The Reproductive System
... Maintains testes at 3°C lower than normal body temperature to protect sperm viability Muscles move testes up toward body or lower away from body ...
... Maintains testes at 3°C lower than normal body temperature to protect sperm viability Muscles move testes up toward body or lower away from body ...
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E
... scrotum. (E) Scrotal, on the scrotum or between the genital ...
... scrotum. (E) Scrotal, on the scrotum or between the genital ...
The Reproductive System
... 1. Lack of this (these) causes the blood vessels to kink and the endometrium to slough off (menses) 2. Causes the endometrial glands to begin the secretion of nutrients 3. The endometrium is repaired and grows thick and velvety 4. Maintains the myometrium in an inactive state if implantation of an e ...
... 1. Lack of this (these) causes the blood vessels to kink and the endometrium to slough off (menses) 2. Causes the endometrial glands to begin the secretion of nutrients 3. The endometrium is repaired and grows thick and velvety 4. Maintains the myometrium in an inactive state if implantation of an e ...
1. Anococcygeal liament 2. Deep transverse perineal muscle 3
... Insertion: Lateral surfaces of bulb of penis & corpus spongiosum penis. Some end on the corpus cavernosum penis. Function: The pair of muscles get the urine and ejaculate out They also make a pressure on the deep vein of the penis and contribute to the erection. In females Origin: Perineal body Inse ...
... Insertion: Lateral surfaces of bulb of penis & corpus spongiosum penis. Some end on the corpus cavernosum penis. Function: The pair of muscles get the urine and ejaculate out They also make a pressure on the deep vein of the penis and contribute to the erection. In females Origin: Perineal body Inse ...
Accessory Sex Organs - Academic Script
... ejaculatory duct, and urethra. The major accessory sex glands, which provide most of the semen, are the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral gland. The female reproductive tract consists of two oviducts, the uterus and the vagina. The oviducts (or fallopian tubes), which connect the ovaries ...
... ejaculatory duct, and urethra. The major accessory sex glands, which provide most of the semen, are the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral gland. The female reproductive tract consists of two oviducts, the uterus and the vagina. The oviducts (or fallopian tubes), which connect the ovaries ...
ADENOCARCINOMA: A cancerous tumour developing from the
... Digital rectal examination; usually to feel the prostate gland DYSURIA: Painful passage of urine EMBOLISATION: Blocking the artery to an organ by introducing foam, coils or gel under X-ray control using a small catheter placed in the artery ENURESIS: Incontinence of urine at night usually considered ...
... Digital rectal examination; usually to feel the prostate gland DYSURIA: Painful passage of urine EMBOLISATION: Blocking the artery to an organ by introducing foam, coils or gel under X-ray control using a small catheter placed in the artery ENURESIS: Incontinence of urine at night usually considered ...
Document
... The information below is a complete jumble. Reconstruct the information so that you can understand the process of a Tubal Ligation and a Vasectomy. Match the information to the questions below. An operation designed to sterilise a man. Periods will continue as normal, because the ovaries will contin ...
... The information below is a complete jumble. Reconstruct the information so that you can understand the process of a Tubal Ligation and a Vasectomy. Match the information to the questions below. An operation designed to sterilise a man. Periods will continue as normal, because the ovaries will contin ...
Unit 6 – Reproductive System
... c. Are a collection of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms d. Exact symptoms vary from person to person 7. Is the abnormal growth of prostate cells, but is not cancerous. a. Endometriosis b. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy c. Testicular Cancer d. PMS 8. Is the most common form of cancer in ...
... c. Are a collection of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms d. Exact symptoms vary from person to person 7. Is the abnormal growth of prostate cells, but is not cancerous. a. Endometriosis b. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy c. Testicular Cancer d. PMS 8. Is the most common form of cancer in ...
Unit 6 – Reproductive System
... c. Are a collection of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms d. Exact symptoms vary from person to person 7. Is the abnormal growth of prostate cells, but is not cancerous. a. Endometriosis b. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy c. Testicular Cancer d. PMS 8. Is the most common form of cancer in ...
... c. Are a collection of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms d. Exact symptoms vary from person to person 7. Is the abnormal growth of prostate cells, but is not cancerous. a. Endometriosis b. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy c. Testicular Cancer d. PMS 8. Is the most common form of cancer in ...
Introduction to Urology
... below bladder, surrounds urethra and ejaculatory duct 2 x 4 x 3 cm Bulbourethral ...
... below bladder, surrounds urethra and ejaculatory duct 2 x 4 x 3 cm Bulbourethral ...
0474 ch 23(453-475).
... are affected by erectile dysfunction (ED), the inability to achieve an erection. Although ED is more common in men over the age of 65, it can occur at any age and can have many causes. Until recently, ED was believed to be caused by psychological factors, such as stress or depression. It is now know ...
... are affected by erectile dysfunction (ED), the inability to achieve an erection. Although ED is more common in men over the age of 65, it can occur at any age and can have many causes. Until recently, ED was believed to be caused by psychological factors, such as stress or depression. It is now know ...
Renal artery
... – Embedded in ant. Wall of vagina. – Opens in the vestibule between the clitoris ant. and the vaginal opening post. – In urogenital diaphragm the External urethral sphincter, supplied by pudendal nerve. ...
... – Embedded in ant. Wall of vagina. – Opens in the vestibule between the clitoris ant. and the vaginal opening post. – In urogenital diaphragm the External urethral sphincter, supplied by pudendal nerve. ...
Urogenital Systems
... Hagfishes & Lampreys = no testis ducts. Gnathostomes = archinephric ducts drain the testes (also drain the kidneys in all nonamniote ganthostomes). ...
