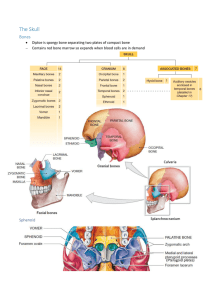
The Head
... 2. Right and left parietal bones 3. Right and left temporal bones 4. Occipital bone B. Bones are joined by immovable joints 1. Sagittal – between right parietal and left parietal (down midline) 2. Coronal – anterior side of right and left parietal to posterior side of frontal 3. Lambdoid – posterior ...
... 2. Right and left parietal bones 3. Right and left temporal bones 4. Occipital bone B. Bones are joined by immovable joints 1. Sagittal – between right parietal and left parietal (down midline) 2. Coronal – anterior side of right and left parietal to posterior side of frontal 3. Lambdoid – posterior ...
PPT 1 MB embryology skeletal system
... protective case around the brain, and the viscerocranium, which forms the skeleton of the face. The neurocranium is most conveniently divided into two portions: (a) the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain as a vault; and(b) the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, w ...
... protective case around the brain, and the viscerocranium, which forms the skeleton of the face. The neurocranium is most conveniently divided into two portions: (a) the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain as a vault; and(b) the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, w ...
Document
... Lightening the skull bones and providing an extensive area of mucous epithelium Pulling mucus back toward the throat Providing the superior and posterior boundary of the nasal complex Providing the lateral and inferior boundaries of the orbital complex ...
... Lightening the skull bones and providing an extensive area of mucous epithelium Pulling mucus back toward the throat Providing the superior and posterior boundary of the nasal complex Providing the lateral and inferior boundaries of the orbital complex ...
Embryology Lec13 Dr.Ban Skeletal system Skeletal development
... grows, it is gradually converted into bone through the process of endochondral ossification. This is a slow process and the cartilage is not completely converted to bone until the skull achieves its full adult size. At birth, the brain case and orbits of the skull are disproportionally large compare ...
... grows, it is gradually converted into bone through the process of endochondral ossification. This is a slow process and the cartilage is not completely converted to bone until the skull achieves its full adult size. At birth, the brain case and orbits of the skull are disproportionally large compare ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 09-19
... The Foramen Magnum is a large hole on the inferior side of the occipital bone The spinal cord is continuous up through the foramen magnum to become the brainstem Suture joints hold the cranial bones tightly together o Fibrous connective tissue ties bones together so they can’t move relative to ...
... The Foramen Magnum is a large hole on the inferior side of the occipital bone The spinal cord is continuous up through the foramen magnum to become the brainstem Suture joints hold the cranial bones tightly together o Fibrous connective tissue ties bones together so they can’t move relative to ...
The Axial Skeleton •The basic features of the human skeleton have
... •Facial bones protect and support entrances to the digestive and respiratory tracts. •Superficial facial bones; maxillary, lacrimal, nasal, mandible, and zygomatic bones provide areas of attachment of muscles that control facial expression, and assist in manipulation of food. •The palatine bone (dee ...
... •Facial bones protect and support entrances to the digestive and respiratory tracts. •Superficial facial bones; maxillary, lacrimal, nasal, mandible, and zygomatic bones provide areas of attachment of muscles that control facial expression, and assist in manipulation of food. •The palatine bone (dee ...
osteology of head and neck
... The lambda is the meeting point between the sagittal and lambdoid suture. In the fetal skull this is the site of postreior fontanelle which closes at two or three months of age. ...
... The lambda is the meeting point between the sagittal and lambdoid suture. In the fetal skull this is the site of postreior fontanelle which closes at two or three months of age. ...
Document
... bone, with contributions from the sphenoid and temporal bones. The anterior portion by the basal portion of the occipital bone (the basiocciput) and the basisphenoid. These 2 regions combine to form the midline clivus. The lateral wall by the posterior surface of the petrous temporal bone and the la ...
... bone, with contributions from the sphenoid and temporal bones. The anterior portion by the basal portion of the occipital bone (the basiocciput) and the basisphenoid. These 2 regions combine to form the midline clivus. The lateral wall by the posterior surface of the petrous temporal bone and the la ...
The Skeleton - Northwest ISD Moodle
... False Pelvis: portion superior to the pelvic brim True Pelvis: region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of t ...
... False Pelvis: portion superior to the pelvic brim True Pelvis: region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of t ...
Skull part 2
... Skull • Usually consists of 22 bones, all of which (except the lower jaw) are firmly interlocked along lines called “sutures”. – Cranium = 8 bones – Facial skeleton = 13 bones + lower jaw – Lower jaw bone is called the mandible, and is the only movable bone. ...
... Skull • Usually consists of 22 bones, all of which (except the lower jaw) are firmly interlocked along lines called “sutures”. – Cranium = 8 bones – Facial skeleton = 13 bones + lower jaw – Lower jaw bone is called the mandible, and is the only movable bone. ...
