ENF204 Microbiology and Parasitology
... with living beings inhabiting another living organism (host) from which they obtain their food. The course introduces the student to the various sources of infectious and parasitic diseases and, framed within the context of Ecuador’s reality, emphasizes the role that a member of a health team plays ...
... with living beings inhabiting another living organism (host) from which they obtain their food. The course introduces the student to the various sources of infectious and parasitic diseases and, framed within the context of Ecuador’s reality, emphasizes the role that a member of a health team plays ...
ENVR 112 Microbial Agents of Infectious Diseases
... Virulence: A quantitative measure of the ability of a microorganism to cause disease (pathogenicity). LD50 (lethal dose 50%): The number of organisms needed to cause death in 50% of the infected hosts. ID50 (infectious dose 50): The number of organisms needed to cause an infection in 50% of the host ...
... Virulence: A quantitative measure of the ability of a microorganism to cause disease (pathogenicity). LD50 (lethal dose 50%): The number of organisms needed to cause death in 50% of the infected hosts. ID50 (infectious dose 50): The number of organisms needed to cause an infection in 50% of the host ...
Mono
... Mono has a long incubation period. It can take 1-2 months for symptoms to appear. Many people are infectious without symptoms. ...
... Mono has a long incubation period. It can take 1-2 months for symptoms to appear. Many people are infectious without symptoms. ...
Urogenital diseases usually not sexually transmitted
... • One of the greatest killers of all time was the pandemic of swine flu also known as Spanish flu ( 1918-1919) when 20-40 million people died • Caused by the unsanitary conditions by world war I ...
... • One of the greatest killers of all time was the pandemic of swine flu also known as Spanish flu ( 1918-1919) when 20-40 million people died • Caused by the unsanitary conditions by world war I ...
CF, gene ther, vir, DNA tech
... 4. Insertion of Gene isn’t always permanent • e.g. Gaucher Disease: temporary cure until GCase gene “popped” out of chromosome ...
... 4. Insertion of Gene isn’t always permanent • e.g. Gaucher Disease: temporary cure until GCase gene “popped” out of chromosome ...
Infectious Etiologies of Acute Otitis Media
... of age.2 All children had been diagnosed with AOM based on the presence of middle ear fluid and at least two local signs (e.g., erythema, fullness, loss of tympanic membrane landmarks, acute perforation with purulent otorrhea). Investigators cultured for bacteria using sheep blood agar, eosin-methyl ...
... of age.2 All children had been diagnosed with AOM based on the presence of middle ear fluid and at least two local signs (e.g., erythema, fullness, loss of tympanic membrane landmarks, acute perforation with purulent otorrhea). Investigators cultured for bacteria using sheep blood agar, eosin-methyl ...
Microbiology Part 1 Kingdom Monera and the viruses
... 1892 Dimitri Iwanowski (Russian biologist) worked with tobacco mosaic- a disease which causes light green patches on tobacco leaves and stunts leaf growth. He assumed that the fluid containing (TMV- tobacco mosaic virus)contained a poison from a bacterium. The term "virus" (is the Latin word for poi ...
... 1892 Dimitri Iwanowski (Russian biologist) worked with tobacco mosaic- a disease which causes light green patches on tobacco leaves and stunts leaf growth. He assumed that the fluid containing (TMV- tobacco mosaic virus)contained a poison from a bacterium. The term "virus" (is the Latin word for poi ...
microorganisms
... • The differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells • Classification of microorganisms • Growth and metabolism of microorganisms • The role of microorganisms in diseases • Control of microorganisms through anti-microbial agents and other methodologies • Diseases caused by microorganisms ...
... • The differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells • Classification of microorganisms • Growth and metabolism of microorganisms • The role of microorganisms in diseases • Control of microorganisms through anti-microbial agents and other methodologies • Diseases caused by microorganisms ...
Laboratory Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
... preparations to provide immune protection against a specific disease. o Vaccine. A suspension of attenuated live or killed microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, ricketsiae), or fractions thereof, administred to induce immunity and thereby prevent infectious disease. o Toxoid. A modified bacterial toxin ...
... preparations to provide immune protection against a specific disease. o Vaccine. A suspension of attenuated live or killed microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, ricketsiae), or fractions thereof, administred to induce immunity and thereby prevent infectious disease. o Toxoid. A modified bacterial toxin ...
Laboratory Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
... preparations to provide immune protection against a specific disease. o Vaccine. A suspension of attenuated live or killed microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, ricketsiae), or fractions thereof, administred to induce immunity and thereby prevent infectious disease. o Toxoid. A modified bacterial toxin ...
... preparations to provide immune protection against a specific disease. o Vaccine. A suspension of attenuated live or killed microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, ricketsiae), or fractions thereof, administred to induce immunity and thereby prevent infectious disease. o Toxoid. A modified bacterial toxin ...
19-3 Diseases Caused by Bacteria and Viruses
... Many bacterial diseases can be prevented by vaccines. ...
... Many bacterial diseases can be prevented by vaccines. ...
Instructions / Assembly
... Change cloth, sponge or towels frequently to avoid redeposition of soil. Change the solution at least daily or when use solution becomes visibly soiled. ...
... Change cloth, sponge or towels frequently to avoid redeposition of soil. Change the solution at least daily or when use solution becomes visibly soiled. ...
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity (Chapter 15) Lecture
... attack by antibodies and immune cells e.g. Neisseria gonorrhoeae -has many versions of the Opa gene -can alter which one is being expressed e.g. influenza virus -constant genetic recombination between flu viruses: always new spike proteins ...
... attack by antibodies and immune cells e.g. Neisseria gonorrhoeae -has many versions of the Opa gene -can alter which one is being expressed e.g. influenza virus -constant genetic recombination between flu viruses: always new spike proteins ...
