Unit 13―The “Fixed” Stars
... It is generally understood that the outline, and hence the included stars in any constellation, would not be exactly as they are if we could start over and redefine them as we might see them via later history. Unfortunately, most of the early developments in astronomy were made by people living in t ...
... It is generally understood that the outline, and hence the included stars in any constellation, would not be exactly as they are if we could start over and redefine them as we might see them via later history. Unfortunately, most of the early developments in astronomy were made by people living in t ...
The formation of the galaxy is believed to be similar
... stars have higher metallicity, which is most likely? Gas ejected from the a) spheroid stars enriched the material now in the disk stars. b) spheroid stars decreased their metallicity. c) spheroid decreased its angular momentum. d) disk stars puffed out the spheroid stars into a rounder shape. ...
... stars have higher metallicity, which is most likely? Gas ejected from the a) spheroid stars enriched the material now in the disk stars. b) spheroid stars decreased their metallicity. c) spheroid decreased its angular momentum. d) disk stars puffed out the spheroid stars into a rounder shape. ...
Chapter 15
... energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that happens, radiation pressure from the core will puff up the star's outer layers, so Gamma Hydra will get much bigger ...
... energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that happens, radiation pressure from the core will puff up the star's outer layers, so Gamma Hydra will get much bigger ...
Unit 2―The Stars and Their Diurnal Motion
... 8. The Stars. From the very beginning of a study in astronomy, and as frequently as possible, students should practice watching the stars by night, to become acquainted with the constellations and their movements. To get started in your night time viewing, you should have printed out the maps and ch ...
... 8. The Stars. From the very beginning of a study in astronomy, and as frequently as possible, students should practice watching the stars by night, to become acquainted with the constellations and their movements. To get started in your night time viewing, you should have printed out the maps and ch ...
26.2 Stars - Clinton Public Schools
... Most stars are found along a diagonal band running from the bright hot stars on the upper left to the dim cool stars on the lower right. Astronomers call this diagonal band on the H-R diagram the main sequence. About 90% of all stars are found on the main sequence. The sun lies near the middle of th ...
... Most stars are found along a diagonal band running from the bright hot stars on the upper left to the dim cool stars on the lower right. Astronomers call this diagonal band on the H-R diagram the main sequence. About 90% of all stars are found on the main sequence. The sun lies near the middle of th ...
ET: Astronomy 230 Outline Important Caveat
... • About 2/3 of all stars are in multiple systems. – Is this good or bad? • Disks around stars are very common, even most binary systems have them. • Hard to think of a formation scenario without a disk at some point– single or binary system. • Disk formation matches our solar system parameters. • We ...
... • About 2/3 of all stars are in multiple systems. – Is this good or bad? • Disks around stars are very common, even most binary systems have them. • Hard to think of a formation scenario without a disk at some point– single or binary system. • Disk formation matches our solar system parameters. • We ...
The Milky Way - University of North Texas
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by ...
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by ...
PHYS_3380_091905_bw - in a secure place with other
... The square of any planet's period, P, of orbital revolution is proportional to the cube of its mean distance, r, from the sun. I.e., the more distant a planet, the slower it moves on average. ...
... The square of any planet's period, P, of orbital revolution is proportional to the cube of its mean distance, r, from the sun. I.e., the more distant a planet, the slower it moves on average. ...
ASTROPHYSICS UNIVERSE - Physics
... Once you know its luminosity you can know how far away it is (more on this later). ...
... Once you know its luminosity you can know how far away it is (more on this later). ...
Measuring Stars` Properties - Test 1 Study Guide
... 3. Read off absolute luminosity from HR diagram 4. Measure apparent luminosity and calculate distance • works best if many close-by stars ...
... 3. Read off absolute luminosity from HR diagram 4. Measure apparent luminosity and calculate distance • works best if many close-by stars ...
Enhanced lithium depletion in Sun-like stars with orbiting planets.
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
Cepheid Calibration
... The apparent brightness of a light source varies inversely as the square of its distance. In other words, if the distance between an observer and a light source is doubled, the light source will appear four times as faint to the observer. Astronomers can use this inverse square law to estimate dist ...
... The apparent brightness of a light source varies inversely as the square of its distance. In other words, if the distance between an observer and a light source is doubled, the light source will appear four times as faint to the observer. Astronomers can use this inverse square law to estimate dist ...
Chapter 26.2 notes
... Most stars are found along a diagonal band running from the bright hot stars on the upper left to the dim cool stars on the lower right. Astronomers call this diagonal band on the H-R diagram the main sequence. About 90% of all stars are found on the main sequence. The sun lies near the middle of th ...
... Most stars are found along a diagonal band running from the bright hot stars on the upper left to the dim cool stars on the lower right. Astronomers call this diagonal band on the H-R diagram the main sequence. About 90% of all stars are found on the main sequence. The sun lies near the middle of th ...
HD 140283: A Star in the Solar Neighborhood that Formed Shortly
... the distance estimates using ground-based spectroscopy and photometry of the six reference stars (whose V magnitudes range from 11.9 to 16.6). Due to space limitations, the details of this process will be published elsewhere, but we summarize here. For spectral classification, we obtained digital sp ...
... the distance estimates using ground-based spectroscopy and photometry of the six reference stars (whose V magnitudes range from 11.9 to 16.6). Due to space limitations, the details of this process will be published elsewhere, but we summarize here. For spectral classification, we obtained digital sp ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... • Step 2: Determine star’s Luminosity, L • Use combined formula to calculate d, the distance to the star • Sometimes easier to use ratios of distances ...
... • Step 2: Determine star’s Luminosity, L • Use combined formula to calculate d, the distance to the star • Sometimes easier to use ratios of distances ...