Bony Thorax - Northwest ISD Moodle
... False Pelvis: portion superior to the pelvic brim True Pelvis: region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of t ...
... False Pelvis: portion superior to the pelvic brim True Pelvis: region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of t ...
doc - CLAS Users
... foramen magnum: The large opening in the occipital bone on the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes to join the base of the brain. frontal trigone: A concave smooth triangular area on the frontal bone just behind the orbits. Its base is formed by the supraorbital torus and its apex ...
... foramen magnum: The large opening in the occipital bone on the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes to join the base of the brain. frontal trigone: A concave smooth triangular area on the frontal bone just behind the orbits. Its base is formed by the supraorbital torus and its apex ...
bones associated with the skull
... parietals, note the lambdoidal suture. The large foramen magnum allows for the passage of the brain stem. On either side of the foramen magnum, note the occipital condyles. These condyles articulate with the fossa of the first cervical vertebra. Near the base of each condyle are two openings. The hy ...
... parietals, note the lambdoidal suture. The large foramen magnum allows for the passage of the brain stem. On either side of the foramen magnum, note the occipital condyles. These condyles articulate with the fossa of the first cervical vertebra. Near the base of each condyle are two openings. The hy ...
Skull 1 Checklist Bones of the Skull Axial skeleton Skull Auditory
... The paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities within skull bones that open into the nasal cavity. The sinuses are named according to the bone in which they are found. ...
... The paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities within skull bones that open into the nasal cavity. The sinuses are named according to the bone in which they are found. ...
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 5: The vertebrate skeleton Axial
... pair of openings, located on the rear of the skull. Among reptiles these are especially large in turtles, exposing most of the braincase. - Infratemporal fenestrae (sing. fenestra): paired openings in the lower, temporal region. They have evolved independently between reptiles more derived than turt ...
... pair of openings, located on the rear of the skull. Among reptiles these are especially large in turtles, exposing most of the braincase. - Infratemporal fenestrae (sing. fenestra): paired openings in the lower, temporal region. They have evolved independently between reptiles more derived than turt ...
The Skull
... Carotid canal is for internal carotid artery Jugular foramen is for jugular vein and for the glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory cranial nerves ...
... Carotid canal is for internal carotid artery Jugular foramen is for jugular vein and for the glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory cranial nerves ...
Bony Thorax - Northwest ISD Moodle
... False Pelvis: portion superior to the pelvic brim True Pelvis: region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of t ...
... False Pelvis: portion superior to the pelvic brim True Pelvis: region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone and forms a deep “bowl” containing the pelvic organs Pelvic Inlet: pelvic brim; widest dimension is along the frontal plane Pelvic Outlet: inferior margin of t ...
the skull - Mayfield City Schools
... cranial nerves to control eye movement. • Pterygoid processes: anchors muscles used in chewing • Foramen rotundum and Foramen ovale ...
... cranial nerves to control eye movement. • Pterygoid processes: anchors muscles used in chewing • Foramen rotundum and Foramen ovale ...
Skull notes
... Skull • Usually consists of 22 bones, all of which (except the lower jaw) are firmly interlocked along lines called “sutures”. – Cranium = 8 bones – Facial skeleton = 13 bones + lower jaw – Lower jaw bone is called the mandible, and is the only movable bone. ...
... Skull • Usually consists of 22 bones, all of which (except the lower jaw) are firmly interlocked along lines called “sutures”. – Cranium = 8 bones – Facial skeleton = 13 bones + lower jaw – Lower jaw bone is called the mandible, and is the only movable bone. ...
Untitled
... fissure - cleft-like opening between adjacent parts of bones through which vessels & nerves pass ...
... fissure - cleft-like opening between adjacent parts of bones through which vessels & nerves pass ...
The Axial and Appendicular Skeletons
... • Be able to differentiate between the axial and appendicular skeleton • Be able to describe and recognize the bones of the axial and appendicular skeletons • Know the terminology indicative of the various bone features that will be studied ...
... • Be able to differentiate between the axial and appendicular skeleton • Be able to describe and recognize the bones of the axial and appendicular skeletons • Know the terminology indicative of the various bone features that will be studied ...
Axial Skeleton - North Seattle College
... sides Consists of vomer, septal cartilage (hyaline cartilage), and perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone ...
... sides Consists of vomer, septal cartilage (hyaline cartilage), and perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone ...
The Skeletal System
... Contributes to medial wall of orbit, roof and walls of nasal cavity, and nasal septum Crista galli, cribiform plate and cribiform foramen Perpendicular plate and middle nasal conchae ...
... Contributes to medial wall of orbit, roof and walls of nasal cavity, and nasal septum Crista galli, cribiform plate and cribiform foramen Perpendicular plate and middle nasal conchae ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.