Have You Seen Canopus Tonight?
... other bright stars on the sky, about 310 light years by current estimates. However, other very bright looking stars as Rigel (900 light years?) or Deneb (1,000 light years?) are more distant. Nevertheless, this still makes Canopus a splendid and imposing star as we shall see. We know, too, that Cano ...
... other bright stars on the sky, about 310 light years by current estimates. However, other very bright looking stars as Rigel (900 light years?) or Deneb (1,000 light years?) are more distant. Nevertheless, this still makes Canopus a splendid and imposing star as we shall see. We know, too, that Cano ...
Stargazing For Beginners: A Binocular Tour of the Southern Night Sky
... been completely updated with new star maps and descriptions, and up-todate scientific information. Once you tour the sky through all four seasons with this course, not one person in a thousand will know more about the night sky than you do. The course begins with a few words about how to select and ...
... been completely updated with new star maps and descriptions, and up-todate scientific information. Once you tour the sky through all four seasons with this course, not one person in a thousand will know more about the night sky than you do. The course begins with a few words about how to select and ...
Review 3 (11-18-10)
... • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Nothing stops the collapse and produces an object so compact that escape velocity is higher than speed of light; hence, not even light can escape. •NOTE: these are the masses of the dead stars NOT the masses they had when they were on the main sequence ...
... • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Nothing stops the collapse and produces an object so compact that escape velocity is higher than speed of light; hence, not even light can escape. •NOTE: these are the masses of the dead stars NOT the masses they had when they were on the main sequence ...
sections 12-15 instructor notes
... Bright O and B-type stars are not aligned with the Galactic plane, but concentrate towards a great circle inclined to the plane by ~16°. That feature is known as Gould’s Belt, and is interpreted as a Venetian blind effect resulting from the tilt of the local spiral feature to the Galactic plane, wi ...
... Bright O and B-type stars are not aligned with the Galactic plane, but concentrate towards a great circle inclined to the plane by ~16°. That feature is known as Gould’s Belt, and is interpreted as a Venetian blind effect resulting from the tilt of the local spiral feature to the Galactic plane, wi ...
star
... and dust to form new stars. They are spherical and have a dense concentration of stars in the center. Globular clusters can contain more than a million stars. Globular clusters usually do not have short-lived blue stars because these stars have already died out. Astronomers estimate that the oldest ...
... and dust to form new stars. They are spherical and have a dense concentration of stars in the center. Globular clusters can contain more than a million stars. Globular clusters usually do not have short-lived blue stars because these stars have already died out. Astronomers estimate that the oldest ...
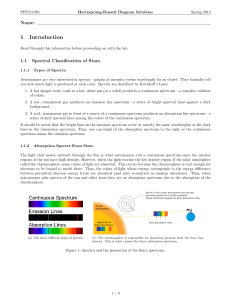
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM
... Milky Way is a continuing process—the stars in the Galaxy didn’t all form at the same time. The main sequence in the middle of the plot, where we have the largest number of stars, is quite broad—much wider than the error on the colour measurement (which is <0.025 magnitudes, remember). This is a rea ...
... Milky Way is a continuing process—the stars in the Galaxy didn’t all form at the same time. The main sequence in the middle of the plot, where we have the largest number of stars, is quite broad—much wider than the error on the colour measurement (which is <0.025 magnitudes, remember). This is a rea ...
Presentation - Relativity Group
... • Apparent brightness refers to the amount of a star’s light which reaches us per unit area. • the farther away a star is, the fainter it appears to us • how much fainter it gets obeys an inverse ...
... • Apparent brightness refers to the amount of a star’s light which reaches us per unit area. • the farther away a star is, the fainter it appears to us • how much fainter it gets obeys an inverse ...
Small star patterns for telescopes and binoculars Demelza Ramakers
... can find The Fairy Ring a few degrees south of the star Sadr: 1.6° west of the Cresent Nebula. ...
... can find The Fairy Ring a few degrees south of the star Sadr: 1.6° west of the Cresent Nebula. ...
