The Mighty Hunter in the Winter Sky By Shannon Jackson
... appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other stars and constellations are moving. Polaris is marking the North Pole ...
... appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other stars and constellations are moving. Polaris is marking the North Pole ...
Comparing Heights of 4th graders to Kindergarteners
... abstract ideas such as orbits, scale of the solar system, and the universe in ways that they will be able to understand. In this lesson, students will gain an understanding of the movement of the stars through the night sky. They will also gain an understanding of the constellations and in particula ...
... abstract ideas such as orbits, scale of the solar system, and the universe in ways that they will be able to understand. In this lesson, students will gain an understanding of the movement of the stars through the night sky. They will also gain an understanding of the constellations and in particula ...
Astronomy in Ancient Cultures
... times. Early astronomy was about observing the motion of these celestial objects. ...
... times. Early astronomy was about observing the motion of these celestial objects. ...
A Sense of Scale and The Motions of Earth The guitar player
... As the Earth orbits around the Sun, the Sun appears from the Earth to `cross the Constellations. It takes 1 year for the Sun to cross all constellations in the zodiac. ...
... As the Earth orbits around the Sun, the Sun appears from the Earth to `cross the Constellations. It takes 1 year for the Sun to cross all constellations in the zodiac. ...
Early Astronomy
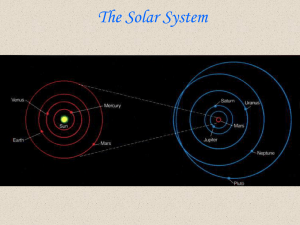
... The planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn) appeared only as points of light on the sky, like the stars, but unlike the Sun and Moon. These objects received special attention because they: moved against the background of stars, are always located within several degrees of the ecliptic ...
... The planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn) appeared only as points of light on the sky, like the stars, but unlike the Sun and Moon. These objects received special attention because they: moved against the background of stars, are always located within several degrees of the ecliptic ...
Jeopardy - University of Nebraska–Lincoln
... Stars of this classification (0.08-0.4 solar masses) are fully convective and thought to be the most common type of star in the universe. ...
... Stars of this classification (0.08-0.4 solar masses) are fully convective and thought to be the most common type of star in the universe. ...
Constellations activities (PDF 185KB)
... Due to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, the constellations seen in the night sky change throughout the year. The constellations Orion and Scorpius are located at opposite sides of the Celestial Sphere (the imaginary sphere of stars that surrounds our Solar System). So as Orion sets in the west, Sco ...
... Due to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, the constellations seen in the night sky change throughout the year. The constellations Orion and Scorpius are located at opposite sides of the Celestial Sphere (the imaginary sphere of stars that surrounds our Solar System). So as Orion sets in the west, Sco ...
Simple Winter Star - Dark Sky Discovery
... You may have seen other star-charts before that were a confusing mass of dots and lines and Greek letters, and you have to hold them over your head to use them. Our star charts here are far simpler and have fewer stars. You can just hold these up in front of you when you’re facing the appropriate di ...
... You may have seen other star-charts before that were a confusing mass of dots and lines and Greek letters, and you have to hold them over your head to use them. Our star charts here are far simpler and have fewer stars. You can just hold these up in front of you when you’re facing the appropriate di ...
Stellarium Night Sky Search Key Commands Constellations buttons
... 2. Planets in the Night Sky Are there any planets above the horizon at this time? If so, list them and in parentheses put the constellation they are currently in. [Hint: Because the solar system lies basically in one plane, all of the planets will be near the ecliptic.] ...
... 2. Planets in the Night Sky Are there any planets above the horizon at this time? If so, list them and in parentheses put the constellation they are currently in. [Hint: Because the solar system lies basically in one plane, all of the planets will be near the ecliptic.] ...
Animals in Estonian Folk Astronomy
... There have been attempts to create a sky map in Estonian language. In 1886, Ado Grenzstein published the first star map in the Estonian language, published as an extra to the Olevik newspaper and printed using the wood engraving technique. This map (Grenzstein 1886) can be considered a true pseudom ...
... There have been attempts to create a sky map in Estonian language. In 1886, Ado Grenzstein published the first star map in the Estonian language, published as an extra to the Olevik newspaper and printed using the wood engraving technique. This map (Grenzstein 1886) can be considered a true pseudom ...
Document
... How did the Greeks make sense of all this? • They assumed that the earth is at the center of the universethe geocentric theory. • They believed that the stars were attached to an extremely large sphere- the celestial sphere. • The celestial sphere must rotate once a day around the earth, carrying a ...
... How did the Greeks make sense of all this? • They assumed that the earth is at the center of the universethe geocentric theory. • They believed that the stars were attached to an extremely large sphere- the celestial sphere. • The celestial sphere must rotate once a day around the earth, carrying a ...
Locating things in the Sky
... We use a system called Right Ascention (RA) and Declination (dec). RA is like longitute and describes how far round an object is, and declination is like latitude and describes how far up or down an object is. We can use these measurements to determine the location of all things in the sky. Example: ...
... We use a system called Right Ascention (RA) and Declination (dec). RA is like longitute and describes how far round an object is, and declination is like latitude and describes how far up or down an object is. We can use these measurements to determine the location of all things in the sky. Example: ...