PDF
... and its consequences for weather prediction, agriculture, economical activities and so on. Since ancient times, we have used stars as location beacons for our position on Earth and in space. Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea was able to find out that Earth’s axis was precessing by comparing his ...
... and its consequences for weather prediction, agriculture, economical activities and so on. Since ancient times, we have used stars as location beacons for our position on Earth and in space. Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea was able to find out that Earth’s axis was precessing by comparing his ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radiu ...
... • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radiu ...
17 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... The forces caused by the momentum of sunlight are small and can usually be neglected if the body in question is very massive and/or a long way from the Sun. But the forces of radiation can be significant for near-Earth and main belt asteroids and can dominate all other forces for very small part ...
... The forces caused by the momentum of sunlight are small and can usually be neglected if the body in question is very massive and/or a long way from the Sun. But the forces of radiation can be significant for near-Earth and main belt asteroids and can dominate all other forces for very small part ...
13.5 The HR Diagram By the early 1900s, astronomers had learned
... We find from such measurements that all stars have nearly the same composition of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, with a trace of the heavier elements. Most have surface temperatures between about 3000 and 30,000 K and masses between about 0.1 and 30 M⊙. The HR diagram offers a simple, pictorial ...
... We find from such measurements that all stars have nearly the same composition of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, with a trace of the heavier elements. Most have surface temperatures between about 3000 and 30,000 K and masses between about 0.1 and 30 M⊙. The HR diagram offers a simple, pictorial ...
Star-S_Teacher_Guide - The University of Texas at Dallas
... hydrogen and helium. Our own star has been a main sequence star for the last 4.5 billion years, and will continue to convert hydrogen to helium for the next 5 billion years. Not all stars are the same, however. Some stars take longer than the Sun to convert the hydrogen in their cores into helium, a ...
... hydrogen and helium. Our own star has been a main sequence star for the last 4.5 billion years, and will continue to convert hydrogen to helium for the next 5 billion years. Not all stars are the same, however. Some stars take longer than the Sun to convert the hydrogen in their cores into helium, a ...
30-1 - Fremont Peak Observatory Association
... Right before the bright part of the Milky Way makes its appearance there are several bright globs in Ophiuchus. Technically this is the bulge of the Milky Way, but seeing the bulge requires an exceptionally dark sky. M 10, 12, and 14 are all an easy star hop from each other. There are also several b ...
... Right before the bright part of the Milky Way makes its appearance there are several bright globs in Ophiuchus. Technically this is the bulge of the Milky Way, but seeing the bulge requires an exceptionally dark sky. M 10, 12, and 14 are all an easy star hop from each other. There are also several b ...
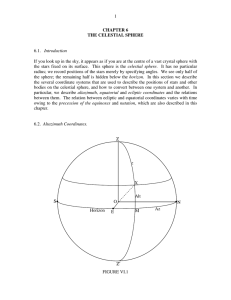
CHAPTER 6 THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... “sidereal” hours, and you may then want to come back and re-read this.) While it is useful to know the hour angle of a star at a particular time for a particular observer, we still need a coordinate that is fixed on the celestial sphere. To do this, we refer to a point on the celestial equator, whic ...
... “sidereal” hours, and you may then want to come back and re-read this.) While it is useful to know the hour angle of a star at a particular time for a particular observer, we still need a coordinate that is fixed on the celestial sphere. To do this, we refer to a point on the celestial equator, whic ...
Eclipses Old Dead Guys Part I Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy
... The planet in the orbit shown in the drawing at right obeys Kepler’s Laws. Use this drawing to answer the next four questions. 1) According to Kepler’s Second Law, during which one of the portion of the planet’s orbit (B, C, or D), would the planet take the same amount of time as it took for the por ...
... The planet in the orbit shown in the drawing at right obeys Kepler’s Laws. Use this drawing to answer the next four questions. 1) According to Kepler’s Second Law, during which one of the portion of the planet’s orbit (B, C, or D), would the planet take the same amount of time as it took for the por ...
2 Coordinate systems
... In order to find something one needs a system of coordinates. For determining the positions of the stars and planets where the distance to the object often is unknown it usually suffices to use two coordinates. On the other hand, since the Earth rotates around it’s own axis as well as around the Sun ...
... In order to find something one needs a system of coordinates. For determining the positions of the stars and planets where the distance to the object often is unknown it usually suffices to use two coordinates. On the other hand, since the Earth rotates around it’s own axis as well as around the Sun ...
L87 THE b PICTORIS MOVING GROUP B. ZUCkERMAN AND
... three systems that were originally suggested to be members of the Tucana stream (HIP 92680, 95261, and 95270; Zuckerman & Webb 2000). HIP 95261 (HR 7329) has a brown dwarf companion of probable age ∼10 Myr and mass ∼35 times that of Jupiter (Lowrance et al. 2000; Guenther et al. 2001). The associati ...
... three systems that were originally suggested to be members of the Tucana stream (HIP 92680, 95261, and 95270; Zuckerman & Webb 2000). HIP 95261 (HR 7329) has a brown dwarf companion of probable age ∼10 Myr and mass ∼35 times that of Jupiter (Lowrance et al. 2000; Guenther et al. 2001). The associati ...
Constellation

In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These areas had their origins in Western-traditional asterisms from which the constellations take their names. There are 88 officially recognized constellations, covering the entire sky.Thus, any given point in a celestial coordinate system can unambiguously be assigned to a constellation. It is usual in astronomy to give the constellation in which a given object is found along with its coordinates in order to convey a rough idea in which part of the sky it is located. For example, saying the Horsehead Nebula is near Orion's Belt in the constellation Orion immediately locates it just south of the ecliptic and conveys that it is best observable in winter from the Northern Hemisphere.