior nasal branches. (from sphenopalatine ganglion). - Postero-inferior part Nasopalatine nerve. ( long sphenopalatine nerve). N.B: The nasopalatine nerve, greater and lesser palatine nerves, medial and lateral posterior superior nasal nerves, and the ...
... - Postero-superior part Medial posterior superior nasal branches. (from sphenopalatine ganglion). - Postero-inferior part Nasopalatine nerve. ( long sphenopalatine nerve). N.B: The nasopalatine nerve, greater and lesser palatine nerves, medial and lateral posterior superior nasal nerves, and the ...
The Skeleton
... sight, taste, and smell, (3) provide openings for air and food passage, (4) secure the teeth, and (5) anchor the facial muscles of expression, which we use to show our feelings. As you will see, the individual skull bones are well suited to their assignments. Most skull bones are flat bones. Except ...
... sight, taste, and smell, (3) provide openings for air and food passage, (4) secure the teeth, and (5) anchor the facial muscles of expression, which we use to show our feelings. As you will see, the individual skull bones are well suited to their assignments. Most skull bones are flat bones. Except ...
Muscoloskeletal System - Cape Breton University
... Wrist and hand joints Support hand, use both thumbs to palpate Metacarpophanlangeal joints Use thumb and index finger in a pinching motion to palpate interphalangeal joints ...
... Wrist and hand joints Support hand, use both thumbs to palpate Metacarpophanlangeal joints Use thumb and index finger in a pinching motion to palpate interphalangeal joints ...
Bones of the gluteal region
... The ischial tuberosity is covered by gluteus maximus when one stands. In the sitting position the muscle slips away laterally .To palpate this bony point, therefore, feel for it uncovered by gluteus maximus in the flexed position of the hip. ...
... The ischial tuberosity is covered by gluteus maximus when one stands. In the sitting position the muscle slips away laterally .To palpate this bony point, therefore, feel for it uncovered by gluteus maximus in the flexed position of the hip. ...
Muscles of Mastication
... LATERAL: THE SIDE OF THE BODY OR A BODY PART THAT IS FARTHER FROM THE MIDDLE OR CENTER OF ...
... LATERAL: THE SIDE OF THE BODY OR A BODY PART THAT IS FARTHER FROM THE MIDDLE OR CENTER OF ...
Clinical Notes of Head & Neck
... bodies such as fish bones. The presence of such a foreign body immediately causes the patient to gag violently ...
... bodies such as fish bones. The presence of such a foreign body immediately causes the patient to gag violently ...
Module 38 / Gross Anatomy and the Upper Respiratory
... The nasal cavity is divided into right and left sides by the nasal septum. This dividing wall’s anterior portion is made of cartilage; bone contributed by the vomer and part of the ethmoid bones of the skull make up the posterior. The roof of the nasal cavity consists of parts of the ethmoid and sph ...
... The nasal cavity is divided into right and left sides by the nasal septum. This dividing wall’s anterior portion is made of cartilage; bone contributed by the vomer and part of the ethmoid bones of the skull make up the posterior. The roof of the nasal cavity consists of parts of the ethmoid and sph ...
Ppts/Gross Anatomy Case 3
... involving a strip of skin extending from the ipsilateral lower lip and chin and proceeding anterior to the ear and superior to the scalp. There was anesthesia to the ipsilateral lingual gingiva (mandibular region),floor of the mouth and mandibular teeth There was a reduction of the volume of ...
... involving a strip of skin extending from the ipsilateral lower lip and chin and proceeding anterior to the ear and superior to the scalp. There was anesthesia to the ipsilateral lingual gingiva (mandibular region),floor of the mouth and mandibular teeth There was a reduction of the volume of ...
Development and growth of the mandible
... foramen. Also the bony trough grow rapidly forwards towards the middle line where it comes into close relationship with the similar bone of the opposite side, but from which it is separated by connective tissue. A similar spread of ossification in the backward direction produces at first a trough of ...
... foramen. Also the bony trough grow rapidly forwards towards the middle line where it comes into close relationship with the similar bone of the opposite side, but from which it is separated by connective tissue. A similar spread of ossification in the backward direction produces at first a trough of ...
The Pelvic Girdle
... Receives ground forces during walking and transmits them upward toward the vertebral column Supports and protects pelvic viscera Provides attachment site for muscles Makes up bony portion of birth canal Lippert, p247 ...
... Receives ground forces during walking and transmits them upward toward the vertebral column Supports and protects pelvic viscera Provides attachment site for muscles Makes up bony portion of birth canal Lippert, p247 ...
Sofia Ramos April 19, 2012 Journal 17 Spring 2012 C I: Troy Hill In
... In Evaluation of Upper Extremity we are learning about the cervical spine. There are seven cervical vertebrae. C1, also known as atlas, has no vertebral body. It supports the weight of the skull through two concave facet surfaces forming the atlanto-occipital joint. The primary movement is flexion, ...
