Basic Maths - London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
... § 5. Topics in Term 1 modules using basic maths skills Graphs Descriptive statistics (visual representation of relationship between variables) Linear regression Problem solving Applying basic maths skills Thinking through appropriate strategies using these skills Powers and square root Va ...
... § 5. Topics in Term 1 modules using basic maths skills Graphs Descriptive statistics (visual representation of relationship between variables) Linear regression Problem solving Applying basic maths skills Thinking through appropriate strategies using these skills Powers and square root Va ...
Chapter 5 Notes
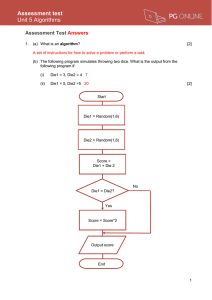
... Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities 5.1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction Graph of an inequality: ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ________ ...
... Algebra Chapter 5 Notes Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities 5.1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction Graph of an inequality: ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ________ ...
a downloadable Instructors Guide (Word document)
... inquire whether the rationals are distinguishable in terms of properties of their decimal expansions (i.e. repeating decimals) even though the arithmetic of real numbers remains a mystery. Surely we need to do better in discussing real numbers than to follow the text's reasoning: Among all infinite ...
... inquire whether the rationals are distinguishable in terms of properties of their decimal expansions (i.e. repeating decimals) even though the arithmetic of real numbers remains a mystery. Surely we need to do better in discussing real numbers than to follow the text's reasoning: Among all infinite ...
1 - TeacherWeb
... 26. The coordinates of quadrilateral ABCD are A(-5,-4), B(1,-2), C(2, 3), and D(-4, 1). Show that both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 27. Trapezoid PQRS has parallel bases PQ and SR .The coordinates of the vertices are P (0, 0), Q (k, 5), R (7,-1), and S (k,-3). a. Express the slope of PQ in ...
... 26. The coordinates of quadrilateral ABCD are A(-5,-4), B(1,-2), C(2, 3), and D(-4, 1). Show that both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 27. Trapezoid PQRS has parallel bases PQ and SR .The coordinates of the vertices are P (0, 0), Q (k, 5), R (7,-1), and S (k,-3). a. Express the slope of PQ in ...
notes for algebra 2 cp final
... there is a dotted or solid line o <, > = dotted line o , = solid line one side of the graph is shaded (by testing a point) o If TRUE, then shade the area that includes the test point o If FALSE, then shade the area that does not include the test point ...
... there is a dotted or solid line o <, > = dotted line o , = solid line one side of the graph is shaded (by testing a point) o If TRUE, then shade the area that includes the test point o If FALSE, then shade the area that does not include the test point ...
Counting
... • Every sequence of n2 + 1 distinct numbers contains a subsequence of length n+1 that is either strictly increasing or strictly ...
... • Every sequence of n2 + 1 distinct numbers contains a subsequence of length n+1 that is either strictly increasing or strictly ...
2011 Non-Calculator - San Gorg Preca College
... Answer: ____________ (b) How many stops did Mr. Camilleri make? Answer: ____________ (c) For how long did he stop at Marsa? Answer: ____________ (d) At what time did he arrive at Hamrun? Answer: ____________ (e) How long did it take him to arrive from Marsa to Hamrun? Answer: ____________ (f) How lo ...
... Answer: ____________ (b) How many stops did Mr. Camilleri make? Answer: ____________ (c) For how long did he stop at Marsa? Answer: ____________ (d) At what time did he arrive at Hamrun? Answer: ____________ (e) How long did it take him to arrive from Marsa to Hamrun? Answer: ____________ (f) How lo ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.