Name of disease
... The viruses cannot reproduce independently. They need living cells on hosts. Once a virus attaches itself to its host cell, it injects the genetic material into the cell. This genetic material instructs the host cell to manufacture more viruses. In this way, the virus multiplies itself inside our ce ...
... The viruses cannot reproduce independently. They need living cells on hosts. Once a virus attaches itself to its host cell, it injects the genetic material into the cell. This genetic material instructs the host cell to manufacture more viruses. In this way, the virus multiplies itself inside our ce ...
43. Tumor Viruses
... In summary, two different mechanisms—mutation and increased expression— appear to be able to activate the quiescent "proto-oncogene" into a functioning oncogene capable of transforming a cell. Cellular oncogenes provide a rationale for carcinogenesis by chemicals and radiation; e.g., a chemical carc ...
... In summary, two different mechanisms—mutation and increased expression— appear to be able to activate the quiescent "proto-oncogene" into a functioning oncogene capable of transforming a cell. Cellular oncogenes provide a rationale for carcinogenesis by chemicals and radiation; e.g., a chemical carc ...
MICROBIOLOGY ORAL TOPIC SUGGESTIONS Current diseases or
... MICROBIOLOGY ORAL TOPIC SUGGESTIONS Current diseases or events: Anthrax Antimicrobial cleaning products Antimicrobial resistance Astro microbiology (microorganisms in space) Avian flu Biofilms Bioterrorism and Microbiology Cholera (Vibrio cholera) CMV (cytomegalovirus virus) Ebola Emerging infectiou ...
... MICROBIOLOGY ORAL TOPIC SUGGESTIONS Current diseases or events: Anthrax Antimicrobial cleaning products Antimicrobial resistance Astro microbiology (microorganisms in space) Avian flu Biofilms Bioterrorism and Microbiology Cholera (Vibrio cholera) CMV (cytomegalovirus virus) Ebola Emerging infectiou ...
Naming and classifying microorganisms
... • New laboratory techniques, involving analysis of DNA and RNA, have caused some bacteria to be reclassified. • Sometimes organisms which have been in separate genera are combined into one genus; other times organisms previously in the same genus are split out ...
... • New laboratory techniques, involving analysis of DNA and RNA, have caused some bacteria to be reclassified. • Sometimes organisms which have been in separate genera are combined into one genus; other times organisms previously in the same genus are split out ...
SCHEDULE 5
... 1. Any reference in this Schedule to a micro-organism includes – (a) intact micro-organisms; (b) micro-organisms which have been genetically modified by any means, but retain the ability to cause serious harm to animal health; (c) any nucleic acid derived from a micro-organism listed in this Schedul ...
... 1. Any reference in this Schedule to a micro-organism includes – (a) intact micro-organisms; (b) micro-organisms which have been genetically modified by any means, but retain the ability to cause serious harm to animal health; (c) any nucleic acid derived from a micro-organism listed in this Schedul ...
Type 2, Unicellular - Association of Surgical Technologists
... with rifamycin, chloroquine, sulfonamides, and trimethoprim.11 In the hospital setting, most infections are caused by bacteria and viruses (Figures 4, 5, and 6), although fungi and parasites occasionally are involved. Because viruses are particles that live inside the host’s cells, antiviral agents ...
... with rifamycin, chloroquine, sulfonamides, and trimethoprim.11 In the hospital setting, most infections are caused by bacteria and viruses (Figures 4, 5, and 6), although fungi and parasites occasionally are involved. Because viruses are particles that live inside the host’s cells, antiviral agents ...
Microbes & Disease
... Diseases such as typhoid and cholera are transmitted through water, and can cause diarrhoea ...
... Diseases such as typhoid and cholera are transmitted through water, and can cause diarrhoea ...
PICORNAVIRIDAE
... - first inactivated vaccine used (Salk 1950’s). - first picornavirus to be sequenced. - first infectious cDNA clone of an animal virus. - first picornavirus structure to be solved. ...
... - first inactivated vaccine used (Salk 1950’s). - first picornavirus to be sequenced. - first infectious cDNA clone of an animal virus. - first picornavirus structure to be solved. ...
3 Virus Replication Cycles
... adapt to their hosts have been able to exist in nature. This chapter focuses on experiments such as one-step growth curves, which are used to study virus–host interactions. These studies have provided information about the events that occur at each step of the infection cycle (attachment, penetratio ...
... adapt to their hosts have been able to exist in nature. This chapter focuses on experiments such as one-step growth curves, which are used to study virus–host interactions. These studies have provided information about the events that occur at each step of the infection cycle (attachment, penetratio ...
Microsoft Word
... presence of viruses that infect bacterial cells. He found the clearance of bacterial cultures in the presence of filterable agents which could be transmitted to another culture, causing similar effects [2]. In fact, it was d’Herelle who introduced the name “bacteriophage” [3]. He conducted experime ...
... presence of viruses that infect bacterial cells. He found the clearance of bacterial cultures in the presence of filterable agents which could be transmitted to another culture, causing similar effects [2]. In fact, it was d’Herelle who introduced the name “bacteriophage” [3]. He conducted experime ...
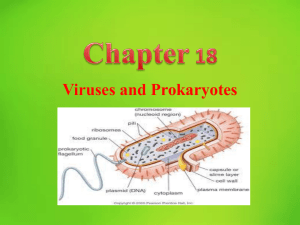
Viruses and Prokaryotes Chapter 18
... diseases in plants. • Finally, prions are the least likely to be living. These are just proteins that cause other proteins to act incorrectly. ...
... diseases in plants. • Finally, prions are the least likely to be living. These are just proteins that cause other proteins to act incorrectly. ...