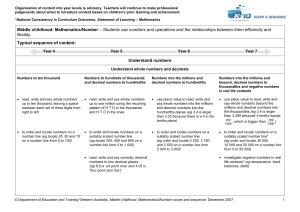
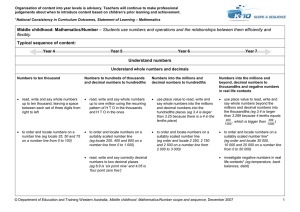
8.uncertaintyandsignificant
... Exact numbers that are counted or defined and not measured have zero uncertainty and infinite “sig figs”. “sig figs” 2.50 cm 3 girls 62.33 kJ 1 cm = 10 mm 12.3 oC 200 lb 1 cm3 = 1 mL ...
... Exact numbers that are counted or defined and not measured have zero uncertainty and infinite “sig figs”. “sig figs” 2.50 cm 3 girls 62.33 kJ 1 cm = 10 mm 12.3 oC 200 lb 1 cm3 = 1 mL ...
Numbers and Numeral Systems
... If we divide both sides of (3.2) by 8 and drop the remainder we are left with 7 = d 3 . The net result is that 3761 = (d 3 d 2 d 1 d 0 )8 = 72618 . We note that during the computations we never had any choice in how to determine the four-digits, they were determined uniquely. We therefore conclude t ...
... If we divide both sides of (3.2) by 8 and drop the remainder we are left with 7 = d 3 . The net result is that 3761 = (d 3 d 2 d 1 d 0 )8 = 72618 . We note that during the computations we never had any choice in how to determine the four-digits, they were determined uniquely. We therefore conclude t ...
A RIGOROUS TIME BOUND FOR FACTORING INTEGERS For real
... prime factors. Proving that there are sufficiently many smooth forms comes down to proving that there are sufficiently many smooth numbers that are built up from prime numbers p for which the Kronecker symbol (~) equals 1. It is to guarantee the existence of sufficiently many such primes that the GR ...
... prime factors. Proving that there are sufficiently many smooth forms comes down to proving that there are sufficiently many smooth numbers that are built up from prime numbers p for which the Kronecker symbol (~) equals 1. It is to guarantee the existence of sufficiently many such primes that the GR ...
Math 7A Unit 1
... Are all Whole Numbers Counting Numbers? _______________________________________ Are all Integers Whole Numbers? ______________________________________________ Are all Integers Counting Numbers? ____________________________________________ Are all Rational Numbers Integers? __________________________ ...
... Are all Whole Numbers Counting Numbers? _______________________________________ Are all Integers Whole Numbers? ______________________________________________ Are all Integers Counting Numbers? ____________________________________________ Are all Rational Numbers Integers? __________________________ ...
SMOOTH NUMBERS AND THE QUADRATIC SIEVE Carl
... prime factors up to its logarithm, and is not a power. We insist that n not be a power in order to ensure that n is divisible by at least two different odd primes. It is easy to check if a number is a power by taking roots via Newton’s method, and for close calls to integers, exponentiating that int ...
... prime factors up to its logarithm, and is not a power. We insist that n not be a power in order to ensure that n is divisible by at least two different odd primes. It is easy to check if a number is a power by taking roots via Newton’s method, and for close calls to integers, exponentiating that int ...
36(2)
... relation (2.1) in depth, but with different boundary conditions. In the following, {£} represents the entry in the nxh row, p^ column of a square array. 2. GENERALIZED PASCAL SQUARES Bondarenko [3] presents an extremely useful collation of the myriad results concerning Pascal triangles and their gen ...
... relation (2.1) in depth, but with different boundary conditions. In the following, {£} represents the entry in the nxh row, p^ column of a square array. 2. GENERALIZED PASCAL SQUARES Bondarenko [3] presents an extremely useful collation of the myriad results concerning Pascal triangles and their gen ...
Chapter 1 Ways to Choose
... A function from set A to set B is a rule by which we associate to each element of A a single element of B. Let f : A → B be a function. The most important implication in dealing with functions is that for two disjoint subsets Bl and B2 of B (i.e., Bl ∩ B2 = ∅) we have disjoint preimages [i.e., f −l ...
... A function from set A to set B is a rule by which we associate to each element of A a single element of B. Let f : A → B be a function. The most important implication in dealing with functions is that for two disjoint subsets Bl and B2 of B (i.e., Bl ∩ B2 = ∅) we have disjoint preimages [i.e., f −l ...
3-6
... 3-6 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Additional Example 3: Consumer Application Jodi and three of her friends are making a tile design. The materials cost $10.12. If they share the cost equally, how much should each person pay? $10.12 should be divided into four equal groups. Divide $10.12 by 4. ...
... 3-6 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Additional Example 3: Consumer Application Jodi and three of her friends are making a tile design. The materials cost $10.12. If they share the cost equally, how much should each person pay? $10.12 should be divided into four equal groups. Divide $10.12 by 4. ...