Algebra 1 Sequences (replacing sections 4.6 and 11.1) Name: Part
... Try to best complete each sequence. 3, 6, 9, _____, _____, _____, _____ 21, 16, 11, _____, _____, _____, _____ 10, 9.8, 9.6, _____, _____, _____, _____ 3, 9, 27, _____, _____, _____, _____ 32, 16, 8, _____, _____, _____, _____ 3, 6, 12, _____, _____, _____, _____ 81, 54, 36, _____, _____, _____ 3, 7 ...
... Try to best complete each sequence. 3, 6, 9, _____, _____, _____, _____ 21, 16, 11, _____, _____, _____, _____ 10, 9.8, 9.6, _____, _____, _____, _____ 3, 9, 27, _____, _____, _____, _____ 32, 16, 8, _____, _____, _____, _____ 3, 6, 12, _____, _____, _____, _____ 81, 54, 36, _____, _____, _____ 3, 7 ...
(pdf)
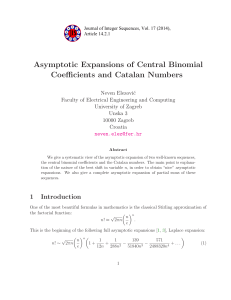
... The remaining case of p = 2 needs to be treated separately but is trivial. In fact, we can derive a complete characterization of integers that are sums of two squares: Corollary 2.10 (Fermat's two square theorem, second version). A natural number n can be written as a sum of two squares if and only ...
... The remaining case of p = 2 needs to be treated separately but is trivial. In fact, we can derive a complete characterization of integers that are sums of two squares: Corollary 2.10 (Fermat's two square theorem, second version). A natural number n can be written as a sum of two squares if and only ...
1 nCk sequences and their difference sequences
... What induces these regularities, becomes apparent when we look at the bit representation of C, as demonstrated in Figure 1. To avoid confusion we let bar, rather than one, denote a bit that is set. An nCk number is an n-bit field with k bars and an nCk sequence is a sequence of nCk numbers. A nCk se ...
... What induces these regularities, becomes apparent when we look at the bit representation of C, as demonstrated in Figure 1. To avoid confusion we let bar, rather than one, denote a bit that is set. An nCk number is an n-bit field with k bars and an nCk sequence is a sequence of nCk numbers. A nCk se ...
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS PARENT GUIDE Six Weeks 4
... Understanding how to describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence A sequence of numbers is a set of numbers written in a particular order. For example, 7, 11, 15, 19 is a sequence of four numbers. The number 7 is the first term in the sequence, 11 is ...
... Understanding how to describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence A sequence of numbers is a set of numbers written in a particular order. For example, 7, 11, 15, 19 is a sequence of four numbers. The number 7 is the first term in the sequence, 11 is ...
ARML Lecture VII - Number Theory
... Whenever the word remainder appears, you should immediately think modulos. Likewise, determining the last few digits of a number should make you consider modulos. The above theorems are merely suppliments to the algebra that can be performed on modular equations, which we outline here. The rules of ...
... Whenever the word remainder appears, you should immediately think modulos. Likewise, determining the last few digits of a number should make you consider modulos. The above theorems are merely suppliments to the algebra that can be performed on modular equations, which we outline here. The rules of ...
Full text
... = Fn+1 . All of these are mentioned in the OEIS for the Fibonacci sequence A000045 [10]. In [6] problem 5.4.13 asks to show that an is the nth Padovan number, satisfying the recurrence an+3 = an+1 + an , if only odd parts ≥ 3 are allowed. The Padovan numbers also count the number of compositions int ...
... = Fn+1 . All of these are mentioned in the OEIS for the Fibonacci sequence A000045 [10]. In [6] problem 5.4.13 asks to show that an is the nth Padovan number, satisfying the recurrence an+3 = an+1 + an , if only odd parts ≥ 3 are allowed. The Padovan numbers also count the number of compositions int ...