Set 3 AStronomy questions
... 21) ASTRONOMY Short Answer What is the astronomical term for a planet’s orbital point that is closest to the Sun? ANSWER: PERIHELION TOSS-UP 7) ASTRONOMY Multiple Choice Which of the following is NOT true: W) the rotation of the Sun’s surface is faster at the equator than at the poles X) the apparen ...
... 21) ASTRONOMY Short Answer What is the astronomical term for a planet’s orbital point that is closest to the Sun? ANSWER: PERIHELION TOSS-UP 7) ASTRONOMY Multiple Choice Which of the following is NOT true: W) the rotation of the Sun’s surface is faster at the equator than at the poles X) the apparen ...
Marriage and Divorce of Astronomy and Astrology History of Astral
... phenomena. That is, predictions made with his theory were verified by observation. He had an empirically based procedure, contrary to what some have said. His failures are often due to lack of information, or incorrect interpretation of it; to phenomena unnoticed, or not examined closely enough; to ...
... phenomena. That is, predictions made with his theory were verified by observation. He had an empirically based procedure, contrary to what some have said. His failures are often due to lack of information, or incorrect interpretation of it; to phenomena unnoticed, or not examined closely enough; to ...
What is the minimum size of a star that will go supernova? A. Half
... as seen from Earth C. The correct motion of a star Answer: B. The angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth. Stars appear to have fixed positions on the sky. That’s one reason why the constellations are the same year to year. Stars that are close to the Earth however appear t ...
... as seen from Earth C. The correct motion of a star Answer: B. The angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth. Stars appear to have fixed positions on the sky. That’s one reason why the constellations are the same year to year. Stars that are close to the Earth however appear t ...
Starry Night Companion - Starry Night Education
... had been: Instead of the center of the universe, Copernicus said, our world is one of many planets and moons circling the Sun in a celestial clockwork. Some 250 years later the Apollo 8 astronauts became the first humans to see the truth of this with their own eyes. As they made history’s first voya ...
... had been: Instead of the center of the universe, Copernicus said, our world is one of many planets and moons circling the Sun in a celestial clockwork. Some 250 years later the Apollo 8 astronauts became the first humans to see the truth of this with their own eyes. As they made history’s first voya ...
Stellar Magnetic Activity
... Starspots are the fingerprints of magnetic field lines and thereby the most important sign of activity in a star's photosphere. However, they cannot be observed directly (see slide 62, only very large & very near objects are directly observable). Therefore, an indirect approach called 'Doppler imag ...
... Starspots are the fingerprints of magnetic field lines and thereby the most important sign of activity in a star's photosphere. However, they cannot be observed directly (see slide 62, only very large & very near objects are directly observable). Therefore, an indirect approach called 'Doppler imag ...
2009, 1st. Quarter, Vol 24, No 1
... southern band was darker than the northern. I was able to see four moons; Titan, Tethys, Rhea and Dione, while Enceledus escaped me. As it happened, Enceledus and was very close to Dione on the 16th and behind the planet on the 18th. Oh well. Some Saturnian facts on those nights….. ...
... southern band was darker than the northern. I was able to see four moons; Titan, Tethys, Rhea and Dione, while Enceledus escaped me. As it happened, Enceledus and was very close to Dione on the 16th and behind the planet on the 18th. Oh well. Some Saturnian facts on those nights….. ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution The Hertzsprung
... An H-R diagram for the 100 brightest stars in the sky. Such a plot is biased in favour of the most luminous stars--which appear toward the upper rightbecause we can see them more easily than we can the faintest stars. These are the GIANTS and SUPERGIANTS In contrast, the H-R diagram for the brightes ...
... An H-R diagram for the 100 brightest stars in the sky. Such a plot is biased in favour of the most luminous stars--which appear toward the upper rightbecause we can see them more easily than we can the faintest stars. These are the GIANTS and SUPERGIANTS In contrast, the H-R diagram for the brightes ...
The Significance of Mega Stars
... The famous Bayer catalog of stars compiled in 1603 by Johann Bayer assigns Greek letters to the brightest stars visible in each constellation, usually in descending order of apparent brightness (but Bayer was not always consistent in this). In the early 1700s John Flamsteed assigned numbers to the b ...