... In Evaluation of Upper Extremity we are learning about the cervical spine. There are seven cervical vertebrae. C1, also known as atlas, has no vertebral body. It supports the weight of the skull through two concave facet surfaces forming the atlanto-occipital joint. The primary movement is flexion, ...
Measurement: Nasal root width
... Remarks: Pronasale is best seen in the profile view when the head is in normal rest position. It may be difficult to locate if the tip of the nose is flat. Landmark: Sellion(s) Definition: the deepest point of the nasofrontal angle. Remarks: Sellion is often used as the upper limit of the facial ske ...
... Remarks: Pronasale is best seen in the profile view when the head is in normal rest position. It may be difficult to locate if the tip of the nose is flat. Landmark: Sellion(s) Definition: the deepest point of the nasofrontal angle. Remarks: Sellion is often used as the upper limit of the facial ske ...
The ankle is a large joint made up of three bones: The shin bone
... High ankle sprain: The ligament joining the two bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula), called the syndesmotic ligament, is injured. A high ankle sprain causes pain and swelling similar to a true ankle sprain, but can take longer to heal. Ankle fracture: A break in any of the three bones in the a ...
... High ankle sprain: The ligament joining the two bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula), called the syndesmotic ligament, is injured. A high ankle sprain causes pain and swelling similar to a true ankle sprain, but can take longer to heal. Ankle fracture: A break in any of the three bones in the a ...
Differential Diagnosis of Temporal Bone and Skull Base
... therapy to help minimize intraoperative blood loss. There is a strong association with endolymphatic sac tumors and von Hippel-Lindau disease. Von Hippel-Lindau disease is an autosomal dominant disorder that manifests itself as multiple hemangioblastomas of the retina and CNS with associated renal c ...
... therapy to help minimize intraoperative blood loss. There is a strong association with endolymphatic sac tumors and von Hippel-Lindau disease. Von Hippel-Lindau disease is an autosomal dominant disorder that manifests itself as multiple hemangioblastomas of the retina and CNS with associated renal c ...
The carpal bones are a small cluster of 8. From anatomical position
... rests right on top of it. The navicular bone is in front of the talus on the medial side. The cuboid bone is shaped just like its name: cubed and it is on the lateral side. The cuneiforms are distal to the navicular and it goes #1 from medial to #3 lateral. p.209-210 ...
... rests right on top of it. The navicular bone is in front of the talus on the medial side. The cuboid bone is shaped just like its name: cubed and it is on the lateral side. The cuneiforms are distal to the navicular and it goes #1 from medial to #3 lateral. p.209-210 ...
Brief review of the anatomy of the head, spine, brain, and spinal cord.
... which blood vessels and nerves enter and exit the skull. The posterior fossa consists of an inclined central plane, known as the clivus, over which lies the brain stem, and two lateral and posterior concave expansions that contain the cerebellar hemispheres. The foramen magnum is at the bottom of th ...
... which blood vessels and nerves enter and exit the skull. The posterior fossa consists of an inclined central plane, known as the clivus, over which lies the brain stem, and two lateral and posterior concave expansions that contain the cerebellar hemispheres. The foramen magnum is at the bottom of th ...
handbook of forensic neuropathology
... which blood vessels and nerves enter and exit the skull. The posterior fossa consists of an inclined central plane, known as the clivus, over which lies the brain stem, and two lateral and posterior concave expansions that contain the cerebellar hemispheres. The foramen magnum is at the bottom of th ...
... which blood vessels and nerves enter and exit the skull. The posterior fossa consists of an inclined central plane, known as the clivus, over which lies the brain stem, and two lateral and posterior concave expansions that contain the cerebellar hemispheres. The foramen magnum is at the bottom of th ...
Chapter 8
... ramus of ischium – fuses with pubis 3) Pubis – inferior, anterior portion; forms pubic symphysis superior ramus – forms part of acetabulum inferior ramus – site of pubic symphysis body – junction of rami pubic crest obturator foramen – large hole between ischium and pubis acetabulum – deep, rimmed s ...
... ramus of ischium – fuses with pubis 3) Pubis – inferior, anterior portion; forms pubic symphysis superior ramus – forms part of acetabulum inferior ramus – site of pubic symphysis body – junction of rami pubic crest obturator foramen – large hole between ischium and pubis acetabulum – deep, rimmed s ...
Critique of the Cranium
... If the distance from the orbital rim to the cranial cortices are not equal The side that exhibits the greatest distance is the side that the patient’s face is rotated away from The side with the least amount of distance is the side in which the face was ...
... If the distance from the orbital rim to the cranial cortices are not equal The side that exhibits the greatest distance is the side that the patient’s face is rotated away from The side with the least amount of distance is the side in which the face was ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.