... Hagfishes & Lampreys = no testis ducts. Gnathostomes = archinephric ducts drain the testes (also drain the kidneys in all nonamniote ganthostomes). ...
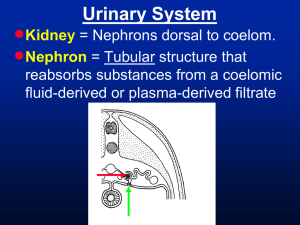
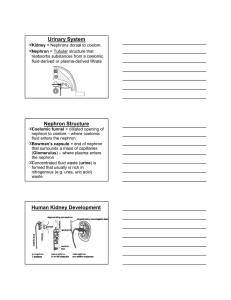
• Urinary System Nephron Structure
... • Hagfishes & Lampreys = no testis ducts. • Gnathostomes = archinephric ducts drain the testes (also drain the kidneys in all nonamniote ganthostomes). ...
... • Hagfishes & Lampreys = no testis ducts. • Gnathostomes = archinephric ducts drain the testes (also drain the kidneys in all nonamniote ganthostomes). ...
pediatric urology
... Torsion: Rotation of the shaft or the shaft skin (usually to the left) Webbing: Webbed angle between the penis and scrotum Buried or Hidden Penis: Penis obscured by pubic fat Phimosis: Tight opening of the uncircumcised penis preventing retraction of the foreskin Epispadias: Opening of the urethra ( ...
... Torsion: Rotation of the shaft or the shaft skin (usually to the left) Webbing: Webbed angle between the penis and scrotum Buried or Hidden Penis: Penis obscured by pubic fat Phimosis: Tight opening of the uncircumcised penis preventing retraction of the foreskin Epispadias: Opening of the urethra ( ...
Lesions, Swelling, Pain and Dysfunction: Men’s Health Update
... 3. Vas deferens: Tube which carries sperm from the testicles to the urethra 4. Scrotum: Sac which hold the testicles 5. Urethra: Tube which carries urine from the bladder and semen through the penis ...
... 3. Vas deferens: Tube which carries sperm from the testicles to the urethra 4. Scrotum: Sac which hold the testicles 5. Urethra: Tube which carries urine from the bladder and semen through the penis ...
Unit 6
... • Ur/o/logist: A physician who specializes in treating male and female urinary system disorders and male reproductive system. • Ur/o/genital or genit/o/urinary: Pertaining to urinary tract and genitals • Ur/o/pathy: Any disease of urinary tract ...
... • Ur/o/logist: A physician who specializes in treating male and female urinary system disorders and male reproductive system. • Ur/o/genital or genit/o/urinary: Pertaining to urinary tract and genitals • Ur/o/pathy: Any disease of urinary tract ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Pelvis
... be associated with damage to the anal sphincters and canal. (Note: The clinical use of the term mediolateral is technically inappropriate here; it actually refers to an incision that is initially a median incision that then turns laterally as it ...
... be associated with damage to the anal sphincters and canal. (Note: The clinical use of the term mediolateral is technically inappropriate here; it actually refers to an incision that is initially a median incision that then turns laterally as it ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy
... b. They prevent follicle development and ovulation by feedback inhibition of FSH & LH c. Women stop taking the pill one week of every 3 weeks so the endometrium can be shed in menstruation d. The pill does not prevent STDs 2. Norplant - time release capsule implanted under a woman’s upper arm skin a ...
... b. They prevent follicle development and ovulation by feedback inhibition of FSH & LH c. Women stop taking the pill one week of every 3 weeks so the endometrium can be shed in menstruation d. The pill does not prevent STDs 2. Norplant - time release capsule implanted under a woman’s upper arm skin a ...
reproductive system
... blood vessels and interstitial cells or Leydig cells. Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens [a male sex hormone, such as testosterone. Androgens stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male ...
... blood vessels and interstitial cells or Leydig cells. Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens [a male sex hormone, such as testosterone. Androgens stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male ...
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 3: Reproduction
... Key Concept A: Structures and Functions of the Male Reproductive System p.474-481 A1. Functions of the male reproductive organs A2. Structure of the male reproductive organs A3. Structure of the human sperm A4. Supporting structures for sperm Key Concept B: Structures and functions of the female rep ...
... Key Concept A: Structures and Functions of the Male Reproductive System p.474-481 A1. Functions of the male reproductive organs A2. Structure of the male reproductive organs A3. Structure of the human sperm A4. Supporting structures for sperm Key Concept B: Structures and functions of the female rep ...
the reproductive system
... – Encircles the prostatic urethra – Secretes about 25–30% of the volume of seminal fluid – Contains substances that • Enhance sperm motility • Enzymes that clot & then liquefy semen ...
... – Encircles the prostatic urethra – Secretes about 25–30% of the volume of seminal fluid – Contains substances that • Enhance sperm motility • Enzymes that clot & then liquefy semen ...
Human penis

The human penis is an external male intromittent organ that additionally serves as the urinal duct. The main parts are the root (radix); the body (corpus); and the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin and the foreskin covering the glans penis. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus (/miːˈeɪtəs/), lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen.The penis is homologous to the clitoris. An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. The most common form of genital alteration is circumcision, removal of part or all of the foreskin for various cultural, religious and, more rarely, medical reasons. There is controversy surrounding circumcision.While results vary across studies, the consensus is that the average erect human penis is approximately 12.9–15 cm (5.1–5.9 in) in length with 95% of adult males falling within the interval 10.7–19.1 cm (4.2–7.5 in). Neither age nor size of the flaccid penis accurately predicts erectile length.