... The famous Bayer catalog of stars compiled in 1603 by Johann Bayer assigns Greek letters to the brightest stars visible in each constellation, usually in descending order of apparent brightness (but Bayer was not always consistent in this). In the early 1700s John Flamsteed assigned numbers to the b ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outwa ...
... an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outwa ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outwa ...
... an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outwa ...
2016 Annual Report - International Dark
... change for 4-5 days, and set in its opposite position. Watching the sun from a particular place on earth gives the observer fixed reference points from which to memorize this annual cycle in order to bring the people of the community into a harmony with the seasonal cycles. The construction of build ...
... change for 4-5 days, and set in its opposite position. Watching the sun from a particular place on earth gives the observer fixed reference points from which to memorize this annual cycle in order to bring the people of the community into a harmony with the seasonal cycles. The construction of build ...
(12) United States Patent
... The invention relates to mechanical computers that can be used for performing calculations relating to the positions of the sun, stars, and other objects in the sky. More particularly, the invention relates to an improved astrolabe having a rotating rete and plate. 2. Description of the Prior Art An ...
... The invention relates to mechanical computers that can be used for performing calculations relating to the positions of the sun, stars, and other objects in the sky. More particularly, the invention relates to an improved astrolabe having a rotating rete and plate. 2. Description of the Prior Art An ...
Galactic Archaeology: Current Surveys
... 10 km/s. The values of the stellar atmospheric parameters are obtained through a dedicated pipeline (Lee et al. 2008), developed for the broad range of targets and giving metallicity estimates to ∼ 0.2 dex, and for high signal-to-noise spectra, an estimate of the relative abundance of the ‘alpha-ele ...
... 10 km/s. The values of the stellar atmospheric parameters are obtained through a dedicated pipeline (Lee et al. 2008), developed for the broad range of targets and giving metallicity estimates to ∼ 0.2 dex, and for high signal-to-noise spectra, an estimate of the relative abundance of the ‘alpha-ele ...
Is Draco II one of the faintest dwarf galaxies? First study from Keck
... way to optimise the number of high-priority bright candidate members. The priorities were set as both a function of spatial location (higher priority towards the center of the system) and location in the colour-magnitude diagram (CMD). All targets are selected using the PS1 photometry and higher pri ...
... way to optimise the number of high-priority bright candidate members. The priorities were set as both a function of spatial location (higher priority towards the center of the system) and location in the colour-magnitude diagram (CMD). All targets are selected using the PS1 photometry and higher pri ...
The Milky Way
... The Galactic Center does not emit visible light. There are too many stars in the way that block our view to the Galactic Center. The Galactic Center is always hidden behind the sun. The Milky Way does not have a center. There is too much dust and gas in the way that blocks our view to the Galactic C ...
... The Galactic Center does not emit visible light. There are too many stars in the way that block our view to the Galactic Center. The Galactic Center is always hidden behind the sun. The Milky Way does not have a center. There is too much dust and gas in the way that blocks our view to the Galactic C ...
Jul 2016 - Bays Mountain Park
... July is here and with it, hot and miserable weather. I enjoy the holidays during the summer for the most part, but I cannot stand the hot, humid heat that comes with it. Even if it is clear on one of these nights, it is usually too hot and muggy to go out and observe or image our beautiful night sky ...
... July is here and with it, hot and miserable weather. I enjoy the holidays during the summer for the most part, but I cannot stand the hot, humid heat that comes with it. Even if it is clear on one of these nights, it is usually too hot and muggy to go out and observe or image our beautiful night sky ...
Constellation

In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These areas had their origins in Western-traditional asterisms from which the constellations take their names. There are 88 officially recognized constellations, covering the entire sky.Thus, any given point in a celestial coordinate system can unambiguously be assigned to a constellation. It is usual in astronomy to give the constellation in which a given object is found along with its coordinates in order to convey a rough idea in which part of the sky it is located. For example, saying the Horsehead Nebula is near Orion's Belt in the constellation Orion immediately locates it just south of the ecliptic and conveys that it is best observable in winter from the Northern Hemisphere.