Sixth Grade 2012-2013 Scope and Sequence UNIT I: Number
... (Supplementary Material: www.mathaids.com Four Quadrant Pairs & Prentice Hall Materials Smart Lesson ...
... (Supplementary Material: www.mathaids.com Four Quadrant Pairs & Prentice Hall Materials Smart Lesson ...
Mainly Natural Numbers - Smarandache Notions Journal
... alternating iteration of the Smarandache function and the sum of divisors function (σ-function). Some light is thrown on loops and invariants resulting from this iteration. Interesting results are found but the results produce new and very intriguing questions. Chapter IV. An interesting iteration q ...
... alternating iteration of the Smarandache function and the sum of divisors function (σ-function). Some light is thrown on loops and invariants resulting from this iteration. Interesting results are found but the results produce new and very intriguing questions. Chapter IV. An interesting iteration q ...
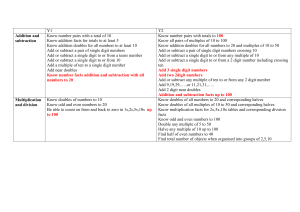
Y1 Y2 Addition and subtraction Know number pairs with a total of 10
... Know sums and differences of multiples of 10 Know pairs of 2 digit numbers with total of 100 Know addition doubles for multiples of 10 to 100 Add and subtract groups of small numbers Add or subtract a 2 digit number to or from a multiple of 10 Add near doubles to 100 Add HTU+U, HTU+T, HTU+H Know mul ...
... Know sums and differences of multiples of 10 Know pairs of 2 digit numbers with total of 100 Know addition doubles for multiples of 10 to 100 Add and subtract groups of small numbers Add or subtract a 2 digit number to or from a multiple of 10 Add near doubles to 100 Add HTU+U, HTU+T, HTU+H Know mul ...
8. Complex Numbers and Polar Coordinates
... (2) Use De Voivre’s Theorem to simplify, write the answer in standard form. [30] ...
... (2) Use De Voivre’s Theorem to simplify, write the answer in standard form. [30] ...
Full text
... An integer m is a pronic number if m is the product of two consecutive integers. We shall show that the only Lucas number which is a product of two consecutive integers is LQ = 2. The author has been informed by the referee that the results of this paper appeared recently in a Chinese journal (in Ch ...
... An integer m is a pronic number if m is the product of two consecutive integers. We shall show that the only Lucas number which is a product of two consecutive integers is LQ = 2. The author has been informed by the referee that the results of this paper appeared recently in a Chinese journal (in Ch ...
Full text
... The above approach would work if we were to replace Y n − 1 by Q(Y n ) for a fixed polynomial Q. It would also extend to the case when the coefficients of Q are polynomials in n. The same remark holds for the coefficients of P . In these cases, the roots do not depend on roots of unity, which means ...
... The above approach would work if we were to replace Y n − 1 by Q(Y n ) for a fixed polynomial Q. It would also extend to the case when the coefficients of Q are polynomials in n. The same remark holds for the coefficients of P . In these cases, the roots do not depend on roots of unity, which means ...
Prime Spacing and the Hardy-Littlewood
... Conjecture B. For the Prime Number Theorem I will follow the treatment of A. E. Ingham in his book “The Distribution of Prime Numbers”, and for the Hardy-Littlewood Conjecture B, I will present a heuristic proof that can also be found in Michael Rubinstein’s paper “A Simple Heuristic Proof of Hardy ...
... Conjecture B. For the Prime Number Theorem I will follow the treatment of A. E. Ingham in his book “The Distribution of Prime Numbers”, and for the Hardy-Littlewood Conjecture B, I will present a heuristic proof that can also be found in Michael Rubinstein’s paper “A Simple Heuristic Proof of Hardy ...
11 Factors and Multiples - e
... is no remainder. However, when 6 is divided by 4 or 5 which are not factors of 6, there is a remainder of 2 and 1 respectively. If a certain whole number can be divided by another whole number such that there is no remainder, then we identify the second number as a factor of the first number. Since ...
... is no remainder. However, when 6 is divided by 4 or 5 which are not factors of 6, there is a remainder of 2 and 1 respectively. If a certain whole number can be divided by another whole number such that there is no remainder, then we identify the second number as a factor of the first number. Since ...