Half-term Test 1 Pupil Book 2 1 Half
... Find the difference between the two answers. Try this again for the digits 2, 3, 4 and 5. What do you notice? Does this work for any four consecutive digits? Investigate. ...
... Find the difference between the two answers. Try this again for the digits 2, 3, 4 and 5. What do you notice? Does this work for any four consecutive digits? Investigate. ...
PPT Review 1.1-1.3
... "illegal" of square rooting a negative doesn't happen. This means the "stuff" under the square root must be greater than or equal to zero (maths way of saying "not negative"). So the answer is: All real numbers x such that x ≠ 4 ...
... "illegal" of square rooting a negative doesn't happen. This means the "stuff" under the square root must be greater than or equal to zero (maths way of saying "not negative"). So the answer is: All real numbers x such that x ≠ 4 ...
ppt - Pacific University
... • A and B are sets, F is a function from A to B; F: A B – Fis one-to-one if it never maps two different elements to the same place, if F(a) F(c) whenever a c – F is onto if it hits every element of B, for each b B this is an a A such that F(a) = b – A and B are the same size if there is a on ...
... • A and B are sets, F is a function from A to B; F: A B – Fis one-to-one if it never maps two different elements to the same place, if F(a) F(c) whenever a c – F is onto if it hits every element of B, for each b B this is an a A such that F(a) = b – A and B are the same size if there is a on ...
To post:
... There are 5 ways to choose the vowel, 6 places to put the vowel, P(21, 5) ways to place the consonants so the answer is the product of these numbers: 5•6•P(21, 5) c. How many contain exactly two vowels? This can be broken down into two parts—placing the vowels and placing the consonants. There are C ...
... There are 5 ways to choose the vowel, 6 places to put the vowel, P(21, 5) ways to place the consonants so the answer is the product of these numbers: 5•6•P(21, 5) c. How many contain exactly two vowels? This can be broken down into two parts—placing the vowels and placing the consonants. There are C ...
topic 14 guided notes
... Percent A special kind of _____ in which the first ______ is compared to ____. Review Terms Ratio Today’s Concept Since percents are comparing the 1st term to 100, the second term must always be 100. If the original ratio does not have a bottom term of 100, you must come up with a proportion to make ...
... Percent A special kind of _____ in which the first ______ is compared to ____. Review Terms Ratio Today’s Concept Since percents are comparing the 1st term to 100, the second term must always be 100. If the original ratio does not have a bottom term of 100, you must come up with a proportion to make ...
chapter 2 (from IBO site) File
... Rounding to significant figures: When counting significant figures your count should begin at the first non-zero number. ...
... Rounding to significant figures: When counting significant figures your count should begin at the first non-zero number. ...
Section 3.1
... Steps for Evaluation Absolute Extrema on a Closed Interval To find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum points for a continuous function f on the closed interval [a, b]. 1. Find the critical numbers of f (values of x where f ( x) 0 or f (x) is undefined) that are contained in [a, b]. Import ...
... Steps for Evaluation Absolute Extrema on a Closed Interval To find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum points for a continuous function f on the closed interval [a, b]. 1. Find the critical numbers of f (values of x where f ( x) 0 or f (x) is undefined) that are contained in [a, b]. Import ...
LAUSD Interim Assessment 1 – Grade 5 Lesson Mid
... Student is able to explain that George’s answer is incorrect and possibly elaborates on why (i.e., the 4 in 484 isn’t really a 4, it’s 400). ...
... Student is able to explain that George’s answer is incorrect and possibly elaborates on why (i.e., the 4 in 484 isn’t really a 4, it’s 400). ...
Medium / Short Term Maths plan
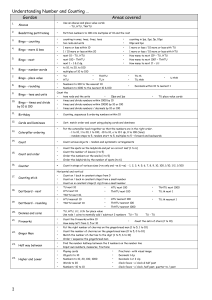
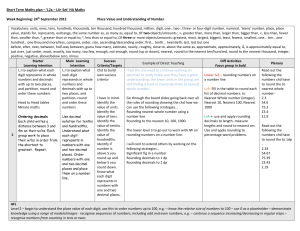
... Level 2 – begin to understand the place value of each digit; use this to order numbers up to 100, e.g. – know the relative size of numbers to 100 – use 0 as a placeholder – demonstrate knowledge using a range of models/images · recognise sequences of numbers, including odd and even numbers, e.g. – c ...
... Level 2 – begin to understand the place value of each digit; use this to order numbers up to 100, e.g. – know the relative size of numbers to 100 – use 0 as a placeholder – demonstrate knowledge using a range of models/images · recognise sequences of numbers, including odd and even numbers, e.g. – c ...
CS342 Data Structures - William Paterson University
... exist positive numbers c and N such that f(n) cg(n) for all n N. It reads "f is big-Omega of g" and implies cg(n) is the lower bound of f(n). • The above definition implies: f(n) is (g(n)) if and only if g(n) is O(f(n)). • Similar to big-O situation, there can be infinite number solutions for ...
... exist positive numbers c and N such that f(n) cg(n) for all n N. It reads "f is big-Omega of g" and implies cg(n) is the lower bound of f(n). • The above definition implies: f(n) is (g(n)) if and only if g(n) is O(f(n)). • Similar to big-O situation, there can be infinite number solutions for ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.