
Chap 1
... (3) The reals, R, which lie in one-to-one correspondence with the points on the number line. Each set above is a subset of the next. In symbols, Z ⊆ Q ⊆ R. The numbers that are elements of R but not of Q are known as irrationals. You have probably also heard each of the following terms as well: coun ...
... (3) The reals, R, which lie in one-to-one correspondence with the points on the number line. Each set above is a subset of the next. In symbols, Z ⊆ Q ⊆ R. The numbers that are elements of R but not of Q are known as irrationals. You have probably also heard each of the following terms as well: coun ...
Example - Radford University
... (which is correct) but (a + b) + c = -30 which is incorrect. The problem is that (a + b) is +110 for this example, which exceeds the range of +99, and so only the rightmost two digits (+10) are retained in the intermediate result. This is a problem that we need to keep in mind when representing real ...
... (which is correct) but (a + b) + c = -30 which is incorrect. The problem is that (a + b) is +110 for this example, which exceeds the range of +99, and so only the rightmost two digits (+10) are retained in the intermediate result. This is a problem that we need to keep in mind when representing real ...
Q1. Circle the number which is closer to 1000 Explain how you know
... Write all the numbers between 50 and 100 that are factors of 180 ...
... Write all the numbers between 50 and 100 that are factors of 180 ...
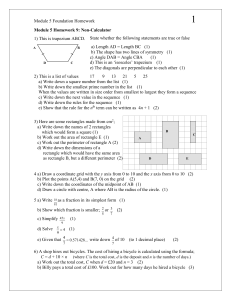
Module 5 Homework 1: Non-Calculator
... shapes joined to make the solid (2) 9 a) Draw the net of a cube with side length 2cm (2) b) Draw a rectangle with an area of 12cm2 (2) 10 a) Plot the following points on a coordinate grid; A:(6,8) B:(2, 4) (1) b) Write the coordinates of the midpoint, M, of line segment AB (2) c) Match up each of th ...
... shapes joined to make the solid (2) 9 a) Draw the net of a cube with side length 2cm (2) b) Draw a rectangle with an area of 12cm2 (2) 10 a) Plot the following points on a coordinate grid; A:(6,8) B:(2, 4) (1) b) Write the coordinates of the midpoint, M, of line segment AB (2) c) Match up each of th ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.














![then 6ET, deg 0^ [log X] + l, and \EQ(8).](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014679564_1-c7df27976606f97a6ee0c094f387d93b-300x300.png)







