
Chemical bonding
... length – the distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy that is, the average distance between two bonded atoms ...
... length – the distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy that is, the average distance between two bonded atoms ...
Cl Cl and
... 27. Why don’t elements of group 4 form ions of charge 4+? Why don’t they form ions of charge 4–? Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do eleme ...
... 27. Why don’t elements of group 4 form ions of charge 4+? Why don’t they form ions of charge 4–? Too much energy is needed to remove 4 electrons from an atom. Too much energy is needed to insert 4 electrons into an atom in order to overcome the repulsive forces between like charges. 28. Why do eleme ...
Investigating Chemistry - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Groups 13-16 are referred to by the first element or simply the group number. Group 17 is the Halogens. Group 18 is the Noble Gases. Elements 58-71 and 90-103 are called the Inner Transition Metals. ...
... Groups 13-16 are referred to by the first element or simply the group number. Group 17 is the Halogens. Group 18 is the Noble Gases. Elements 58-71 and 90-103 are called the Inner Transition Metals. ...
Biology Ch. 2 Review
... 11. Potassium ions (K+) have a positive charge. What happens to a potassium atom’s electrons when it becomes an ion? Loses one electron. ...
... 11. Potassium ions (K+) have a positive charge. What happens to a potassium atom’s electrons when it becomes an ion? Loses one electron. ...
Chapter 2: Matter
... The raw materials that make up sand are transformed into something new when heated at ...
... The raw materials that make up sand are transformed into something new when heated at ...
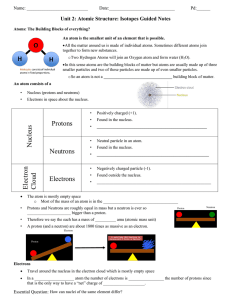
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... 2. Drag one proton and one electron to the atom. Record the Element:__________________ 3. Drag an additional proton to the model. Record the Element:________________________ 4. Drag an additional proton to the model. Record the Element:______________________ 5. What happened when additional protons ...
... 2. Drag one proton and one electron to the atom. Record the Element:__________________ 3. Drag an additional proton to the model. Record the Element:________________________ 4. Drag an additional proton to the model. Record the Element:______________________ 5. What happened when additional protons ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 2 Chemistry
... there are 92 naturally occurring elements, from hydrogen up to uranium http://serc.carleton.edu/images/usingdata/nasaimages/periodic-table.gif ...
... there are 92 naturally occurring elements, from hydrogen up to uranium http://serc.carleton.edu/images/usingdata/nasaimages/periodic-table.gif ...
GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties]
... GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties] What is Atom? An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small; typical sizes are a ...
... GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties] What is Atom? An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small; typical sizes are a ...
CHAPTER 2
... nucleus 3. -nearly all of the atom’s mass is in the nucleus 4. -the nuclear diameter is 1/10,000 to 1/100,000 times less than the atom’s radius ...
... nucleus 3. -nearly all of the atom’s mass is in the nucleus 4. -the nuclear diameter is 1/10,000 to 1/100,000 times less than the atom’s radius ...
The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of
... The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of the Atom A. A Closer Look at the Nucleus Since Bohr, the model of the atom has become even more sophisticated. Scientists had to explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and the ...
... The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of the Atom A. A Closer Look at the Nucleus Since Bohr, the model of the atom has become even more sophisticated. Scientists had to explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and the ...
Atomic Theory Magic Squares Democritus _____ Dalton _____
... 3. Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons 4. The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons 7. Formed the first atom ...
... 3. Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons 4. The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons 7. Formed the first atom ...
m5zn_2b75b651bf15359
... Atoms with fewer protons have lower binding energy while atoms with more protons have higher binding energy ...
... Atoms with fewer protons have lower binding energy while atoms with more protons have higher binding energy ...
Ch 3: Atoms
... atomic # (Z) - (always a whole number, smaller number on the periodic table) = # of protons in the nucleus - also indicates the # of electrons if the element is not charged atomic mass – the average mass of all of the isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number ...
... atomic # (Z) - (always a whole number, smaller number on the periodic table) = # of protons in the nucleus - also indicates the # of electrons if the element is not charged atomic mass – the average mass of all of the isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number ...
PreAP Chemistry
... 19. Challenge Nitrogen has two naturally occurring isotopes, N-14 and N-15. Its atomic mass is 14.007. Which isotope is more abundant? Explain. ...
... 19. Challenge Nitrogen has two naturally occurring isotopes, N-14 and N-15. Its atomic mass is 14.007. Which isotope is more abundant? Explain. ...
Name
... b. a lithium atom loses one electron to form a ________________ c. a fluorine atom gains one electron to form a _______________ C. How do the structures of atoms differ? 1. The atomic number, Z, of an atom equals the ____________________ ___________________________________________________________ 2. ...
... b. a lithium atom loses one electron to form a ________________ c. a fluorine atom gains one electron to form a _______________ C. How do the structures of atoms differ? 1. The atomic number, Z, of an atom equals the ____________________ ___________________________________________________________ 2. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... The subscript to the right of the symbol of an element tells the number of atoms of that element in one molecule of the compound. Molecular compounds are composed of molecules and ...
... The subscript to the right of the symbol of an element tells the number of atoms of that element in one molecule of the compound. Molecular compounds are composed of molecules and ...
atom atomic symbol atomic number # protons atomic mass
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
File - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... • According to Rutherford’s model, there is not enough mass with just a proton and an electron. ...
... • According to Rutherford’s model, there is not enough mass with just a proton and an electron. ...
Document
... _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ ____________ ...
... _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ ____________ ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...






![GED Chemistry Note 1[Atoms, Molecules and their properties]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015791288_1-b34903533007e866662649e94180f015-300x300.png)