Stargazing Rules 01162013
... sun, which is why we cannot see it. The first quarter Moon, is straight overhead at sunset and sets at midnight. The third quarter Moon rises at about midnight and is straight overhead at sunrise. A waxing Moon is in the shape of a "D", that is, it bulges to the right. A waning Moon is shaped like a ...
... sun, which is why we cannot see it. The first quarter Moon, is straight overhead at sunset and sets at midnight. The third quarter Moon rises at about midnight and is straight overhead at sunrise. A waxing Moon is in the shape of a "D", that is, it bulges to the right. A waning Moon is shaped like a ...
Friday, August 29
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
Level 4
... Identify that rotation of the Earth causes day and night. Recognize different shapes of the moon, but am unable to discuss why the shape of the moon changes over a period of time. Identify from illustrations, the same objects in the night sky during different seasons. I know… Some facts abou ...
... Identify that rotation of the Earth causes day and night. Recognize different shapes of the moon, but am unable to discuss why the shape of the moon changes over a period of time. Identify from illustrations, the same objects in the night sky during different seasons. I know… Some facts abou ...
CelestialSphere
... Constellations along the ecliptic are called the “Zodiac”. The visible ones change through the year because the Earth orbits the Sun. The constellations themselves are arbitrary groupings of stars in the sky. The stars up at night in the summer are up during the daytime in the winter. ...
... Constellations along the ecliptic are called the “Zodiac”. The visible ones change through the year because the Earth orbits the Sun. The constellations themselves are arbitrary groupings of stars in the sky. The stars up at night in the summer are up during the daytime in the winter. ...
CelestialSphere02
... Constellations along the ecliptic are called the “Zodiac”. The visible ones change through the year because the Earth orbits the Sun. The constellations themselves are arbitrary groupings of stars in the sky. The stars up at night in the summer are up during the daytime in the winter. ...
... Constellations along the ecliptic are called the “Zodiac”. The visible ones change through the year because the Earth orbits the Sun. The constellations themselves are arbitrary groupings of stars in the sky. The stars up at night in the summer are up during the daytime in the winter. ...
Using a Planisphere - Amateur Observers` Society of New York
... chart and watch the stars of Cepheus, Cassiopeia and the Big and Little Dippers. They are called circumpolar: stars that circle the North pole star, Polaris, the end star in the handle of the Little Dipper asterism, but don’t set. Therefore, you could observe any clear night of the year to see the g ...
... chart and watch the stars of Cepheus, Cassiopeia and the Big and Little Dippers. They are called circumpolar: stars that circle the North pole star, Polaris, the end star in the handle of the Little Dipper asterism, but don’t set. Therefore, you could observe any clear night of the year to see the g ...
Print Activity - Let`s Talk Science
... 4. If you don’t have access to glow-in-the-dark stickers, you can cover the end of a flashlight with red cellophane and shine this on the image when you’re outside (this way you can look at the image and the night sky without losing your ‘night vision’). 5. Go outside to a dark area where you have a ...
... 4. If you don’t have access to glow-in-the-dark stickers, you can cover the end of a flashlight with red cellophane and shine this on the image when you’re outside (this way you can look at the image and the night sky without losing your ‘night vision’). 5. Go outside to a dark area where you have a ...
June 2016 night sky chart
... The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while e ...
... The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while e ...
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Research and describe the use of astronomy in ancient civilizations. • Research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy. • Describe and explain the historical origins of the perceived patterns of constellations and the role of constellations in ancie ...
... • Research and describe the use of astronomy in ancient civilizations. • Research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy. • Describe and explain the historical origins of the perceived patterns of constellations and the role of constellations in ancie ...
C H A P T E R 2
... faint stars located in the Northern Hemisphere. These constellations filled in gaps between larger and brighter constellations. Also added were constellations in the Southern Hemisphere that had not been observed by western civilization. When sailors and explores began to sail south of the tropics, ...
... faint stars located in the Northern Hemisphere. These constellations filled in gaps between larger and brighter constellations. Also added were constellations in the Southern Hemisphere that had not been observed by western civilization. When sailors and explores began to sail south of the tropics, ...
FREE Sample Here
... faint stars located in the Northern Hemisphere. These constellations filled in gaps between larger and brighter constellations. Also added were constellations in the Southern Hemisphere that had not been observed by western civilization. When sailors and explores began to sail south of the tropics, ...
... faint stars located in the Northern Hemisphere. These constellations filled in gaps between larger and brighter constellations. Also added were constellations in the Southern Hemisphere that had not been observed by western civilization. When sailors and explores began to sail south of the tropics, ...
Constellation

In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). These areas had their origins in Western-traditional asterisms from which the constellations take their names. There are 88 officially recognized constellations, covering the entire sky.Thus, any given point in a celestial coordinate system can unambiguously be assigned to a constellation. It is usual in astronomy to give the constellation in which a given object is found along with its coordinates in order to convey a rough idea in which part of the sky it is located. For example, saying the Horsehead Nebula is near Orion's Belt in the constellation Orion immediately locates it just south of the ecliptic and conveys that it is best observable in winter from the Northern Hemisphere.